FortiGate and Zero Trust Architecture: What You Need to Know
Traditional networks relied on authenticating once and getting inside and access to all resources. The modern networks operate on ‘Zero trust’ architecture which is a security framework working on the principle of no user, no device, no application is trusted by inheritance. Each requires a strict authorization and verification for each and every access request irrespective of its geographical location and enforces security policies and is based on the principle of ‘least privileges’.
There is a continuous validation of security posture and underlying configurations to ensure robust protection against cyber threats.
Zero trust protection covers data, applications, assets and services and is often known as ‘DAAS’.
FortiGate provides Zero trust architecture for granular control on applications hosted on premises, on cloud or on SaaS. Access is controlled via a combination of client software, FortiGate firewalls, proxies and identity management such as active directory or others.
In this article we will learn more in detail about FortiGate and Zero trust architecture.
Zero Trust Architecture
Traditional network architecture is also referred to at times as the ‘Castle and moat’ model. The network acts as a castle and authorized users are the moat. This approach is useful for perimeter security but it fails to address threats already lurking inside the networks.
The traditional perimeter security-based approach only distrusts objects outside the existing network. Once a threat is able to get into the internal network it has freehand to wreak havoc in the network and bring down any systems. A zero-trust architecture model is based on identification rather than trusting users based on their earlier authentication.
The zero trust architecture terminology is coined by Forrester research associate John Kindervag. He explained how traditional network models fail by trusting forever. Instead administrators have to verify trust at each stage, each device, at various points in the network and if trust is violated then access is blocked.
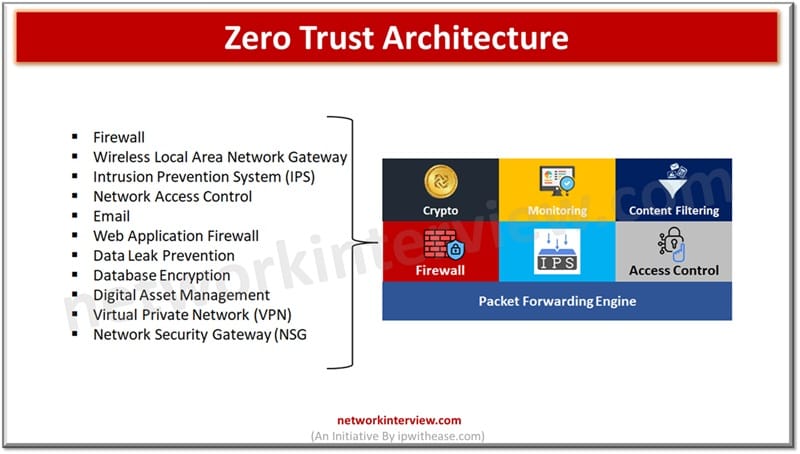
Use of Segmentation Gateways (SGs) was his recommendation to be installed at the heart of the network and incorporate several different protection measures and use a packet-forwarding engine to send protection as required in the networks.
FortiGate and Zero Trust Architecture
Fortinet Zero trust Network access (ZTNA) helps network and security teams jointly to enforce granular level security policies for users working from office or remotely, for on premises or cloud setups. It operates on the principle of ‘least privileges’ and limits users and device access to applications and services as per their defined role. Access policies are enforced by device type, device location, time of the day, and security posture of device. Trust is confirmed at every level of access and for every service and application.
Policies are enforced at six levels in Fortinet when a user requests a service or opens an application the ZTNA is invoked.
- The client software initiate connection request using TLS connection to proxy
- The proxy verifies the access request with user role, ID and security policies based on device location, time of the day etc.
- The proxy sets up TLS connection with service or application post verifying user and device posture
- The proxy broker establishes connection and torn down connection when session is over
- If user requires access to service or application again whole process will start all over again
Fortinet ZTNA can be applied to users irrespective of their location – be it an office or home or any other location with consistent security measures. Users working in corporate offices and remote users are treated in the same manner. ZTNA policies of Fortinet are associated with users and device profiles and users obtain access to certain services or applications and resources for which they are legitimized and only from compliant devices. Fortinet Zero trust network also supports adaptive access in which permissions are adapted dynamically on the basis of user behaviour or system health.
Tag:Fortigate



