Firewall vs Proxy: Detailed Comparison
Both the proxy and the firewall limit or block connections to and from a network but in a different way. While a firewall filters and blocks communication (ports or unauthorized programs that seek unauthorized access to our network), a proxy redirects it.
In this blog, we will discuss the comparison, firewall vs proxy in detail.
FIREWALL
A firewall is a security tool that oversees the flow of incoming and outgoing network traffic. It uses a set of security protocols to determine whether to permit or prohibit specific traffic. Firewalls are essential components of network security and serve as the first line of defense against potential threats. Their primary function is to separate secure and regulated internal networks from untrusted external networks, such as the Internet. Firewalls can be either hardware/software/combination of both.
Types of Firewalls:
1.Packet Filtering
Fundamentally, messages are divided into packets that include the destination address and data. Packets are transmitted individually and often by different routes. Once the packet reach their destination, they are recompiled into the original messages.
Packet filtering is a firewall in its most basic form. Primarily, the purpose is to control Access to specific network segments as directed by a preconfigured set of rules, or rule base, which defines the traffic permitted Access. Packet filters usually function at layers 3 (network) and 4 (transport) of the OSI model.
In general, a typical rule base will include the following elements:
- Source address
- Destination Address
- Source port
- Destination Port
- Protocol
Packet filtering firewalls are the least secure type of firewall, because they cannot understand the context of a given communication, making them easier for intruders to attack.
2.Stateful inspection firewall
Check Point has developed and patented Stateful Inspection technology, which adds layer 4 awareness to the standard packet-filter firewall architecture.
Stateful Inspection and static packet filtering are two different methods of examining a packet. While static packet filtering only looks at the header of a packet to gather information about its source and destination, Stateful Inspection goes a step further by examining the content of the packet up through the application layer to gather more information. This involves monitoring the state of the connection and creating a state table to compile the information. The advantage of this approach is that it allows the firewall to filter packets based on the context established by previous packets that have passed through it.
For Example,
Stateful-inspection firewalls offer protection against port scanning by keeping all ports closed until a specific port is requested.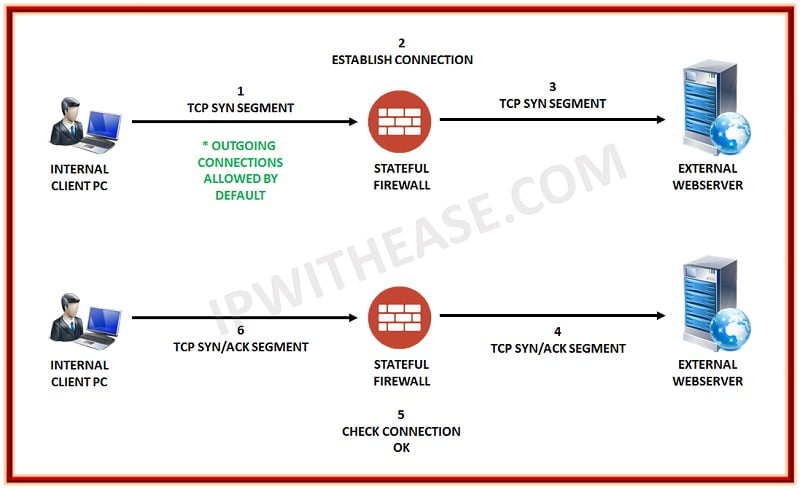
3.Unified threat management (UTM) firewall
A UTM system is a network hardware appliance, virtual appliance, or cloud service that provides businesses with simplified security protection by combining and integrating multiple security services and features. Its purpose is to safeguard businesses from potential security threats.
UTM devices are commonly available as network security appliances that offer comprehensive security to networks from multiple threats. They provide protection against malware and simultaneous attacks that can target different areas of the network.
UTM cloud services and virtual network appliances are gaining popularity for network security, particularly among small and medium-sized businesses. These solutions eliminate the need for on-premises network security appliances, while offering centralized control and simplicity in constructing a layered network security defence.
NGFWs were initially created to address the shortcomings of conventional firewalls in securing networks. They offer a wide range of security features such as application intelligence, intrusion prevention systems, and denial-of-service protection. Unified threat management devices, on the other hand, provide comprehensive network security by combining various security measures like next-generation firewalls, antivirus, VPN, spam filtering, and URL filtering for web content.
4.Next-generation firewall (NGFW)
Firewalls have come a long way from basic packet filtering and stateful inspection. Nowadays, many businesses are utilizing next-generation firewalls to thwart contemporary risks such as application-layer attacks and advanced malware.
As per Gartner, Inc.’s definition, a next-generation firewall must include:
- Standard firewall capabilities like stateful inspection
- Integrated intrusion prevention
- Application awareness & control to block the risky apps
- Upgrade paths to include future information feeds
- Techniques to address evolving security threats
PROXY
A proxy server, which is also known as an application gateway, is responsible for regulating application level traffic by scrutinizing data using header fields, message size, and content. It is a component of the firewall, as a packet firewall alone cannot differentiate between port numbers. The proxy server acts as a proxy and makes decisions on how to handle application specific traffic flow by using URLs.
How does a Proxy server work?
A proxy server is positioned between the client and original server. It operates as a server process, receiving requests from the client to access the server.
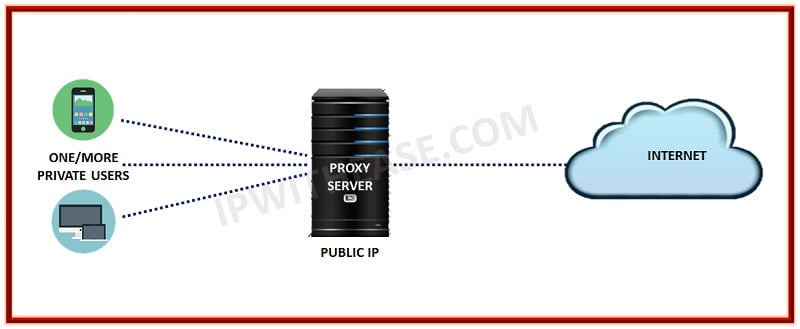
The proxy server performs a complete content check when it receives a request. If the request and its content are deemed valid, the proxy server forwards the request to the actual server as if it were a client. However, if the request is not deemed valid, the proxy server rejects the request and sends an error message to the external user.
One of the benefits of using a proxy server is its ability to cache. This means that when a request for a page is made, the server checks if the response is already stored in the cache. If it is, the server sends the stored response instead of making a new request to the server. This reduces the traffic, load on the main server, and improves the latency.
Comparison: Firewall vs Proxy
Basics:
The Firewall is a security feature that prevents harmful traffic from entering or leaving a public network. It serves as a barrier for incoming and outgoing data. The Proxy Server, on the other hand, is a part of the firewall that allows communication between the client and the server if the client is verified as a legitimate user. It plays a dual role of both client and server.
Filtration:
Firewalls and proxy servers are two different types of network security measures. While a firewall filters IP packets, a proxy server filters requests on the basis of its application level content.
Network Layer:
The firewall relies on data from the network and transport layers, whereas the proxy server also takes into account data from the application layer.
Overhead Generation:
The firewall creates more overhead than a proxy server since the proxy server can handle fewer aspects by using caching.

Final Words
A firewall and proxy server collaborate to safeguard the system from harmful cyber attacks. Both firewalls and proxy servers can be used to add an extra layer of security against malware and intruders when using the internet. As a firewall component, a proxy server can be utilized by many modern firewall providers to enhance security, as well as provide efficiency and feasibility. Therefore, using both can be beneficial for additional security.
Continue Reading:
6 Types of Firewall: Network Security
CASB vs Proxy: Understand the difference
Tag:comparison, firewall