Cloud App vs Web App : Detailed Comparison
Cloud App vs Web App
What is a Cloud App?
Cloud App is an application that operates through the cloud and has some characteristics of both desktop apps and web apps. Cloud App is a more advanced web app. It’s used just as much to access online content over the Internet as web apps, but it’s not totally dependent on a web browser to function.
Characteristics of a Cloud App
- Data is stored in a cloud infrastructure.
- The stored data can be accessed offline & cached locally.
- Different user requirements are also supported here.
- These can be used from either- web browsers and custom-built apps like mobile phones.
- Facilitates access to a greater range of services.
- The data in cloud-based applications are simply stored in the cloud.
- It can further be used for access like- on-demand computing cycle, application development platforms, and is used for storage.
- These cloud-based applications are user-friendly and support various customer’s functional requirements that involve security, compression of data, and the backup schedule.
Benefits of Cloud App
- With the help of cloud apps, less management efforts are required along with service provider interaction.
- Users who are more into on-demand services can match their personal needs and requirements using Cloud. Here location independence along with access to information from any place or device is also offered via it.
- Cloud applications also render broad computing capabilities in both ways- online and offline.
- With cloud applications, users are not required to go for specific software, however only need to pay for the services. This helps in offering them quick access to the necessary applications through the cloud server.
- Without even installing software on the servers, users can still use the app’s functionalities fully.
- The availability and performance of cloud services can charge the work processes while enhancing profitability too.
- Cloud apps can serve multiple users at the same time with different physical and virtual needs.
- Using cloud apps makes it easier to monitor, report fetching and control over resources. This results in offering transparency for both the providers and consumers.
Examples of Cloud Apps
Common examples of cloud app are
- Mozy
- Evernote
- Sugar Sync
- Salesforce
- Dropbox
- NetSuite
- and Zoho.com
Other examples are as web email (Google, Yahoo, Microsoft Hotmail, etc.)
Related – Cloud Computing
Types of Cloud App
- Software as a Service (SaaS): SaaS is the most popular type of cloud app in which users can use cloud-based apps as full-functioning applications. Some examples are CRM, Wrike, HubSpot, and Wix.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS):PaaS is an advanced type of cloud computing that provides solutions infrastructure and computing platform on which users can build their solutions. They are used by businesses platform, engaged in the development, testing, collaboration and deployment of cloud solutions for specific applications. Some examples are
- Microsoft Azure
- Google App Engine and
- Rackspace Cloud Sites.
- Recovery as a Service or RaaS: Businesses use such cloud-based solutions for data recovery, servers, files, databases and whole data centers. It is also known as DRaaS or Disaster Recovery as a Service function for minimizing the downtime effects. Some examples are Geminare, Scaled and Windstream Business.
- Infrastructure as a Service or IaaS: Its an outsourced cloud-based computing infrastructure service. It can be offered either as a development platform or as a managed hosting, such as Google Cloud, IBM Cloud, and more.
- Cloud-based Service Providers helping in Businesses like IBM cloud, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), Oracle Cloud, and Salesforce.com.
- Companies who are using Cloud Services like Slack, Zoom, DigitalOcean, DropBox, Google Drive, Salesforce, and Amazon Web Services.
Related – Microsoft Azure Interview Q&A
What is a Web App?
Web app, as the name suggests are the apps that are designed to be used on a web browser. They are the combination of a server-side script and a client-side script. Furthermore, when it comes to how web-based application work, browsers rely on the web server components. Web apps also provide one of the convenience of accessing the app from anywhere due to its computing model. However, one thing that differentiates cloud apps from web apps is that former offers limited customization options to the users. Also, they are not designed in such a way that they can support varying requirements of consumers.
Characteristics of a Web App
- User data and business processes are stored at one data center.
- Web App can be accessed from anywhere through a Web browser.
- Such apps mainly rely on the Web Server components that are installed on back-end infrastructure systems.
- Each user has access to the part of the application.
- Web App has limited availability and scalability.
Benefits of Web Apps
- Web apps are accessible from any location and that too from any web browser.
- They can run on multiple platforms irrespective of the operating system or device, making cross-platform development more compatible.
- If the browser is compatible enough the web apps can be accessed easily by users. This also reduces the occurrence of compatibility issues.
- The next benefit of the web app is that it requires less support and maintenance from the developer’s front. Hence, it simply reduces the app development cost while offering ease to customers.
- Web app does not require downloads.
- Information about the client is not stored, eliminating issues like piracy or data leak.
- Web Apps do not require updating as they get updated on their own without the need to reinstall apps on devices.
Examples of Web apps
Web Services such as WebEx, e-banking, e-commerce and eBay fall into this category. They are exclusively web-based with limited options for consumer customization.
Types of Web app
- Static web apps: Such apps are not flexible in nature and typically use CSS and HTML. It displays the least contents but can hold animated objects as well such as videos, GIFs, banners, and more.
- Dynamic web apps: Dynamic web apps are client-server solutions, which run on a web browser. However, these type of web pages are different from a static web app as it shows a different content like in case of Twitter, Google, Facebook, and Amazon.
- Portal web app: Such type of web apps are ones which users can access and use the categories of a home page. They are similar to dynamic web apps and include email, web browsers, chats, forums and more.
- Web apps with CMS: They come with constantly updated content. It has a CMS administrator for implementing the updates and changes. Some of the examples are Drupal, Joomla and WordPress for making business and personal blogs including news pages.
- E-Commerce or Online Store: It requires electronic payment methods such as credit cards and PayPal with the capability to support online shopping. E-Commerce app requires to be optimized for both desktop platform and mobile browsing for the best results.
- Animated web apps: It mainly features animation techniques such as JavaScript, Flash and more. It is widely used by freelancers and creative agencies to display their enhanced creativity.
- Web Applications: Some examples are – AliExpress, Twitter Lite, Forbes and Pinterest.
Difference : Cloud App vs Web App
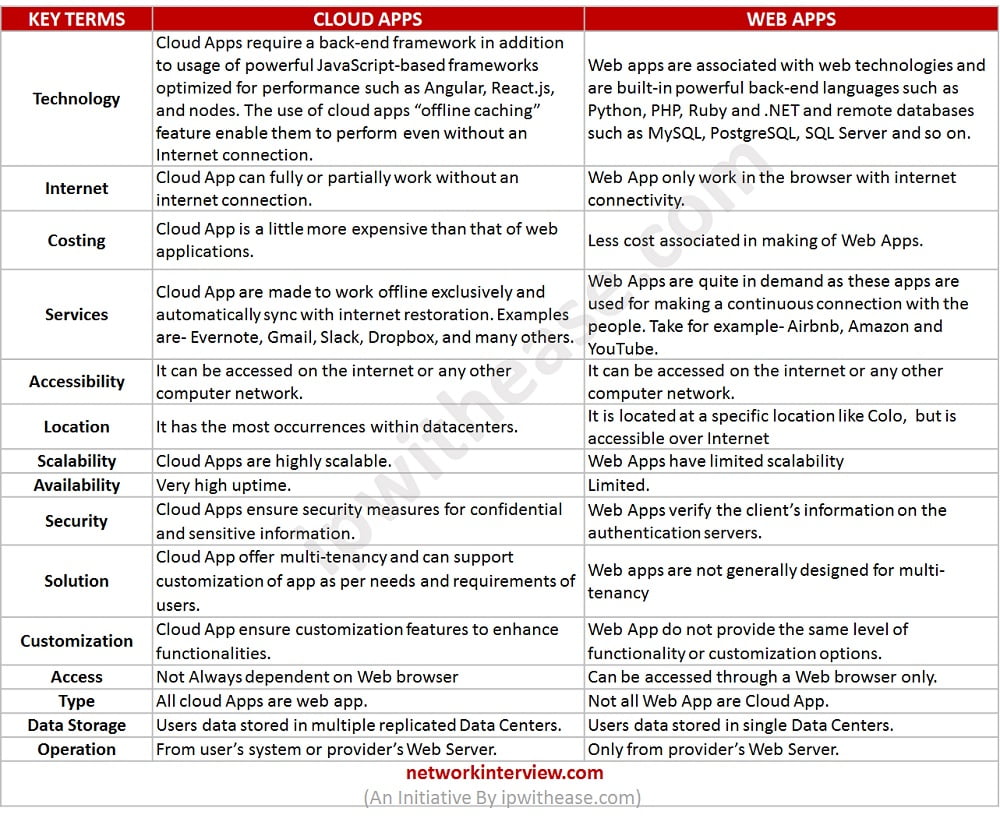
KEY TERMS | CLOUD APPS | WEB APPS |
| Technology | Cloud Apps require a back-end framework in addition to usage of powerful JavaScript-based frameworks optimized for performance such as Angular, React.js, and nodes. The use of cloud apps “offline caching” feature enable them to perform even without an Internet connection. | Web apps are associated with web technologies and are built-in powerful back-end languages such as Python, PHP, Ruby and .NET and remote databases such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQL Server and so on. |
| Internet | Cloud App can fully or partially work without an internet connection. | Web App only work in the browser with internet connectivity. |
| Costing | Cloud App is a little more expensive than that of web applications. | Less cost associated in making of Web Apps. |
| Services | Cloud App are made to work offline exclusively and automatically sync with internet restoration. Examples are- Evernote, Gmail, Slack, Dropbox, and many others. | Web Apps are quite in demand as these apps are used for making a continuous connection with the people. Take for example- Airbnb, Amazon and YouTube. |
| Accessibility | It can be accessed on the internet or any other computer network. | It can be accessed on the internet or any other computer network. |
| Location | It has the most occurrences within datacenters. | It is located at a specific location like Colo, but is accessible over Internet |
| Scalability | Cloud Apps are highly scalable. | Web Apps have limited scalability |
| Availability | Very high uptime. | Limited. |
| Security | Cloud Apps ensure security measures for confidential and sensitive information. | Web Apps verify the client’s information on the authentication servers. |
| Solution | Cloud App offer multi-tenancy and can support customization of app as per needs and requirements of users. | Web apps are not generally designed for multi-tenancy |
| Customization | Cloud App ensure customization features to enhance functionalities. | Web App do not provide the same level of functionality or customization options. |
| Access | Not Always dependent on Web browser | Can be accessed through a Web browser only. |
| Type | All cloud Apps are web app. | Not all Web App are Cloud App. |
| Data Storage | Users data stored in multiple replicated Data Centers. | Users data stored in single Data Centers. |
| Operation | From user’s system or provider’s Web Server. | Only from provider’s Web Server. |
Download the difference table here.
Comparison
- Cloud App has the most occurrences within datacenters. Web App is located at a specific locations like Colo etc but is accessible globally.
- Cloud App is highly scalable while in contrast Web apps are less scalable.
- Cloud App has very high uptime as compared to Web App has limited/lower uptime.
- Both require access to online services using the internet but cloud apps do not depend on web browsers for functioning.
- Cloud apps can functional from a local workstation without the web interface. Cloud apps can be customized to meet user’s requirements. Web apps don’t have the customization options to the developers or users.
- Cloud apps are characterized by a sophisticated back-end to ensure security, maximum uptime, and integration with other third-party systems. It offers scalability for features and functionality. Web apps are stored on a Web server and delivered over the internet through a web interface.
- Cloud apps ensure security for confidential and sensitive information, whereas, web apps verify the clients’ information on the data servers. Cloud Apps are more secure than Web App.
- Web apps are not designed to have the ability of multi-tenancy. They don’t support the varying requirements of different consumers. On the contrary, cloud apps can render multi-tenancy and can support various needs and requirements of users.
Conclusion
Cloud apps and Web apps both have earned customers in today’s market. Software vendors often bundle web apps to sell as “cloud” apps simply because it’s the latest buzz-word technology but web apps do not offer the same richness in functionality and customization you’ll get from cloud apps. Cloud apps serve the purpose of offering great opportunities to let businesses and organizations work conveniently. Starting from on-demand services to the availability of network or accessibility to shared pooled resources, the cloud serves all the purposes.
Tag:cloud, comparison