CEF vs Routing Table : Know the difference
CEF vs Routing Table
RIB (or routing table) and CEF (Cisco Express Forwarding) are two different tables which are used in routing across IP networking platform. Both have common information but perform two distinctly different purposes. CEF technology is new in the networking domain when compared to Routing table. Also, CEF has garnered a lot of appreciation for its ability to reduce the overhead and delays introduced by other techniques of routing.
In this article we will learn about CEF and Routing table.
Sub-Topics to be covered:
- Detail discussion on CEF
- Detail discussion on Routing table
- Comparison of CEF and routing table
- Difference table between CEF vs Routing table
- Conclusion
Cisco Express Forwarding (CEF)
Cisco Express Forwarding (CEF) is a packet switching technique that is the default for most of Cisco platforms. CEF provides the ability to switch packets through advanced Layer 3 IP switching technology via a layer 3 device in a way that minimises the load on router’s processor. This way the routing process can be offloaded to deal with other responsibilities that require larger amounts of processor resources and time like QOS, Encryption etc. CEF is a Cisco proprietary protocol, however other OEM and vendors of Routing and Switching platforms also offer CEF comparable features which are performed in hardware based ASIC.
Related – Central CEF vs Distributed CEF
Routing table
The Routing Information Base is where all IP Routing information is stored. It is not specific to any routing protocol, rather all the routing protocols place all of their routes. Routes are inserted into the routing table whenever a routing protocol running on the router learns a new route. When a destination becomes unreachable the route is first marked unusable and later removed from the routing table from where the route were learned like dynamic routing protocols, directly attached networks and static routes.
Comparison : CEF vs Routing table
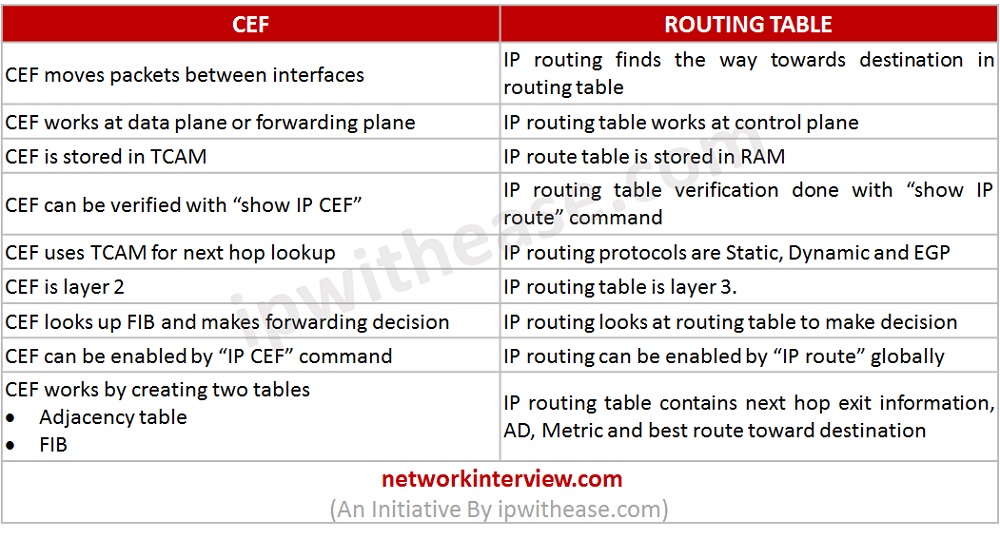
- CEF moves packets between interfaces whereas IP routing finds the way toward destination in routing table.
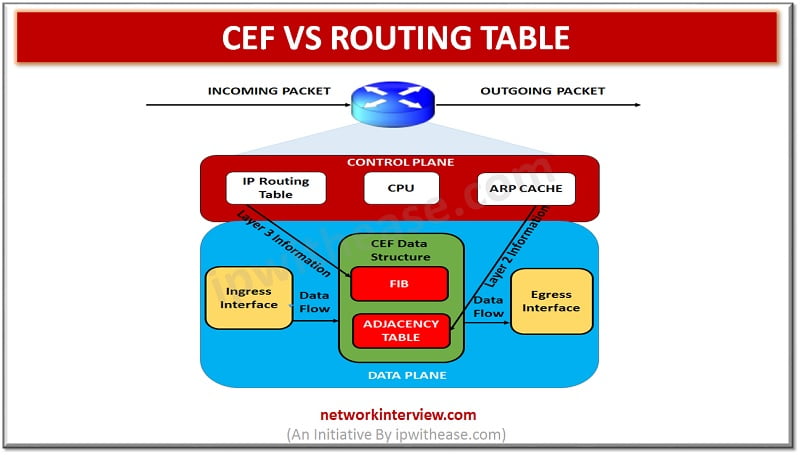
- CEF works at data plane or forwarding plane and IP routing table works at control plane.
- IP route table is stored in RAM and CEF is stored in TCAM.
- IP routing verification is performed by “show IP route” command and CEF can be verified by command “show IP CEF”.
- IP routing protocols are Static, Dynamic and EGP whereas CEF uses TCAM for next hop lookup.
- CEF is layer 2 whereas IP routing is layer 3.
- CEF looks up FIB and makes forwarding decision whereas IP routing looks at routing table to make decision.
- CEF can be enabled by “IP CEF” command while IP routing can be enabled by route protocol name.
- CEF works by creating two tables i.e. Adjacency table and FIB. On the other hand, IP routing table contains next hop exit information, AD, Metric and best route toward destination.
Difference table : CEF vs Routing table
CEF | ROUTING TABLE |
| CEF moves packets between interfaces | IP routing finds the way towards destination in routing table |
| CEF works at data plane or forwarding plane | IP routing table works at control plane |
| CEF is stored in TCAM | IP route table is stored in RAM |
| CEF can be verified with “show IP CEF” | IP routing table verification done with “show IP route” command |
| CEF uses TCAM for next hop lookup | IP routing protocols are Static, Dynamic and EGP |
| CEF is layer 2 | IP routing table is layer 3. |
| CEF looks up FIB and makes forwarding decision | IP routing looks at routing table to make decision |
| CEF can be enabled by “IP CEF” command | IP routing can be enabled by “IP route” globally |
| CEF works by creating two tables ·Adjacency table ·FIB | IP routing table contains next hop exit information, AD, Metric and best route toward destination |
Conclusion
CEF is a packet switching technique, whereas IP routing is a technique of forwarding packet along the best path toward destination. CEF contains two bodies i.e. adjacency table which is layer 2 and FIB which is layer 3. On contrary, IP routing table is layer 3.
Download the difference table here.
Tag:comparison