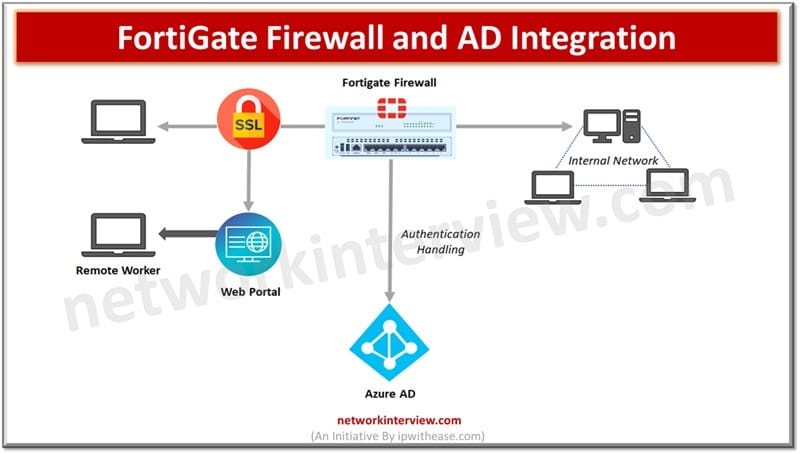
Integrating FortiGate with Active Directory for User-Based Policies
Integration of a FortiGate firewall with Active directory provides a strong defense on authentication and authorizations.
In today’s digital IT landscape cyber threats are constantly evolving and getting more and more sophisticated which calls for ensuring a robust network security for all organizations be it small, medium or large. Firewall technologies in networking play a critical defense mechanism which protects networks against unauthorized access and other malicious traffic.
However, how effectively a firewall will protect networks also depends largely not just on security policies configuration but also how access to firewalls is managed in the network.
In this article we will learn more in detail about integration of FortiGate with Active directory services to manage user-based policies centrally, its key benefits and implementation considerations.
FortiGate Firewall and Active Directory
FortiGate firewalls are strong beasts built with comprehensive security controls such as intrusion prevention, application controls, Web filtering, VPN tunnels etc. and act as a first line of defense in perimeter security while inspecting incoming / outgoing traffic, enforcing security policies on users, devices and applications to disarm the cyber threats.
Active directory is a powerful directory services tool developed by Microsoft to centrally manage all network resources such as users, servers, computers, applications and provide authentication and authorization services for controlled access.
Integration Benefits: FortiGate Firewall and Active Directory
Integration provides numerous benefits as explained below
- Centralized User Authentication – Integration of FortiGate with Active directory let organizations leverage existing user credentials management via AD for authentication services. There is a central source to manage all users which eliminates the need to manage separate user databases, helps in streamlining overall user management process and enhances operational efficiencies.
- Granular Level Access Control – Integration helps AD administrators to create and enforce stronger granular access control policies based on user, groups and OU’s level. The granular policies provide fine-grain control to ensure only authorized users can have access to network resources thereby reducing the instances of unauthorized access or data breaches.
- Dynamic Firewall Rules – This integration enables dynamic updates to firewall rules when changes occur in an active directory such as modification of user group membership, or any attribute changes. The dynamic rules management aligns security policies requirements with organizational requirements and user permissions in real-time and also reduces chances of error due to no human intervention.
- User-based Logging and Reporting – Active directory integration provides visibility into network activities as user identifies are associated with firewall reports and logs. The efficient monitoring and auditing of user behaviour reduces compliance efforts, brings in simplicity in threat detection and improves incident response timing.
- Single Sign-on (SSO) – Integration means SSO enablement for all users accessing the network, resources, services or applications which elevates user experience as there is no need for repetitive logins and reduction in password fatigue.
Implementation Considerations: FortiGate Firewall and AD
- Configuration – Establishment of LDAP or active directory authentication, trust, and defining access control policies need to be performed in a diligent manner ensuring proper configuration of both active directory and FortiGate.
- Security Best Practices – Implement robust security controls such as encryption of communication channels (LDAPS) and strong authentication protocols such as Kerberos to build a strong integration which ensures data confidentiality and integrity.
- Validation and Testing – Integration needs to be tested and validated thoroughly to ensure identification of any potential issues or misconfigurations. Test user authentication, access control and logging functionality before enabling it fully in production.
- Maintenance and Monitoring – Continuous maintenance and monitoring is required to ensure integration works seamlessly. Review of firewall, Active directory logs at periodic intervals are essential, so as the monitoring of changes in Active directory and perform security assessments regularly to ensure security posture is intact.
Conclusion
Integration of active directory and FortiGate firewall is a robust strategy to enhance network security, user management efficiency, and building a secure security posture. By leveraging the capabilities of active directory for centralized management of user identities organizations can enforce granular level access controls, security policies, eliminate operational blocks and mitigate security risks in an efficient way.
Tag:Fortigate



