What is Wireless Mesh Technology?
The requirements which demand less mobility and low cost within a radio range are ideal for people connected with the Internet who work in remote areas and operating businesses. These are: self-healing nature and integration with various different networks which include cellular networks and IEEE 802.11, 802.16 also and flexible to work with more than one protocol.
Today we look more in detail about wireless mesh topology, how it works and its architecture, its features and advantages inclusive of its use cases etc.
About Wireless Mesh Technology
A wireless mesh network (WMN) as they call it is a mesh network created using various wireless nodes with access points. Each node in the network acts as a forwarding node to its neighbouring node to transfer the data. The network is decentralized in its architecture hence forwarding of data is only possible to neighbouring nodes.
Wireless networks may or may not be connected to the Internet. The network topology of wireless mesh networks could be full or partial mesh. A full mesh means every node will communicate to every other node in the network. In partial mesh nodes only communicate to their nearby nodes.
When data is transmitted between two nodes, they do not communicate with each other, data hopping happens from one node to the next node until it reaches its final destination. The nodes are programmed to use adaptive routing algorithms to constantly determine the optimal route between nodes for transmission of data.
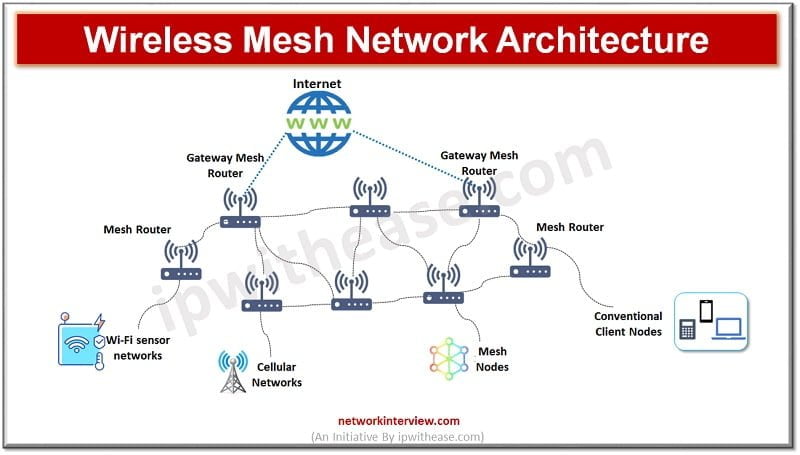
Wireless Mesh Architecture
Wireless Mesh technology is an infrastructure which is a network of routers without the cabling between the nodes. It consists of radio nodes which need not be wired to a cabled port unlike conventional wireless access points. Nodes between the source and destination act as forwarding nodes, shortest hops are predicted to transmit the data to a large distance. Wireless mesh topology is reliable.
Types of Wireless Mesh Networks
Wireless mesh networks are segregated into three types based on nodes functionality in the network as under:
Infrastructure Mesh Architecture:
Acts as wireless backbone for infrastructure in mesh architecture. Client node is passive in mesh architecture via Ethernet links; conventional clients with Ethernet interfaces will be connected to mesh routers. If a traditional network and mesh router are operating under the same radio range it is easier for a mesh network to communicate with a mesh router. In case radio ranges differ, nodes will communicate to the base station for further communication assistance to mesh routers.
Mesh Architecture based on Clients:
Mesh architecture based on client having peer to peer connectivity. Each node acts as a routing node for data transfer. Client performs the role of mesh routing by acting in the forwarding of data packets.
Hybrid Mesh Architecture:
Mesh nodes/routers act as backbone for the entire network operation. Using a network mesh router, it performs routing and forwarding of data packets to the destination.
Features of Wireless Mesh Technology
- Dynamically self-configurable and self-organized
- Adaptive in nature with ease of installation and uninstallation of nodes
- More fault tolerant and robust
- Useful for non-line of sight (NLoS) networks
- Ease of integration and interoperability supports different types of protocols
- Cost of designing network is less as compared to traditional networks
Limitations of Wireless Mesh Technology
- Low processing capabilities lead to latency as data need to hop though several nodes
- Lack of central server makes mesh systems complicated to monitor , control and troubleshoot
- Lack of centralization makes routing and resource management more complex
Use cases
- Battlefield surveillance
- Tunnels
- Mobile video applications
- Home Wi-Fi networks
- Public Wi-Fi networks
- Construction sites
- Connecting IoT devices such as sensors, security systems, smart appliances and monitoring systems
- Hospitals, educational campuses and warehouses
Continue Reading:
Top 10 wireless technology trends
TORA – Ad hoc Wireless Network
Tag:wireless



