Palo Alto Interface Types & Deployment Modes Explained
Introduction to Palo Alto Interface types/ Deployment Modes
The entry and exit point of traffic in a firewall is enabled by the interface configurations of data ports. Palo Alto being a next-generation firewall, can operate in multiple deployments simultaneously as the deployments occur at the interface level and you can configure interfaces to support different deployments.
For instance, the configuration can be done for some Layer 3 interfaces to integrate the Palo Alto firewall into dynamic routing environment, and at the same time other interfaces can be configured to integrate into the Layer 2 switching network. Thus, Palo Alto firewall provides an added advantage of flexibility and ease of deployment in network segmentation.
Palo Alto Interface Types
The firewall provides configuration options for both physical/Ethernet interfaces and logical interfaces.
Physical/Ethernet Interface Types
- Tap Mode
- High availability (HA)
- Log card
- Virtual Wire
- Decrypt mirror
- Layer 2
- Layer 3
- Aggregate Ethernet
Logical interface Types
- VLAN
- Loopback
- Tunnel
- SD-WAN
In this article, we will discuss the major interface types in detail.
TAP: Interface Type/ Deployment Option
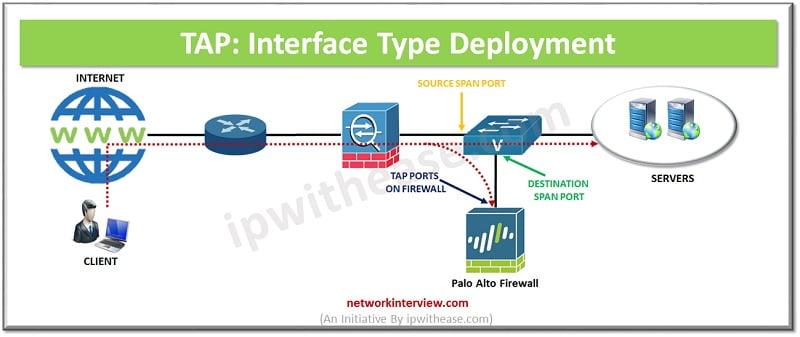
TAP Mode interface type uses mirroring or SPAN feature that allows passive monitoring of the traffic flow across a network. It involves configuration of SPAN in which the tap port on Palo Alto firewall connects to the destination SPAN port of the switch.
PROS
- Organizations can monitor traffic without any changes to the network infrastructure.
- Any threats on your network can be identified by the firewall.
- Tap mode offers the visibility of application, user and content.
CONS
As the traffic is not running through the Palo Alto firewall, so it cannot block any threats to the traffic. The traffic can be monitored and cannot be controlled.
VIRTUAL WIRE (V-WIRE): Interface Type/ Deployment Option
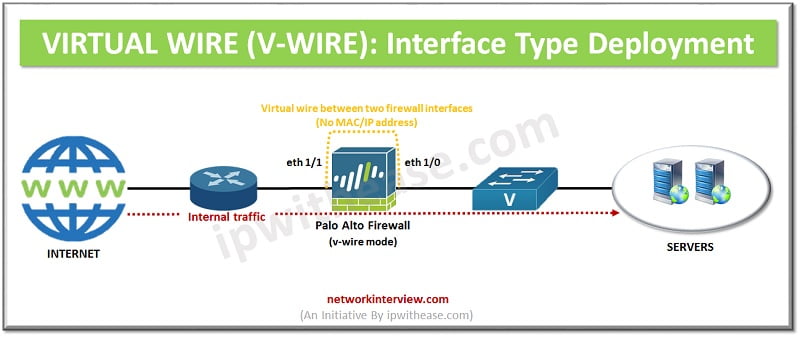
As the name implies, it’s a virtual interface in which a firewall is installed transparently on a network segment by binding two interfaces/ firewall ports. V-wire deployment mode simplifies the installation and configuration as the firewall can be inserted into an existing network. You need not to do any network redesigning or reconfiguration of the adjacent network devices. No MAC or IP addresses need to be assigned to the interfaces.
The virtual wire interfaces have no Layer 2 or Layer 3 addresses as it is directly connected to a Layer 2/Layer 3 networking device/host.
PROS
- The traffic can be monitored as well as controlled, this overcomes the limitation of TAP mode in which traffic can’t be controlled.
- It doesn’t require any redesigning/reconfiguring.
- It supports traffic blocking/allowing based on VLAN (Virtual LAN) tags.
- It support features like App-ID, User-ID, Content-ID, NAT, QoS and SSL decryption.
CONS
It does not support switching, VPN tunnels, or routing as no IP address is assigned to Layer 2 or Layer 3 devices.
LAYER 2: Interface Type/ Deployment Option
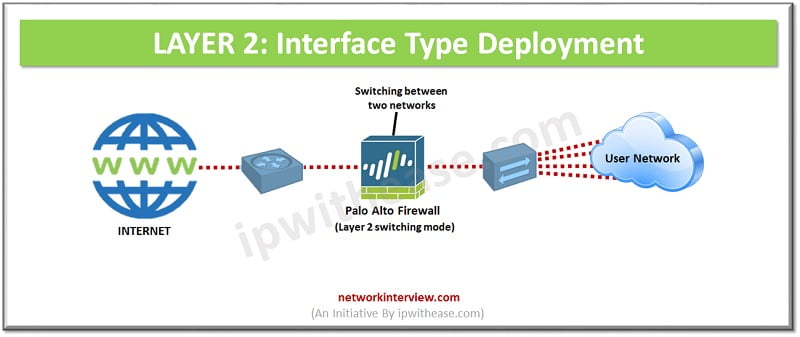
In this type of interface, the firewall is configured to perform switching between two or more network segments. The traffic can be examined as per the policies which provides increased security and visibility within the internal network.
The firewall interfaces do not participate in the Spanning tree topology but they are capable of supporting the access/trunk links. Any bridge protocol data units (BPDU) received are directly transferred to the neighbouring Layer 2 switch without processing.
Layer 2 interface is to be configured when switching is required.
The routing of traffic between VLAN/other networks is achieved via a default gateway. This default gateway is generally a Layer 3 switch.
PROS
The traffic can be examined, monitored and controlled.
It supports features like App-ID, User-ID, Content-ID, NAT, QoS and SSL decryption.
LAYER 3: Interface Type/ Deployment Option
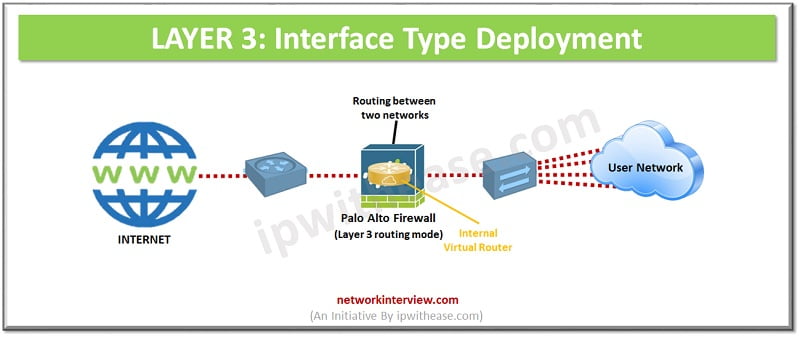
Layer 3 interface type supports IP address configuration. The traffic routes between multiple ports. Each port is configured with an IP address and security zone. Layer 3 interface configuration requires internal virtual router. For each Layer 3 interface virtual router needs to be configured to route the traffic
PROS
- The traffic can be examined, monitored and controlled.
- It support features like App-ID, User-ID, Content-ID, NAT, QoS and SSL decryption.
- It supports sub interfaces with VLAN tags
Continue Reading:
Palo Alto Troubleshooting CLI Commands
NAT Configuration & NAT Types – Palo Alto



