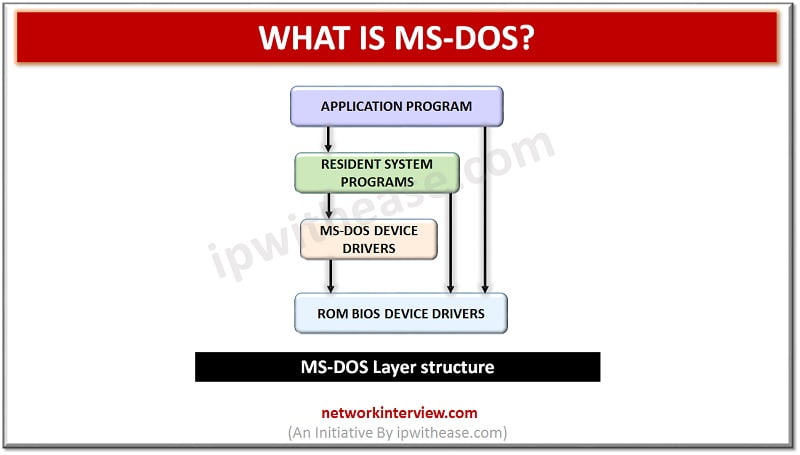
What is MS-DOS ( Microsoft Disk Operating System)?
Introduction to MS-DOS
An Operating System is a set of programs which controls and coordinates the use of computer hardware among various application programs. It provides an environment to user to execute a command or programs.
MS DOS was the Microsoft Disk operating system which dominated operating system market for personal computers (PC) throughout 1980s. The original operating system was developed by American computer programmer Timothy Paterson who was a developer for Seattle computer products wrote the original operating system for Intel Corporation 8086 microprocessor in 1980s.
There are a number of Web Hosting providers available. You may click here to browse the best web hosting providers.
In this article we will learn more about MS-DOS operating system, its features, advantages, and limitations.
Definition – MS DOS
The command line-based MS-DOS was initially named as QDOS (Quick and dirty operating system) and renamed later as 86-DOS. MS-DOS allows users to navigate, open and navigate files and folders on their computers from command line instead of a GUI interface like Windows.
Origin
Its origin dates back with two earlier operating systems CP/M and QDOS. CP/M (Control program for Microcomputers) was created in mid 1970s by Gary Kildall of Digital Research. It was an 8-bit operating system then in 1980s Tom Paterson of Seattle Computer Products developed QDOS (Quick and Dirty Operating System) for Intel new 16-bit 8086 CPU. A year later in 1981 Microsoft purchased exclusive rights to sell the system and renamed MS-DOS and was last updated in 1994 when MS-DOS 6.22 was released. From 1981 through 1997 it underwent several iterations and revisions.
Features
MS-DOS offers file system to organize, read and write files to the disk storage. It is a single user operating system and performs various tasks to ensure the proper operation of systems. It manages files, folders, and allows program loading and execution, control hardware devices such as disk, memory et.c and allocates resources. MS-DOS don’t offer GUI (Graphical User Interface) and has a command line interface. users type command on command line, the commands are interpreted to perform the required task. It contains commands such as PRINT, DEL, RELEASE and COPY.
It uses 16-bit file allocation table (FAT16) and 16-bit interfaces are used to uniquely define the location of the memory of each file. These identifiers are stored in a tabular format with the name File Allocation table. MS-DOS does not support multi-user operating system and it is less secure and it does not have concept of user roles. It is very light weight due to its basic interface and limited features. A machine having MS-DOS typically need 512 KB to 1 MB for operating system and application , data.
The earliest versions of MS-DOS addressed need for larger hard disk drives, with support for multiple directories, networks, and extended characters. The later released versions supported multiple HDD partitions, disk compression, disk fragmentation, enhance memory management and improvements in operating system text editing functions. MS-DOS is not used any longer, but its GUI based operating systems contain and emulation layer which allows for the running of MS-DOS program to provide backward compatibility with legacy based software.
Types of MS-DOS Commands
Instructions given to computer to perform a specific task is known as command. The MS-DOS has many commands to perform each task and these commands are stored in DOS directory of the disk. The MS-DOS commands are of two types. (a) Internal commands are built in commands of MS-DOS and these are stored in Command interpreter file (COMMAND.COM). These commands reside in memory if system is at prompt (C:\>) level some of the internal commands are DATE, TIME, DIR, VER etc. (b) External commands are separate program (.com) files which reside in DOS directory and executed like command some examples are HELP, DOSKEY, BACKUP, RESTORE, FORMAT etc.
DIRECTORY COMMANDS | DESCRIPTION | FILE MANAGEMENT COMMANDS | DESCRIPTION | GENERAL COMMANDS | DESCRIPTION |
| DIR | List all files of specific dir or sub dir | COPY | Copy files | TIME | Display time |
| MD | Make directory or subdirectory | XCOPY | Copy files and directories and its subdirectories | DATE | Display date |
| CD or CHDIR | Navigate or move to specific directory | DEL | Delete files | TYPE | Display file contents |
| RD or RMDIR | Remove directory | REN | Rename file and directory | PROMPT | Customize DOS prompt |
| TREE | Display all directory paths | ATTRIB | Set or show file attributes | ||
| PATH | Set sequential search path for executable files | BACKUP | Backup files and directories | ||
| SUBST | Substitutes a string alias for the pathname | RESTORE | Restore files | ||
| EDIT | Create or edit a file | ||||
| FORMAT | Format a disk / drive | ||||
Download the table: MS-DOS COMMANDS
Characteristics of MS-DOS
- 16-bit operating system
- Command line interface
- Maximum space available is 2 GB
- Single user operating system
- Helps in file management g., creating, editing, deleting files, etc.
MS-DOS: Pros and Cons
PROS
- Direct access to the BIOS and its underlying hardware
- It is lightweight and have no overheads of the multitasking operating system
- Very less memory requirement from 512 KB to 1 MB
CONS
- Multi-tasking not supported
- Difficulty in memory access while addressing more than 640 MB of RAM
- OS does not support automatic IRQ ordering
Continue Reading:
Linux vs Windows Operating system
Software Development vs Web Development
Software Engineer vs Programmer
Tag:software



