Mainframe vs Minicomputer – Sneak Preview
Mainframe dominates 87% of credit card transactions and 71% of fortune 500 companies operations are run through Mainframes.
Minicomputers changed the digital landscape and were designed for direct interaction between systems and its users.
We would learn today about Mainframe and Minicomputer systems.
Mainframe
The first mainframe computer was ‘Harvard Mark’ which was developed in 1930s but was not ready to use till 1943s. It was bulky in size and weighted in tons.
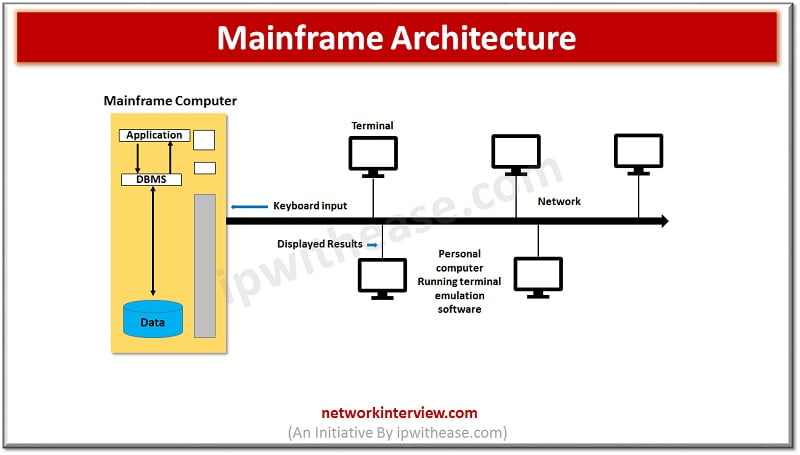
Mainframe computers or as we call them as ‘Big iron’ were used for critical applications for bulk data processing, enterprise resource planning, large scale transaction processing and so on. Mainframes were characterised by hot swapping feature of hardware such as hard disks and memory, backward compatibility to older hardware, extensive Input/Output facilities, operated in batch mode , Virtualization and so on.
Mainframe term is derived from a term called ‘Large cabinet’ which comprises of a Central processing unit (CPU), main memory and a set of peripherals. Mainframes were reliable and sturdy machines which provided high availability as they typically used for business-critical applications where downtimes could be catastrophic. Mainframes used sets of punched cards, magnetic tapes, they operated in batch mode and supported Backoffice applications such as Payroll management, Customer order processing, Financial transactions, Inventory and production control, Payroll processing , Bulk storage of client information, scientific and engineering computations.
IBM Z is the only commercial sold mainframe in the market today.
Mainframe Characteristics
- Required specialized space to operate and skilled technicians
- Support large number of concurrent users
- Can process millions of transactions per second and handle volumes of data
- It is sturdy by design and can work for years smoothly without glitches with proper installation
- Supports large scale memory management
- Errors can be fix quickly without impacting the performance
- Protection of storage data and information and exchange of data on ongoing basis
Minicomputer
Minicomputers were very different from their larger counterpart ‘Mainframes’ in terms of price, function, usage and size.
Advent of Minicomputers changed the landscape of IT industry and brought systems in reach to general users. In 1960 Control Data Corporation (CDC) , Packard Bell, and Digital Equipment Corporation introduced Minicomputers with PDP (Programmed Data Processor).
Minicomputers were used by small and medium industry segments for operating businesses. Minicomputer is also referred as ‘Mid-range’ system.
The minicomputers are characterized by one or more processors, supported multiprocessing, and multi-tasking, and meant to be resilient for high workloads, they can be networked, they don’t require any specific power or cooling requirements.
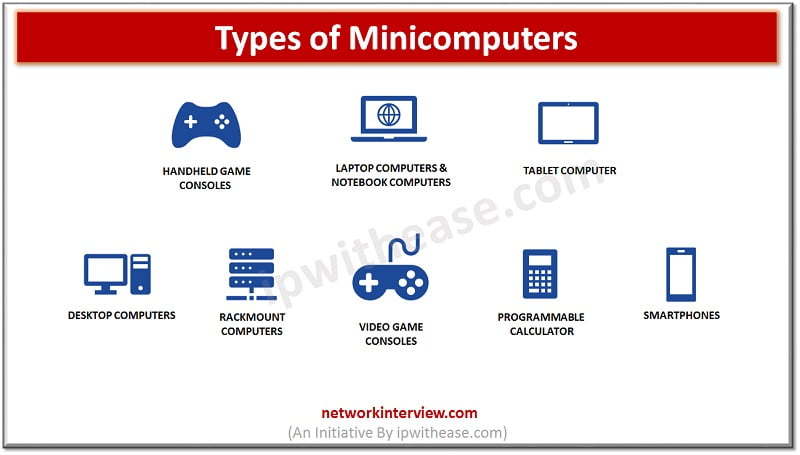
Minicomputers are available in market today in the form of many electronic gadgets such as Smartphones, Tablet PC, iPAD, Drawing tablets , Desktop Mini PC and so on.
These small and powerful gadgets are packed with features and used for gaming, watching videos, net surfing, and a variety of computing tasks. Minicomputers were developed for tasks related to storage of records, calculations, controls etc.
Minicomputer Characteristics
- Smaller size than a mainframe computer
- Low in cost than a super and mainframe computer
- Less powerful than a super and mainframe computer but more powerful than microcomputers
- Perform multitasking and multiprocessing
- Suitable for individual use and small businesses
- Ease of use and maintenance
- Small and lightweight easy to carry
- Fast and reliable
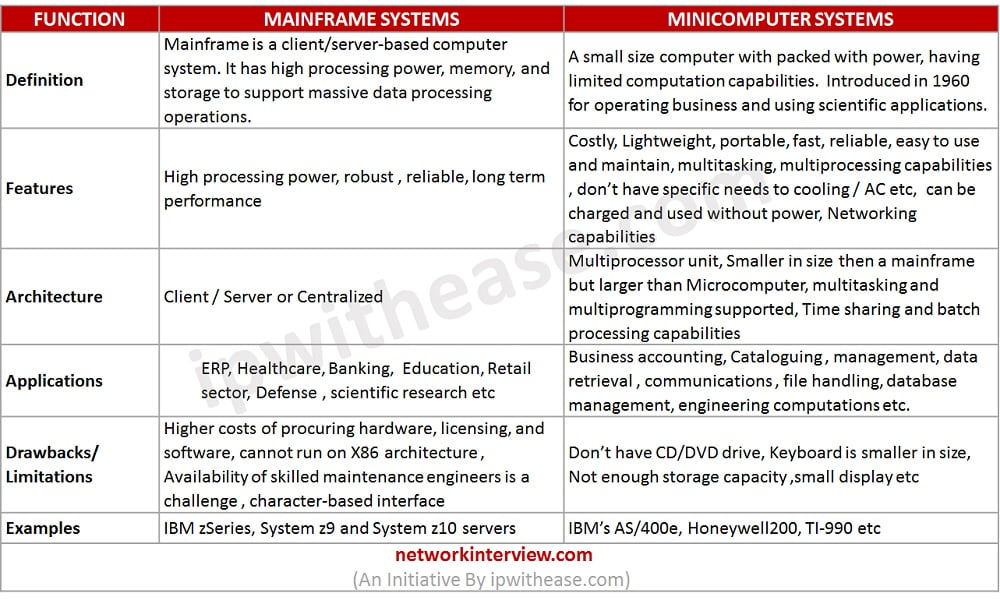
Comparison Table: Mainframe vs Minicomputers
Below table summarizes the difference between Mainframe and Minicomputer systems:
FUNCTION | MAINFRAME SYSTEMS | MINICOMPUTER SYSTEMS |
| Definition | Mainframe is a client/server-based computer system. It has high processing power, memory, and storage to support massive data processing operations. | A small size computer with packed with power, having limited computation capabilities. Introduced in 1960 for operating business and using scientific applications. |
| Features | High processing power, robust , reliable, long term performance | Costly, Lightweight, portable, fast, reliable, easy to use and maintain, multitasking, multiprocessing capabilities , don’t have specific needs to cooling / AC etc, can be charged and used without power, Networking capabilities |
| Architecture | Client / Server or Centralized | Multiprocessor unit, Smaller in size then a mainframe but larger than Microcomputer, multitasking and multiprogramming supported, Time sharing and batch processing capabilities |
| Applications | ERP, Healthcare, Banking, Education, Retail sector, Defense , scientific research etc | Business accounting, Cataloguing , management, data retrieval , communications , file handling, database management, engineering computations etc. |
| Drawbacks/ Limitations | Higher costs of procuring hardware, licensing, and software, cannot run on X86 architecture , Availability of skilled maintenance engineers is a challenge , character-based interface | Don’t have CD/DVD drive, Keyboard is smaller in size, Not enough storage capacity ,small display etc |
| Examples | IBM zSeries, System z9 and System z10 servers | IBM’s AS/400e, Honeywell200, TI-990 etc |
Download the comparison table here.
Continue Reading:
Software Engineer vs Computer Engineer
Tag:comparison, New technology