Bus Network Topology
Network Topology refers to the physical or logical layout of a network.
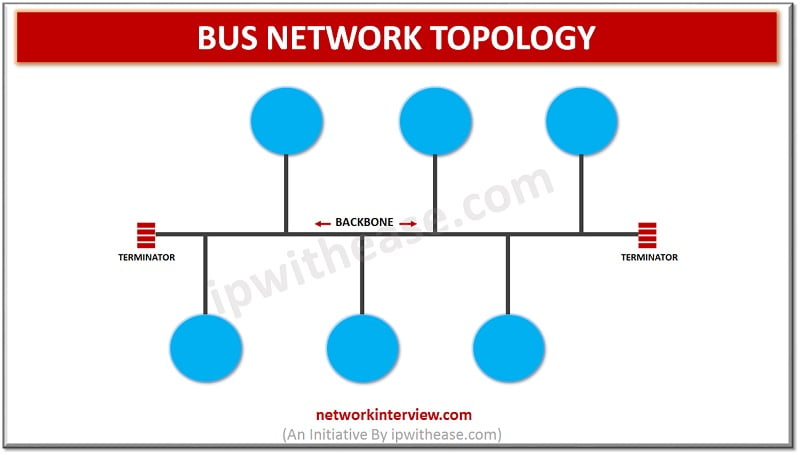
BUS Network Topology
Bus topology is a type of network topology where each node is connected to a single cable known as the backbone. Though there is no limit to the number of nodes that can be attached, but the number of connected nodes affects the performance of the network. In bus topology, the data is transmitted from one node to another through the backbone, in the form of a packet. The data packet contains the address of the destination machine. At each node of transmission the destination address (MAC/IP address) is screened to see if it matches their address. If the address doesn’t match, nothing more is done by the node and if the node addresses match to the address contained in the data then they process on the information.
Depending on the type of computer network card, a coaxial cable or an RJ-45 network cable is used to connect them together.
Advantages of Bus Topology:
- Installation is easy.
- In case of failure of any device, there will be no effect on other devices or network.
- It is economical as compared to other network topology i.e. mesh and star, as the cabling cost is less.
- It is easy to understand topology.
- Easily expandable by joining two cables together.
- It is good for small network setups.
Disadvantages of Bus Topology:
- It is difficult to find faults in the network in case of any device failure.
- The use of terminators is a must to prevent bouncing of signals.
- It is slower because one computer transmits at a time.
- Bus topology is not great for large networks.
- Additional devices slow down the network.
- If a main cable is damaged, the entire system/network will fail.
Related – Mesh Network Topology



