12 Most Important Network Protocols Explained
Network protocols establish rules of communication to control and govern exchange of information following secure, reliable methods. These are a set of rules designed to have a standard framework for interchange over networks. There are a variety of network protocols which exist, some of them are wired like Ethernet and some are wireless like WLANs and Internet communication. The Internet protocol suite has dozens of networking protocols which are used for transmission and broadcast over the Internet.
In today’s lesson we will cover in detail about twelve most important networking protocols, their features, purposes they are meant for and so on.
List of 12 Most Important Network Protocols
The very first important protocol in this list is ARP.
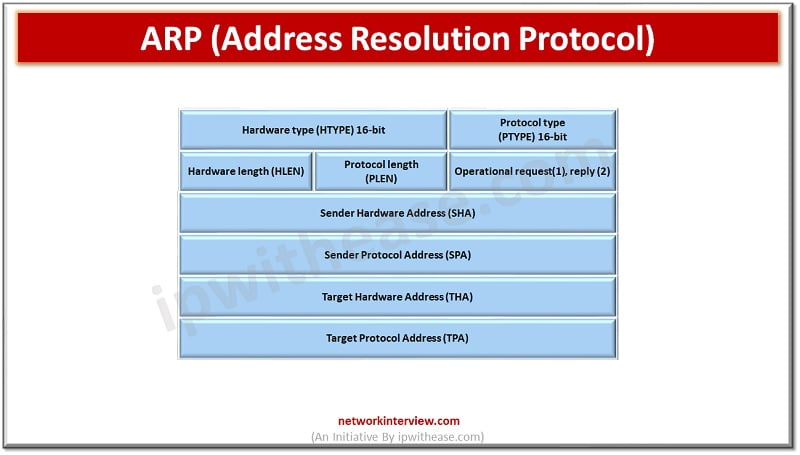
Address Resolution protocol (ARP) –
It is a communication layer protocol used for identification of Media access control (MAC) address given the IP address basically mapping between data link layer and network layer. ARP translates IP address into MAC address, this is required because IP address and MAC address have different lengths. IPv4 addresses are 32 bit long and IPv6 addresses are 128 bit long whereas MAC address is a device physical hardware number which is 12 hexadecimal digits split into six pairs. The translated address is stored in the ARP cache table when a new device joins the network. Below figure depicts the ARP packet structure.
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) –
BGP is an intern domain protocol which uses path vector routing for communication. It is a gateway protocol which is used to exchange routing information between autonomous systems on the Internet. It is an open standard protocol which can run on any window device. It is the only protocol which operates on the Internet backbone and it is an application layer protocol which uses TCP for communication.
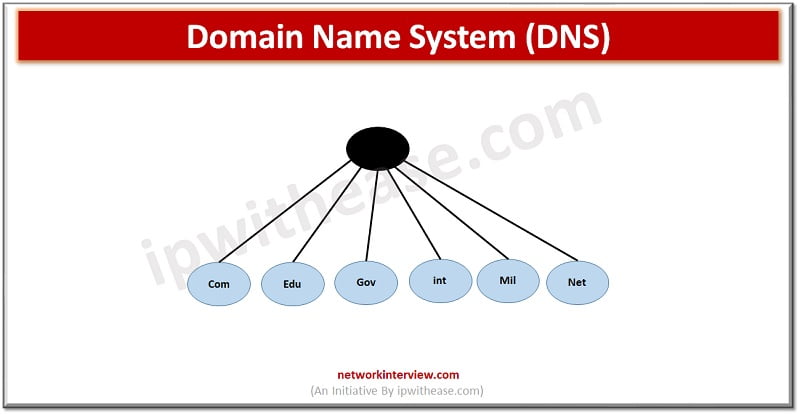
Domain Name System (DNS) –
DNS is an application layer protocol which defines how an application processes runs on different systems and passes messages to each other. It is a directory service which provides mapping between the network host and its numerical address. It is required to enable Internet functioning. Each node in a tree is a domain name, and full domain name is a sequence of symbols specified by dots (.). This service performs translation of domain name into an IP address.
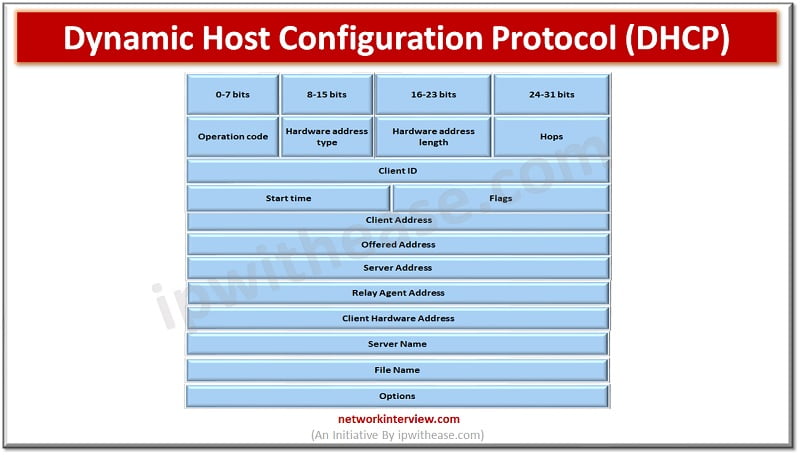
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)-
DHCP works on IP networks and assigns them IP addresses. It allows hosts to communicate effectively with each other. DHCP also assigns subnet mask in addition to IP address, default gateway address, the domain name server address and pertinent configuration parameters. DHCP allows systems to request IP addresses and other network parameters automatically from Internet service providers. The TCP/IP protocol supports DHCP for automatic assignment of a unique IP address to each connected device and keeping a track of them.
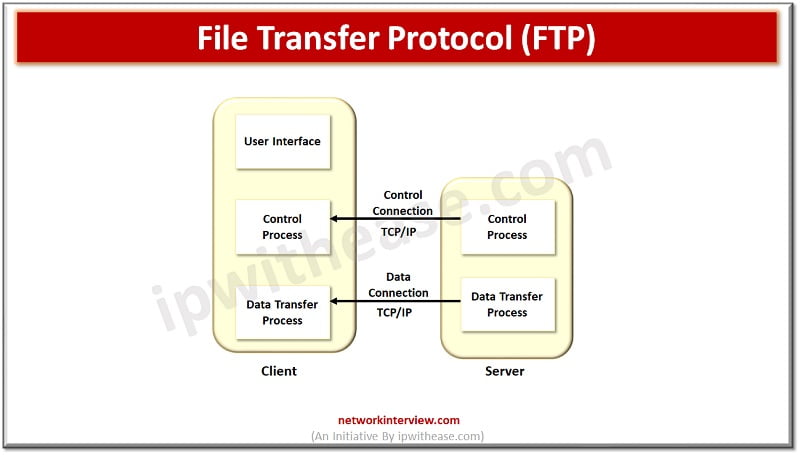
File Transfer Protocol (FTP)-
Is a network protocol based on client / server architecture model. It is an Internet protocol provided by TCP/IP and used to transfer files from one host system to another host system. It is majorly used to transfer web page files and also used to download files from other servers.
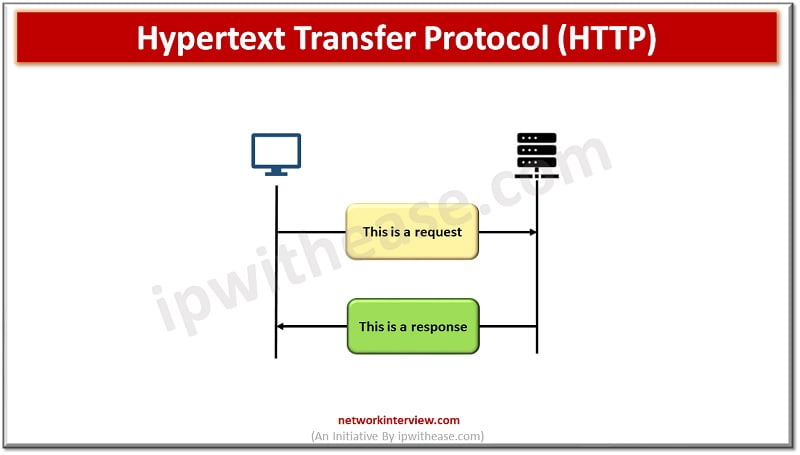
Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) –
HTTP is used to access data on the World Wide Web (WWW). It is used to transfer data in the form of plain text, hypertext, audio, video formats. It is quite similar to FTP as it also transfers files from one host to another host but it is simpler as it uses only one connection i.e., no control connection for files transfer.
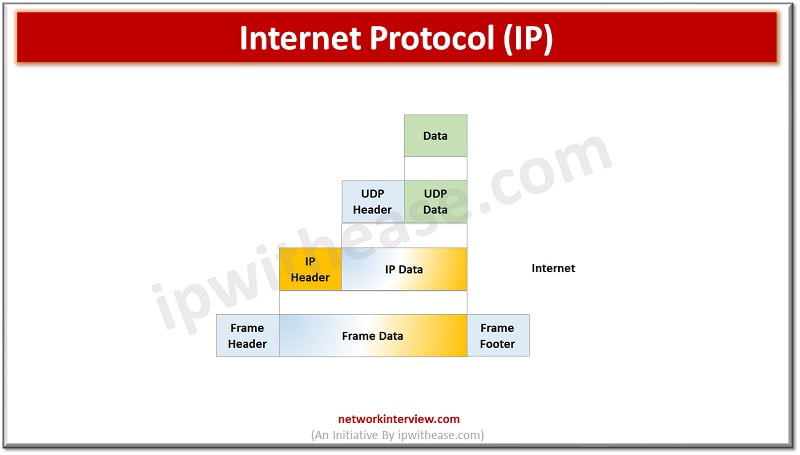
Internet Protocol (IP) –
Internet protocol is used for sending packets from source location to destination location. The main task of IP is to deliver the packets from source to destination based on IP addresses available in the packet header. It defines the packet structure which hides data which is to be delivered as well as the addressing method which labels the datagram with information on source and destination.
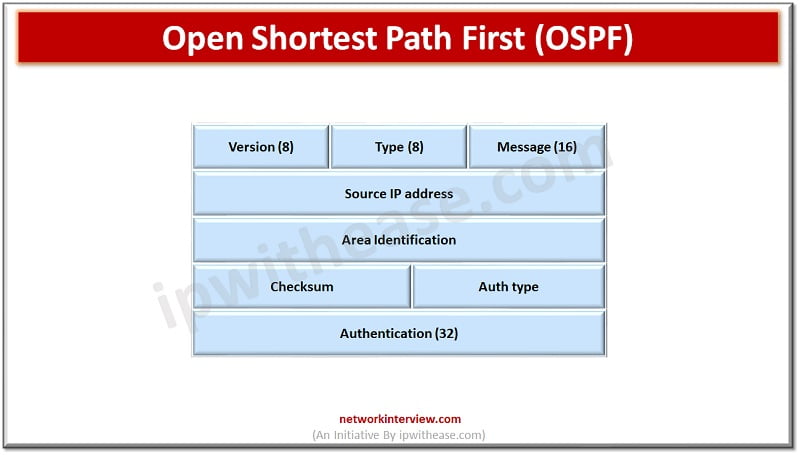
Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) –
OSPF is widely used and supported routing protocol as an interdomain protocol and used within an area or a network. It is an interior gateway protocol which is designed within a single autonomous system. It is based on a link state routing algorithm in which each router contains information of every other domain based on which shortest path is determined and its goal is to learn paths.
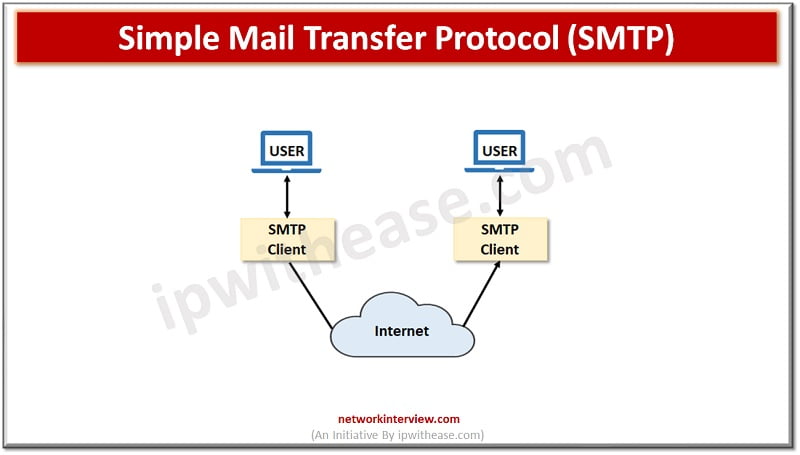
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) –
SNTP is an electronic mail transmission network protocol. It is used to send messages to other systems based on email address. It provides mail exchange between users on the same or different systems and it also supports sending a single message to multiple recipients, messages which include video, audio, and graphics, and also send messages outside the network.
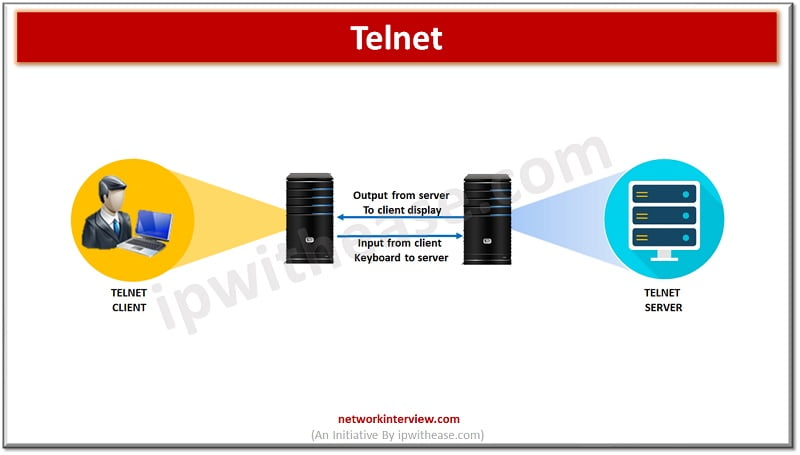
Telnet –
Telnet is an application protocol used on Internet which provides bi-directional interactive session which uses a virtual terminal connection. It establishes connection between remote endpoint and host machine to enable a remote session. Telnet lacks security protections however to secure communication.

Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) –
TCP is a transport layer protocol which facilitates transmission of packets from source to destination. It is a connection-oriented protocol which establishes connection prior to communication. It takes data from the application layer and divides it into several packets and numbers them before transmission.
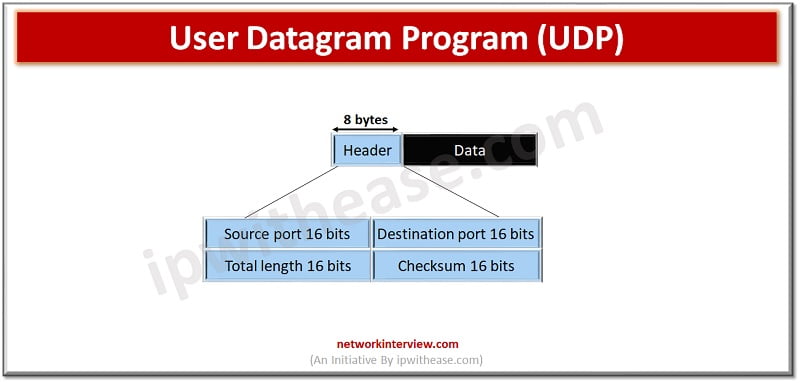
User Datagram Program (UDP) –
UDP is also a transport layer network protocol but it is unreliable as it is a connectionless state and does not provide an acknowledgement mechanism unlike its counterpart TCP. It works by encapsulating the data into a packet and providing its own header then it is encapsulated to the IP packet and sent to destination.
Continue Reading:
Enabling and Configuring Network Configuration Protocol in a Managed Device
Understand and Configure the UDLD Protocol
Tag:Protocols



