What is Zero Configuration Networking?
The information access is made uninterrupted over wired and wireless networks from anywhere, anytime, any device using modern technology. Today end users are mobile and often equipped with digital portable devices and they expect services availability as and when it is needed. They also do not want to be burdened with complex configuration vows before services discovery and its usage. The zero-configuration networking aims to alleviate configuration burden off the users to discover services and devices with very little manual intervention.
In today’s topic we will learn about zero configuration networking, how zero configuration networks work, what are the advantages of zero configuration networks, its limitations and use cases.
Zero Configuration Networking
Zero configuration networks are a set of protocols and techniques which are used together to create an IP network having no specific configuration servers or manual operation requirements to provide services. These networks allow users to connect to systems, scanners, network devices such as printers, to have a functioning network without the need for complex and manual configurations.
Zero configuration networking (Zeroconf) does not require the user to set up domain name services (DNS), Dynamic host configuration (DHCP) or configure manually any other system settings. The Zeroconf comprises automatic resolution, distribution of system host names (mDNS as they called), numeric network IP addresses assignment to network devices (link local addresses auto configuration) and automatic location detection for network devices.
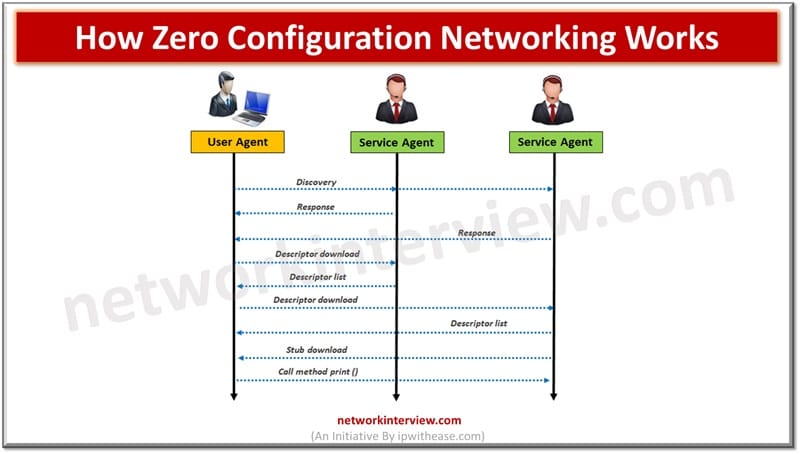
How Zero Configuration Networking Works
Zeroconf uses a number of technologies to achieve its objective. For address selection, link-local addressing is a replacement for conventional DHCP server. This capability is in-built in the IPv6 protocol used by Zeroconf. The multicast service is used for name resolution to let a network device select domain name in local namespace and use a designated multicast IP address to announce it. It uses mDNS for discovery of services.
Every computer on the local network stores individual listings of DNS resource records and joins the respective multicast DNS group. DNS based service discovery relies on a type of messaging to discover services and provide notifications on the local network on its availability.
Advantages of Zeroconf Networks
- Normal users can easily network with one or many devices without the need to perform specific setup / configuration
- Ideal for home and small office networks
- Adhoc networks for meetings and conferences
- If two devices need to share or exchange information spontaneously it is an ideal solution for such scenarios
- Provides plug/play usability for devices and applications
- Networked applications provide a friendly experience to user without any hassles
- It is independent of platform
Limitations of Zeroconf Networks
- Local Network Only: Limited to local network segments, doesn’t scale well across larger networks or subnets.
- Traffic Overhead: Uses multicast for discovery, which can generate excessive traffic in larger networks.
- Scalability Issues: Performance degrades with a high number of devices, making it inefficient for large networks.
- Security Concerns: Lack of authentication or encryption mechanisms, making it vulnerable to attacks.
- Limited Control: Offers minimal configuration options, which may be insufficient for complex environments.
Uses of Zeroconf Networks
- Application of Bonjour also known as Rendezvous used by Apple and introduced in Mac OS X 10.2 (‘Jaguar’) operating system
- Avahi on Linux and windows CE 5.0
- Used by iTunes for service discovery to find music available in local networks
- iChat instant messaging uses it
- Released under ASPL for Windows, POSIX platforms and Java



