What is VPN Split Tunnelling?
VPN or virtual private networks functions on tunnelling and connection encryption to keep internal activity, location, identity, and IP address hidden from public eyes. VPNs can unblock geo locked and censored content, can bypass statewide firewalls and torrents safely to ensure your data reaches its destination securely. VPNs also prevent use of certain websites and services which could capture your location data and cookies and use it for their own functionality.
In today’s topic we will learn about VPN split tunnelling feature, how it works, why it is required, its advantages and use cases.
VPN Split Tunnelling
To better understand how VPN split tunnelling works first we need to understand the functioning of VPN itself. When we use VPN network data is tunnelled and encrypted before being sent to a VPN server. The VPN server acts as a proxy and forwards data to the endpoint on Internet. Tunnelling is important to establish a private connection over public channel i.e. Internet. The process is known as encapsulation.
VPN tunnelling protocols hide data packets within other packets. This keeps important information such as location, IP address etc. hidden from ISP, hackers or other parties who might be interested in prying over your data. When VPN is turned on – all outgoing data flows through the encrypted channel.
Tunnelling itself does not provide encryption – this is achieved using encryption protocols. VPN connections are somewhat slower compared to regular Internet connection due to usage of encryption and data having multiple stops before reaching its final destination.
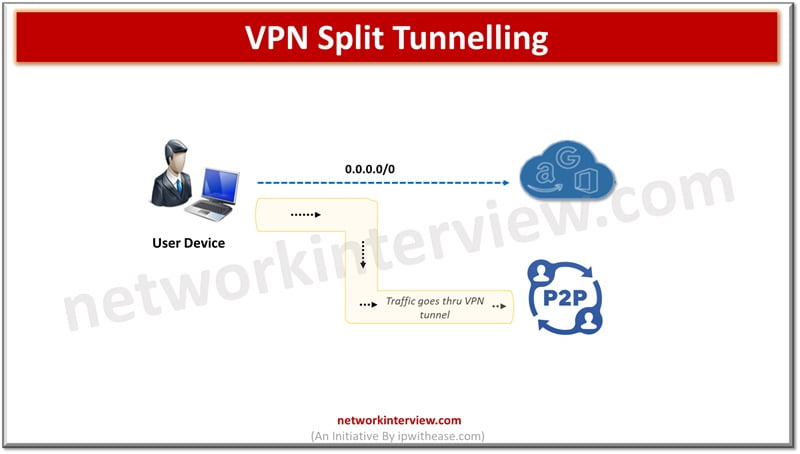
Split tunnelling is a feature which gives more control over what data to encrypt and send through VPN server and what data which needs to travel faster is unencrypted. Some Split VPN providers are NordVPN, Surf Shark VPN, IPVanish etc.
Split tunnelling works with two connections at the same time. The secure VPN connection and a normal open connection to the Internet so one can protect sensitive data without slowing down other Internet activities.
Types of Split Tunelling
VPN split tunnelling is of several types. Let’s look at them more in detail.
- URL based split tunnelling – allows you to choose which URLs you want to be encrypted while passing through a VPN channel. This is usually achieved using VPN browser extension.
- Application based VPN tunnelling – let you choose which applications you want to be encrypted while routed through VPN. And the rest of the traffic travels via a regular open network.
- Inverse split tunnelling – works in reverse manner unlike URL and application-based tunnelling. In inverse split tunnelling you designated only that you won’t want to go through VPN tunnel – all other connections will go through an encrypted tunnel. This type of tunnelling technique is used in two cases.
- One where a user relies on VPNs to keep most of their activity private but has a few websites which they access directly.
- The other scenario is where companies run private VPNs servers to keep most of the business activities protected with VPN networks.
Pros and Cons of Split Tunnelling
PROS
- It alleviates bottlenecks and conserve bandwidth as all network traffic is not forced to pass through VPN server
- Let user access more than one network at the same time and there is no need to connect or disconnect VPN
- It bypasses security controls imposed by VPN tunnel leaving online activity vulnerable to hacking
CONS
- Setup takes time to determine which URL/Apps to be designated to pass through VPN and what not
- Not all VPNs provide split tunnelling feature
- Employees could bypass permissions setup in corporate networks
- Loss of visibility in corporate networks on what employees are doing
Continue Reading:
VPN Encryption: How does it work? What types are there?
ISP vs VPN: Know the difference



