What is Storage Replication? Detailed Explanation
Storage replication – Sneak Preview
Continuous data protection with zero downtime, higher availability and speed requirements govern the business requirements in the current arena.
The purpose of replication is protection from disaster which may occur at one location and operations can resume from alternate location to ensure fault tolerance and avoiding a single point of failure.
Today, we will explore about Storage replication!
Storage Replication
Protection of data is an integral part of Storage replication. Replication helps us in Business continuity.
Storage replication technology enables replication of volumes between servers or clusters to enable redundancies built in the event of failure at the primary data storage location. Storage replication is a subset of ‘disaster recovery’ strategy for enterprises.
Organizations opt for storage replication to ensure in case of failure data storage is always available at alternate site.
Two storage devices can be connected physically or via a Storage Area Network (SAN). In the SAN environment software replicates data from primary storage to secondary storage located at alternate / remote site.
Storage Based Replication Techniques
Full Volume replication (Cloning) –
Initial synchronization happens between source and the replica (Clone). When the Sync is happening between the two replica is not available for access. Post synchronization is completed replica is exact copy of source. The size of clone is same as its source. During subsequent synchronizations only changes are replicated.
Pointer based Virtual replication (Snapshot) –
The target (Snapshot) only contains pointer to actual data however it does not contain data at any point of time. It is virtual replica.
Storage Based Remote Replication Techniques
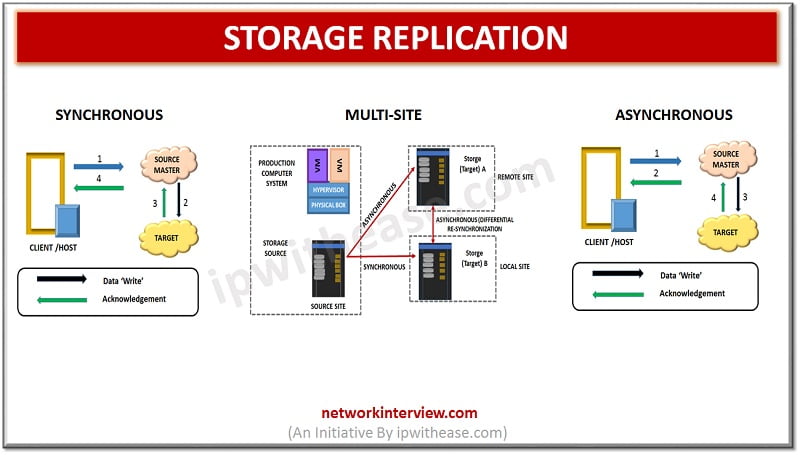
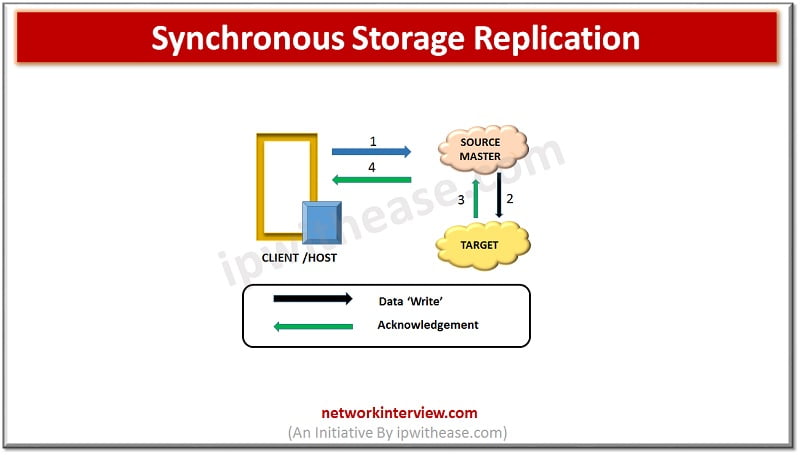
Synchronous Replication – (Also known as “Two stage commit systems)
‘Writes’ are committed to the source and remote target before sending notification of ‘Write complete’ to the production / Primary server. No additional writes will happen until every earlier write has been successfully completed and acknowledged. This is required to ensure that data is always same at source and target. To ensure remote data is consistent writes happen in same sequence as they were received.
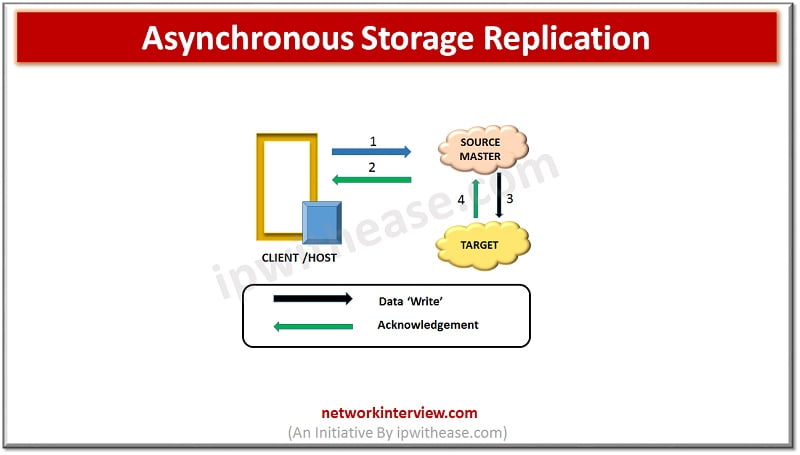
Asynchronous Replication –
It supports data replication across sites which could be 1000 miles apart. As soon as ‘Write’ happens to the source from production server acknowledgement comes immediately from the server. Data can be replicated thousands of kilometers between source and secondary site. Server ‘Write’ requests are accumulated in a buffer at Source site and this delta is transferred at regular interval to remote site. Adequate buffer capacity needs to be planned according to RPO (Recovery Point Objective) and network bandwidth and ‘Writes’ workload needs to be assessed for planning. To conserve network bandwidth Writes are collected and only final data is sent for transmission.
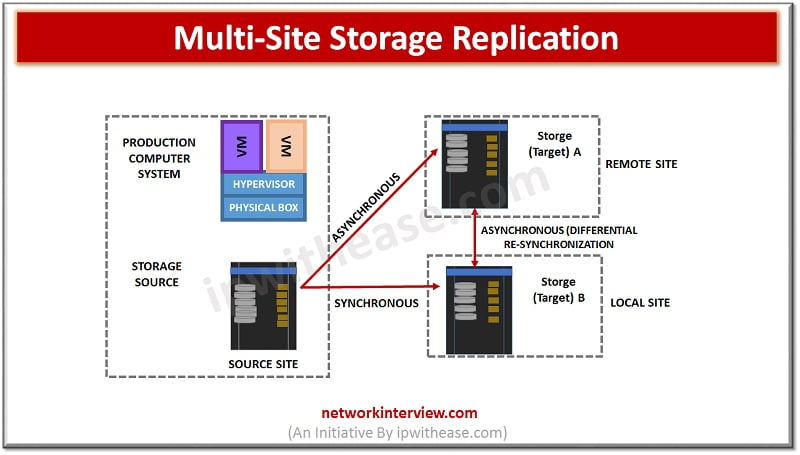
Multi-site Replication –
Source data is replicated to multiple remote sites. Data at source is replicated to two different locations and two different storage. The source to target (Site 1) is synchronous and Source to remote target (Site 2) is Asynchronous (With RPO in minutes).
In normal scenario all three sites are available, but operations continue from primary site. The difference between data is tracked and incremental re-synchronization occurs to ensure data is identical as source.
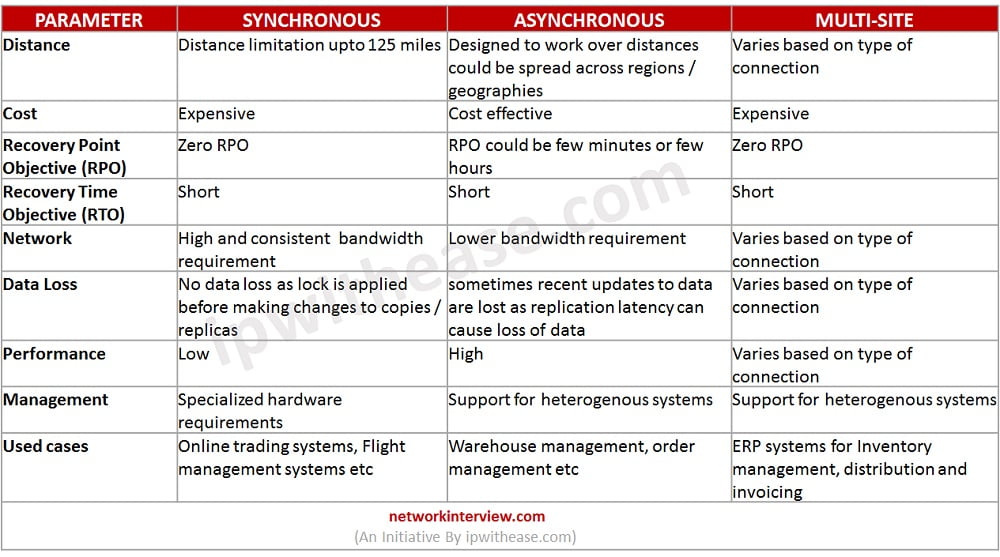
Comparison of Storage Replication techniques
Below table summarizes the comparison between different storage replication techniques:
Download the table here.
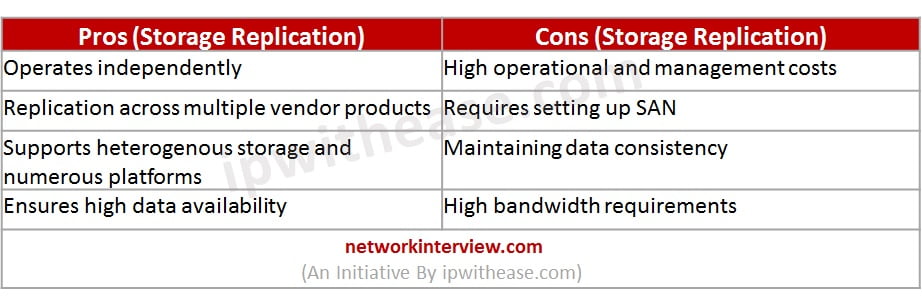
Advantages and disadvantages of Storage replication
Storage replication has its own pros and cons:
Download the table here.
Continue Reading:
File Level Storage and Block Level Storage
Tag:storage