What is HSRP (Hot Standby Router Protocol) ?
Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP)
In this article, we will discuss on HSRP protocol, related terminologies, its operation and configuration. We will cover following points:-
Topic Content
- Understanding FHRP
- Definition of HSRP
- HSRP Packet
- Key Points
- Operation and Configuration of HSRP
- Conclusion
Understanding FHRP
Network resiliency is key component of network design. Modern network requires an important consideration to deal with the network failure. With this understanding, First Hop Redundancy Protocols was developed and employed in majority of network to provide resiliency, availability and redundancy. From the client’s perspective if the gateway goes down, then access to an entire network will go down. First Hop Redundancy protocols (FHRP) will allow default gateway redundancy, it means provision of having more than one default gateway.
In the event of a router failure, there’s a backup device that will kick in and transparent to their users, continue to forward traffic to remote networks, thus avoiding the situation of isolation. We implement a first hop redundancy protocol to deal with gateway redundancy. Below are the 3 types of FHRP technology:-
- Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP)
- Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP)
- Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP)
Related – HSRP vs VRRP
Definition of HSRP
Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) is a CISCO proprietary protocol, provides a mechanism which is designed to support non-disruptive failover of IP traffic in certain circumstances. UDP port is 1985. In this case, two or more routers give an illusion of a virtual router. HSRP allows you to configure routers as standby and only a single router as active at a time. All the routers in a HSRP group share a single MAC address and IP address, which acts as a default gateway to the local network. The Active router forwards the traffic. If active router fails, the Standby router takes up all the responsibilities of the active router and forwards the traffic.
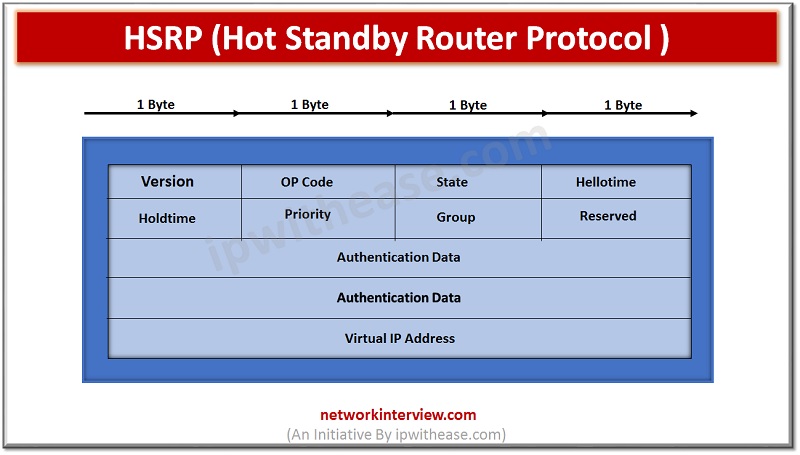
Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) Packet
Version Number is 8 bit HSRP version. Whether it is version 1 or 2.
Opcode is 8 bit.
- Op Code 0 – Hello. The HSRP is running and is capable of becoming the active or standby router.
- Op Code 1 – Coup. The router become the active router.
- Op Code 2 – Resign. The router is no longer the active router.
HSRP States is 8 bit.
1. Active – This is the state of the device that is actively forwarding traffic.
2. Init or Disabled – This is the state of a device that is not yet ready or able to participate in HSRP.
3. Learn – This is the state of a device that has not yet determined the virtual IP address and has not yet seen a hello message from an active device.
4. Listen – This is the state of a device that is receiving hello messages.
5. Speak – This is the state of a device that is sending and receiving hello messages.
6. Standby – This is the state of a device that is prepared to take over the traffic forwarding duties from the active device.
Hello time is 8 bits. The interval between successive HSRP hello messages from a given router is a 3 sec.
Hold time the interval between the receipt of a hello message and the presumption that the sending router has failed after 10 sec.
Priority is 8 bits.
Default priority is 100. Router with a higher priority wins. Priority field is used in election process the active and standby routers. In tie breaking situation, highest IP address wins.
Group is 8 bit.
This field identifies the standby group between 0 to 255.
Reserved is 8 bit.
Authentication Data is a 64 bit.
This field contains a clear text of 8 character reused password. If no authentication data is configured, the RECOMMENDED default value is 0x63 0x69 0x73 0x63 0x6F 0x00 0x00 0x00.
Virtual IP Address is 32 bits.
The virtual IP address used by this group. If the virtual IP address is not configured on a router, then it may be learned from the Hello message from the active router. An address should only be learned if no address was configured and the Hello message is authenticated.
Key terminologies
- Active router: Primary router.
- Standby router: Backup router.
- Standby group: Set of routers that participate in HSRP.
- Virtual MAC address:MAC address is created by HSRP internal mechanism. The first 24 bits will be default i.e. 0000.0c. 16 bits are HSRP IDe. 07.ac. 8 bits is the group number.
- Virtual IP: This IP used by group virtual IP to forward traffic from LAN.
- Priority: Default priority is 100. Router with a higher priority wins. Priority field is used in election process of active and standby routers. In tie breaking situation highest IP address wins.
- Version 1: Multicast address is0.0.2 and uses the UDP port 1985.Group number range from0–255.
- Version 2: Multicast address is0.0.102 and uses the UDP port 1985. Group number range from 0 – 4095.
- Preemption: HSRP Preemption enables the router with the highest priority to immediately become the Active router.
- Interface Tracking: We can choose an interface tracking and if the link goes down it decrements the priority of active router in order for standby router to take over role of active router.
- Load Balancing: Multiple HSRP groups for multiple subnets have both routers in active state for different subnets and passive for the other subnets. This way it is able to utilize all available resource.
Related – HSRP vs VRRP vs GLBP
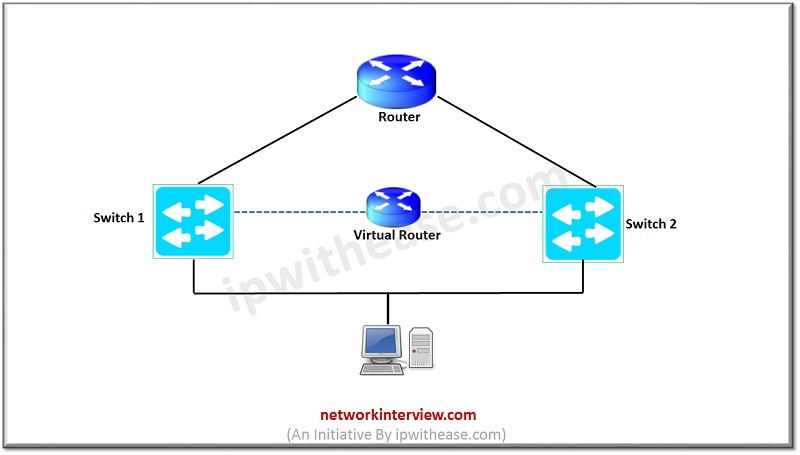
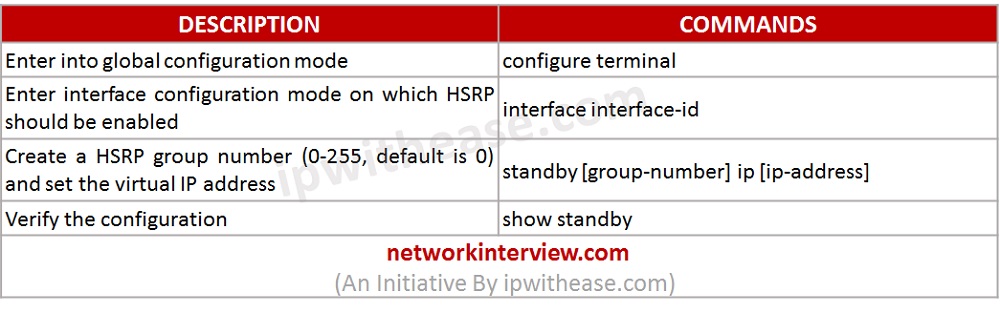
Operation and Configuration of HSRP
- User generates traffic from LAN towards WAN router.
- It uses virtual IP and MAC as a default gateway, the virtual IP address is chosen by the administrator, and the MAC address is auto generated. For version 1, a MAC address is 0000.0c07.acXX where XX is the group number in hex format. For Version 2 MAC address is 0000.0c9f.fXXX, with the last 3 digits again representing group number in hex format.
- HSRP configured in groups. In HSRP group consists of an active router and a standby router. Active router is responsible for ARP requests and handling packet forwarding. Hello messages are sent every 3 seconds to the standby router. HSRP multicast addresses are 224.0.0.2 for v1 and 224.0.0.102 for v2.
Configuring HSRP
Conclusion
In summary, HSRP provides layer 3 redundancy in network via virtual IP and MAC, interface tracking, and load balancing. A group of physical routers, acting as a single virtual router, advertise a single IP address and MAC address into network.
Tag:Protocols



