What Is Circuit Switching?
Before understanding Circuit Switching, let’s explore the basic types of switching.
Switching is an important mechanism that provides communication between different networks or different computer(s) and manages the data flow between the two end points. There are three types of switching techniques –
- Circuit switching
- Packet switching
- Message switching.
Here we will discuss Circuit switching.
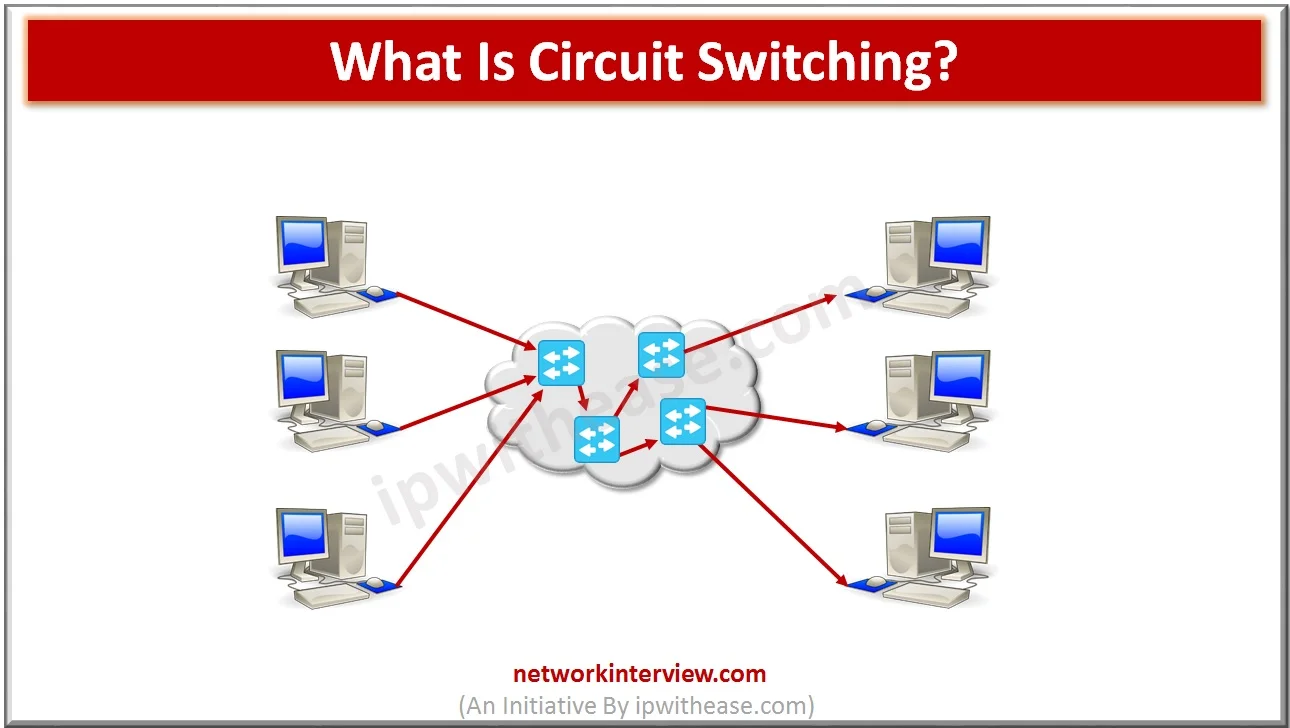
Circuit switching
It is a switching method in which a dedicated physical path is formed between two points in a network i.e. between the sending and the receiving devices. These dedicated paths are created by a set of switches connected by physical links. Circuit switching is the simplest method of data communication that has a fixed data rate and both the subscribers need to operate at this fixed rate.
Phases Of Circuit switching Communication
It has basically three phases :
Establishment or Setup Phase –
A dedicated circuit or path is established between the sender and receiver before the actual data transfer. End-to-End addressing i.e. source address and destination address, is required for creating a connection between two physical devices.
Data Transfer Phase –
Data transfer only starts after the setup phase is completed and a physical, dedicated path is established. The data flow is continuous and there may be periods of silence in data transmitting. Generally all internal connections are made in duplex form. The switches use time slot (TDM) or the occupied band (FDM) to route the data from the sender to the receiver and no addressing method is involved.
TDM (Time Division Multiplexing) and FDM (Frequency Division Multiplexing) are types of multiplexing techniques that are used to transmit multiple signals over a single channel. In FDM, multiple signals are transmitted by occupying different frequency slots while in TDM, the signals get transmitted in multiple time slots.
Disconnect or Teardown Phase –
When one of the subscribers (either the sender or the receiver) needs to disconnect, a disconnect signal is sent to each switch to release the resource and break/disconnect the connection.
Example
One of the major example of Circuit Switching is the Plain Old Telephone System (POTS).
Advantages of Circuit Switching
- The data rate is fixed and dedicated as the connection is established using dedicated physical path.
- Once the circuit is established, there is no waiting time and the data transmission delay is negligible.
- Since a dedicated path is established, it is a good choice for continuous transmission over a long duration.
Disadvantages of Circuit Switching
- Since the connection is dedicated it cannot be used for any other data transmission even if the channel is free.
- It is inefficient in terms of utilization of the system resource. As it is allocated for the entire conversation, we can’t use the resource for other connection.
- More bandwidth is required for the dedicated channels .
- Establishment of physical links between senders and receivers takes huge time prior to the actual data transfer.
FAQs :
- Is circuit switching faster than packet switching?
- Packet switching is faster than Circuit switching. Packet switching is more efficient as all the bandwidth can be used at once and it doesn’t have to deal with a limited number of connections that may not be using all that bandwidth.
- The Internet uses packet switching, not circuit switching as the Internet uses IP (Internet Protocol), which is a packet switching protocol.
- Circuit switching communication involves three phases: setup phase, data transfer phase, and teardown phase.
- Find out the transmission rate of a link that transmits ‘f ‘ frames/sec (Each frame has a single slot and each slot has ‘b’ Bits?
- Since Transmission rate is the amount of data send per second, so
Transmission rate = f * b bits/sec
Tag:switching



