Responsible AI vs Generative AI
Generative AI refers to systems that create new content like text, images, or audio using machine learning models. Whereas, Responsible AI ensures AI systems are developed and used ethically, focusing on fairness, transparency, and safety.
Artificial intelligence is reshaping organizations and redefining the work culture. With Artificial intelligence (AI) emerged two more terms Generative AI and responsible AI. These two terms are closely linked to Artificial intelligence and address different aspects of AI. AI based solutions are deployed in high stake domains such as healthcare, hiring, criminal justice, education etc. which makes it more challenging to address issues related to undue discrimination against minority groups, biases, data manipulation etc.
In today’s topic we will learn about Responsible AI and Generative AI, key principles of both, key features of both, and key differences.
What is Responsible AI
Responsible AI refers to ethical and responsible development and use of artificial intelligent systems which emphasize on ensuring use of AI technologies in a way that it aligns to human values, privacy respect, promoting fairness, non-biases and avoidance of negative consequences.
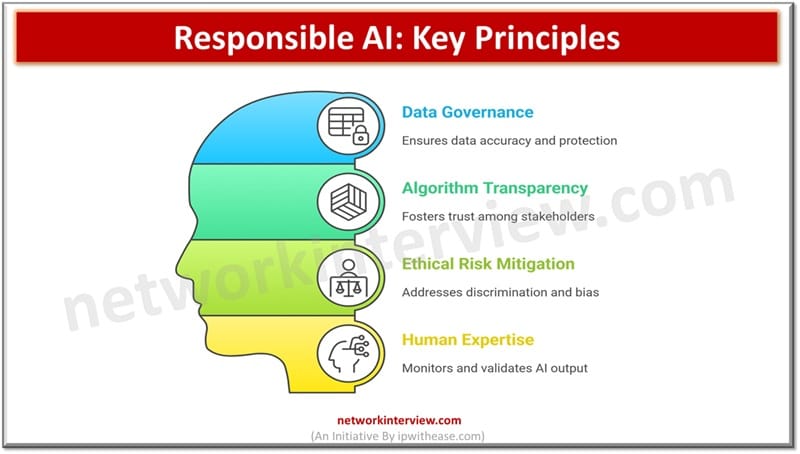
Ethical considerations are essential while dealing with AI and businesses can promote responsible AI usage with:
- Establish data governance to ensure data accuracy, preventing bias, and protection of sensitive information
- Algorithm transparency to foster trust among stakeholders
- Identifying and mitigating ethical risks associated in AI usage such as discrimination and bias
- Human expertise to monitor and validate AI output, alignment to business objectives and meeting regulatory requirements
What is Generative AI
Generative AI systems create any type of new content basis of patterns and existing content. Generative AI can reveal valuable insight but businesses need to be vigilant about bias and misleading outcomes. Generative AI is a subset of AI technologies which are capable of generating new data instances such as text, images, music etc. having resemblance to training data. These technologies leverage patterns learned from larger data sets and create content which is indistinguishable from what is produced by humans.
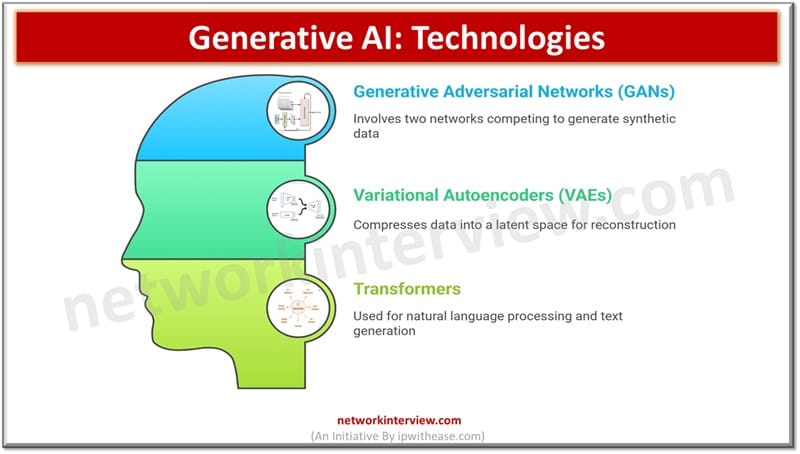
Key Technologies in Generative AI
- Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) involve two neutral networks having the generator and discriminator which compete against each other for generation of new, synthetic data instances which are indistinguishable from what is produced by humans.
- Variational Autoencoders (VAEs) are meant to compress data into a latent space and reconstruct to allow generation of new data instances by sampling
- Transformers are meant for natural language processing, and can also be used for generative tasks such as creation of coherent and contextually relevant text or content.
Uses of Generative AI
- Generative AI is used in content creation such as art, music and text. With AI Service Provider, organizations can leverage these capabilities for scientific research, using simulation models to test ideas and predict outcomes faster.
- Data augmentation and machine models training
- Modelling and simulation in scientific research
Comparison: Responsible AI vs Generative AI
Features | Responsible AI | Generative AI |
| Concept | A broader concept focuses on ethical use and fair use of AI technologies and considers its social impact and biases. | Generative AI is capability of AI systems to generate original and new content |
| Discipline | Responsible AI looks at planning stage in AI development and makes AI algorithm responsible before actual output is computed | Generative AI focuses on content creation based on patterns and existing large data sets |
| Objective | Responsible AI practices works towards ensuring trustworthy, unbiased models which work as intended post deployments | Generative AI focus is data driven learning, and probabilistic modelling for content generation, make decisions, solve problems |
| Limitations |
|
|
Download the comparison table: Responsible AI vs Generative AI



