Pros and Cons of Using Multicast DNS in a Local Network
Domain name system (DNS) is widely used terminology in Internet or public networks. DNS maps host name to IP addresses in a similar fashion as phone books or telephone directory maps a name to a phone number. This is an easier way to remember by name instead of a number.
Prior to DNS, host files needed to be managed manually but with larger networks it became difficult to manage updated copies of hosts mapped to their IP addresses. DNS has another flavour called multicast DNS or mDNS which is also used for same purposes but at local network level.
In today’s topic we will learn about multicast DNS used in local networks, how it works, its limitations and benefits.
What is Multicast DNS?
mDNS or multicast DNS resolves name to IP address in local networks and works in conjunction with DNS-SD (service discovery) protocol in zero configuration networks. Zero configuration networks do not require manual operations moreover they do not rely on DNS server and DHCP for its operations.
DNS-SD let clients discover named list of service type and its instances and resolves these services to hostnames using standard query language of DNS. The mDNS protocol is mentioned in RFC (6762) and DNS-SD protocol is specified in RFC (6763). There are several implementations of mDNS which is Avahi, windows and Bonjour.
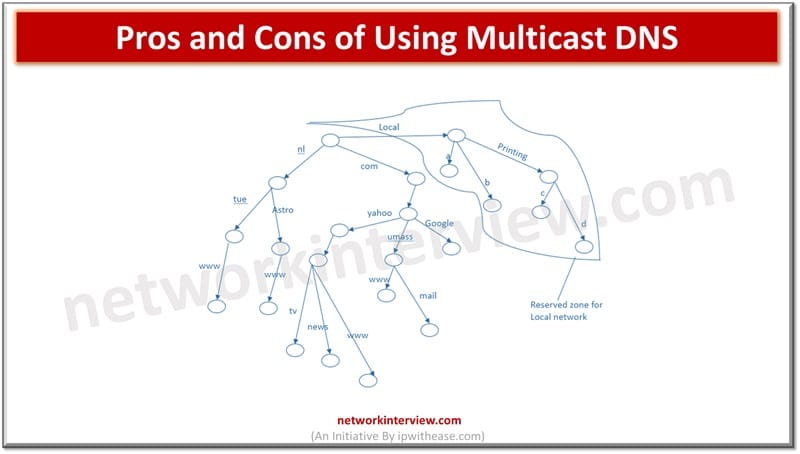
Multicast DNS (mDNS) operates at link level and every node is reachable without routing and mDNS packet is not forwarded by routers. It is also possible to use hierarchical names by users such as ‘c.printing.local’. the domain local is the same as any other domain which appears in the DNS search list but only used locally. If domain name is suffixed with local that means it is processed by mDNS.
It uses the same packet format, programming interfaces and protocol semantics as of standard DNS. mDNS uses UDP (user datagram protocol) packets. mDNS cannot be used for web address resolution as it does not process hostnames with top level domains (TLDs). mDNS packet size is up to 9000 bytes. It uses UDP port 5353 instead of 53 port. UTF-8 is used by mDNS to encode resource record names.
Pros of mDNS Protocol
Key advantages of multicast DNS are:
- mDNS do not require configuration or specific administration
- mDNS do not require any additional infrastructure to operate
- It works even if system infrastructure is failed
- It is cost effective to resolve global domain name
- It does not require error detection mechanism explicitly
- It is meant for smaller networks and quite useful for such scenarios
- It does not require a server or directory establishment
- Additional devices import can be done in quick and dynamic manner
Cons of mDNS Protocol
Key challenges of multicast DNS are:
- It is not suitable for large size networks
- Its performance is not up to the mark as compared to convention DNS in networks having large number of systems / nodes
- Large number of queries and responses generated by mDNS due to its nature of operation, which could result in significant traffic in local networks
- Not meant to be used for multiple IP subnets
- It burdens processing power due to large number of query and response generation
- Data confidential could be a concern as it can be found via open mDNS
- It is prone to be used by cyber criminals for DDoS (Distributed denial of service) attacks
Use Cases for mDNS
- General purpose operating systems run Zero configuration protocols
- Dedicated hardware devices support mDNS such as networked printer, laptop, desktop, digital camera etc.
- iTunes/ iPod
Continue Reading:
How to Configure mDNS Gateway?
What is Split Domain Name System (Split DNS)?
Tag:services



