Path To Become a Network Engineer
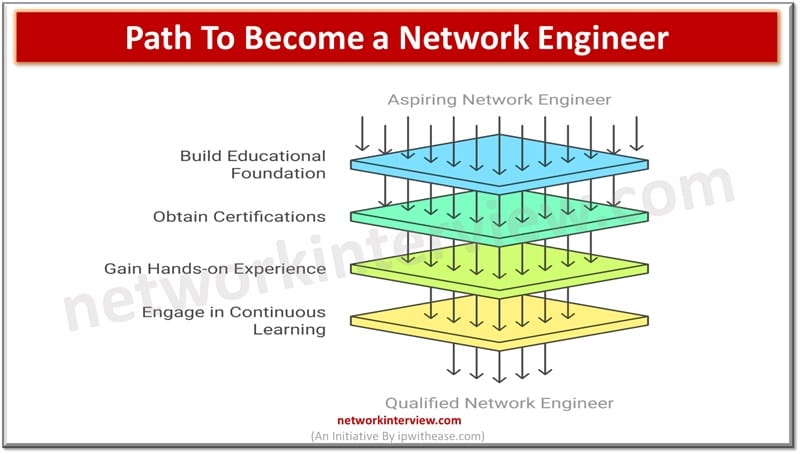
Becoming a network engineer typically requires a mix of education, certifications, hands-on experience, and continuous learning.
Step-by-Step Path to become a Network Engineer
Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you on the path:
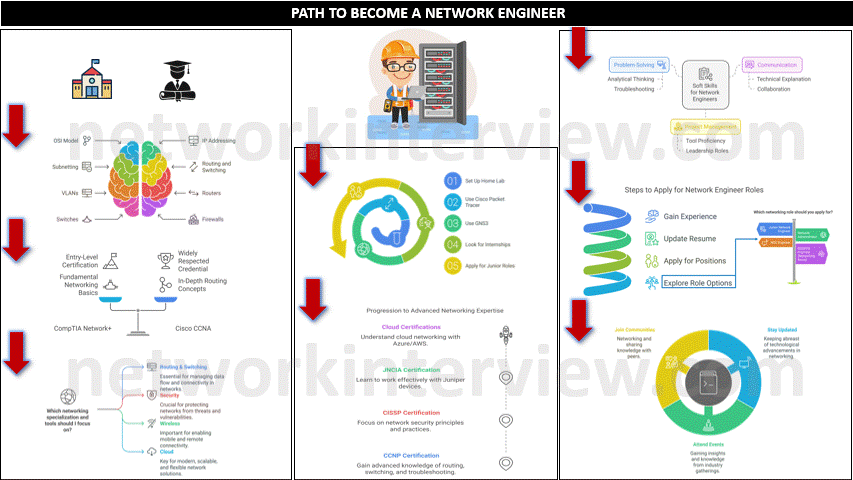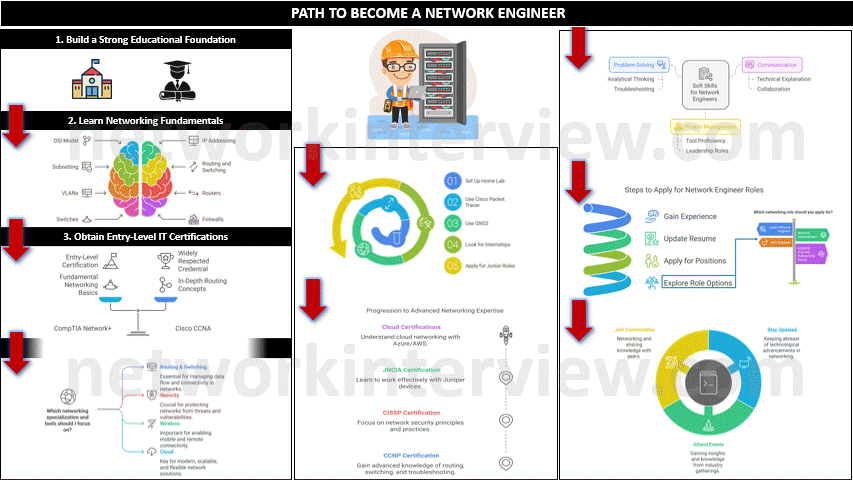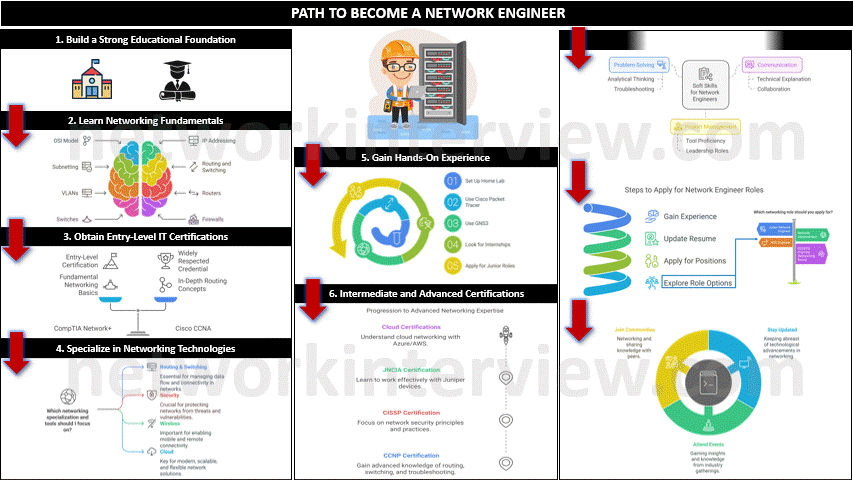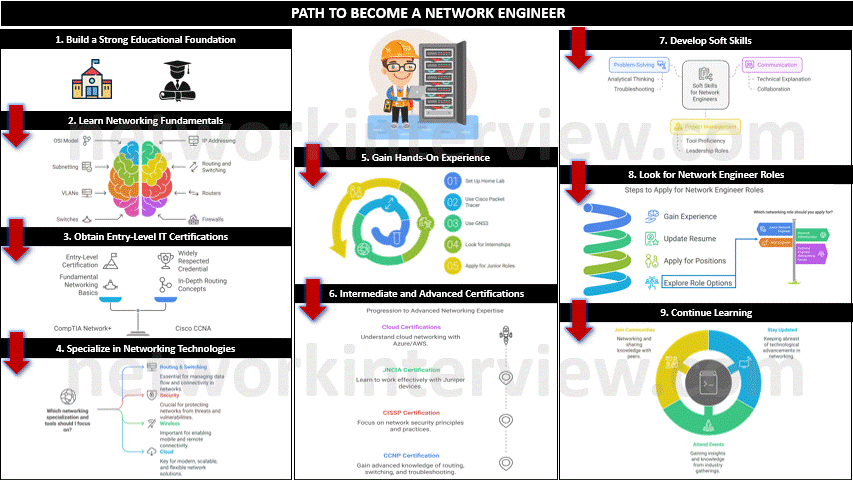
1. Build a Strong Educational Foundation
- High School: Focus on mathematics, computer science, and related subjects.
- Bachelor’s Degree (Optional but helpful): Obtain a degree in Computer Science, Information Technology, or Network Engineering. Some people start with associate degrees or technical certifications, but a formal degree can be helpful.
2. Learn Networking Fundamentals
- Study networking concepts such as OSI Model, IP addressing (IPv4/IPv6), subnetting, routing and switching, and VLANs.
- Familiarize yourself with network hardware like routers, switches, firewalls, and access points.
Related: OSI Model – The 7 Layers
3. Obtain Entry-Level IT Certifications
Certifications demonstrate your knowledge and increase your employability. Start with entry-level certifications like:
- CompTIA Network+: Covers networking fundamentals.
- Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA): Widely respected and covers essential networking concepts, routing, and switching.
4. Gain Hands-On Experience
- Home Lab: Set up a lab with routers, switches, and virtual machines using tools like Cisco Packet Tracer or GNS3 to practice configurations.
- Internships/Entry-Level Jobs: Look for internships or junior roles like IT support or network technician to gain real-world experience.
5. Specialize in Networking Technologies
- Learn different areas of networking such as routing and switching, security, wireless, cloud, and automation.
- Gain experience with tools and technologies such as Wireshark, network analyzers, firewalls, and VPNs.
6. Intermediate and Advanced Certifications
As you progress, focus on more advanced certifications such as:
- Cisco Certified Network Professional (CCNP): More advanced knowledge of routing, switching, and troubleshooting.
- Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP): If you’re interested in network security.
Juniper Networks Certified Associate (JNCIA): For working on Juniper devices. - Microsoft Azure/AWS certifications: To understand cloud networking.
7. Develop Soft Skills
- Problem-Solving: Network engineers frequently troubleshoot network issues, so strong analytical and problem-solving skills are crucial.
- Communication: You’ll need to explain technical concepts to non-technical colleagues and collaborate
- Project Management: Experience with project management tools can help you move into leadership roles.
8. Look for Network Engineer Roles
Once you have gained experience, start applying for network engineer positions. Keep your resume up to date and tailor it to highlight your technical skills and experience.
Networking roles you can look for:
- Junior Network Engineer
- Network Administrator
- Network Operations Center (NOC) Engineer
- Systems Engineer (Networking focus)
9. Continue Learning
- Stay Updated: Networking technologies constantly evolve (e.g., SDN, network automation, cloud networking, 5G), so continuous learning is necessary.
- Attend Webinars, Conferences, and Workshops: Participate in industry events and online courses to stay ahead of trends.
- Join Networking Communities: Engage in forums, online communities (like Reddit’s networking section), or professional groups like Cisco Learning Network.
10. Advance to Senior Roles
With experience, aim for more senior roles, such as:
- Senior Network Engineer
- Network Architect
- Network Consultant
- IT Manager/Director
By following this step-by-step approach, you’ll be on the right path to becoming a successful network engineer.
FAQs for Network Engineer’s Interview
1. Can you explain the difference between TCP and UDP? (To assess your understanding of transport layer protocols and their use cases.)
2. How does a subnet mask work in IP networking? (To evaluate your knowledge of IP addressing and subnetting)
3. Describe the OSI model and how it applies to network troubleshooting. ( To test your foundational knowledge of networking layers.)
4. What is VLAN, and why is it used? (To determine your understanding of segmentation and network design.)
5. Can you explain how OSPF works and its advantages? (To gauge your knowledge of routing protocols.
6. Can you explain the difference between a switch and a router? (A foundational question to test understanding of network devices.)
7. How would you troubleshoot a network outage? (To assess problem-solving approach and tools used for troubleshooting.)
8. How do you secure a network against common threats? (To explore knowledge of firewalls, IDS/IPS, and network access controls.)
9. What would you do if two devices in different VLANs cannot communicate? (Tests troubleshooting in VLAN and inter-VLAN routing.)
10. Describe a challenging network issue you resolved and how you handled it. ( To assess communication skills, teamwork, and technical proficiency.)
Tag:career



