Nand vs Nor Flash Memory: Analysing Best Features
Nand vs Nor Flash Memory
The designing of a system puts up challenges of its own. There are several key aspects that qualified professional system designers take into consideration while conceiving the architecture of a system. One such vital aspect is the selection of Flash memory, and what sort of Flash architecture is best to use. While opting for a parallel interface or a serial interface, it is crucial to analyse in advance whether it would require an error correction code (ECC) or not.
Introduction
In case where the controller or processor supports only a single type of interface then the analysis of Flash memory becomes much easier as there are limited options to look for. But it is not as convenient as it seems to be. There are certain Field-programmable gate array (FPGA) that support serial or parallel NOR flash, while others go with NAND Flash memory in order to store the configured data. In such cases, when in order to choose the right memory, we assess Nand vs Nor Flash Memory we often face difficulty as both are used to capture user data.
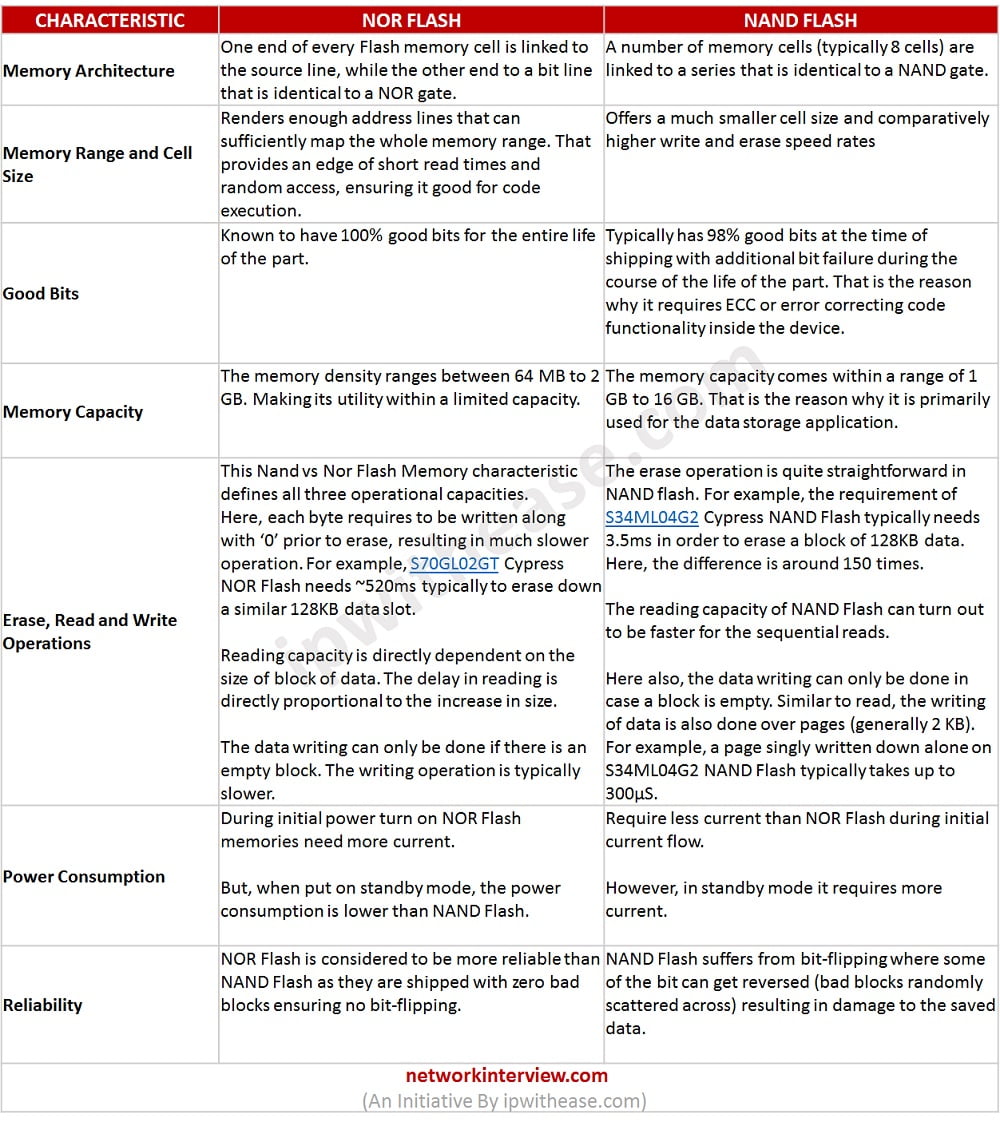
Here, we are going to make the line of difference between NAND and NOR Flash Memory on the grounds of certain pivotal characteristics. You can come across these characteristics in the below table distinguishing the two major forms of Flash memories on various points-
Nand vs Nor Flash Memory : Comparison table
CHARACTERISTIC | NOR FLASH | NAND FLASH |
| Memory Architecture | One end of every Flash memory cell is linked to the source line, while the other end to a bit line that is identical to a NOR gate. | A number of memory cells (typically 8 cells) are linked to a series that is identical to a NAND gate.
|
| Memory Range and Cell Size | Renders enough address lines that can sufficiently map the whole memory range. That provides an edge of short read times and random access, ensuring it good for code execution. | Offers a much smaller cell size and comparatively higher write and erase speed rates |
| Good Bits | Known to have 100% good bits for the entire life of the part. | Typically has 98% good bits at the time of shipping with additional bit failure during the course of the life of the part. That is the reason why it requires ECC or error correcting code functionality inside the device.
|
| Memory Capacity | The memory density ranges between 64 MB to 2 GB. Making its utility within a limited capacity. | The memory capacity comes within a range of 1 GB to 16 GB. That is the reason why it is primarily used for the data storage application.
|
| Erase, Read and Write Operations | This Nand vs Nor Flash Memory characteristic defines all three operational capacities. Here, each byte requires to be written along with ‘0’ prior to erase, resulting in much slower operation. For example, S70GL02GT Cypress NOR Flash needs ~520ms typically to erase down a similar 128KB data slot.
Reading capacity is directly dependent on the size of block of data. The delay in reading is directly proportional to the increase in size.
The data writing can only be done if there is an empty block. The writing operation is typically slower. | The erase operation is quite straightforward in NAND flash. For example, the requirement of S34ML04G2 Cypress NAND Flash typically needs 3.5ms in order to erase a block of 128KB data. Here, the difference is around 150 times.
The reading capacity of NAND Flash can turn out to be faster for the sequential reads.
Here also, the data writing can only be done in case a block is empty. Similar to read, the writing of data is also done over pages (generally 2 KB). For example, a page singly written down alone on S34ML04G2 NAND Flash typically takes up to 300µS. |
| Power Consumption | During initial power turn on NOR Flash memories need more current.
But, when put on standby mode, the power consumption is lower than NAND Flash.
| Require less current than NOR Flash during initial current flow.
However, in standby mode it requires more current. |
| Reliability | NOR Flash is considered to be more reliable than NAND Flash as they are shipped with zero bad blocks ensuring no bit-flipping. | NAND Flash suffers from bit-flipping where some of the bit can get reversed (bad blocks randomly scattered across) resulting in damage to the saved data.
|
Download the comparison table: NAND vs NOR
Conclusion
While having a glance over the segregation table above, we can see that NAND vs NOR Flash Memory have their own set of advantages and disadvantages over each other. In terms of memory range, cell size, good bits, power consumption and reliability, NOR Flash memory can turn out to have an edge, while NAND Flash surpasses it in terms of memory capacity as well as erase, read and write operations. So it is recommended that your priority should be in accordance with the characteristic(s) that you give much preference to while utilizing flash memory.
Related – RAM VS ROM
Tag:comparison