eBGP vs iBGP
Before discussing eBGP vs iBGP, let’s understand the two protocols briefly.
What is eBGP
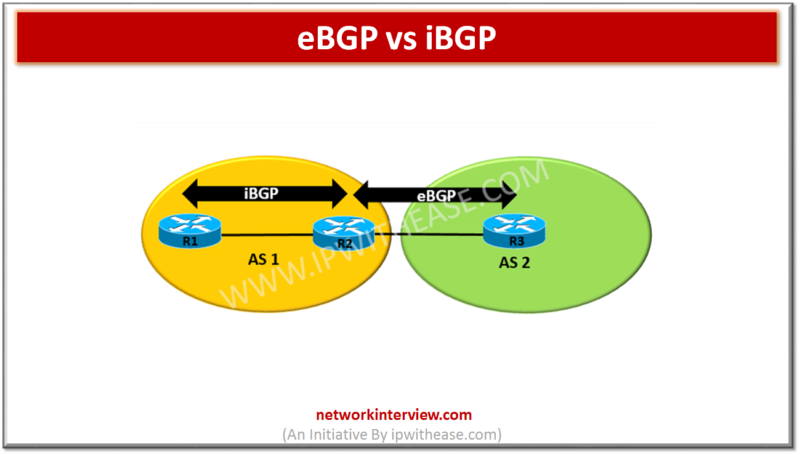
It is abbreviation for External Border Gateway Protocol and is one of the flavors of BGP protocol. eBGP Routing protocol is used between BGP speaking neighbors which belong to different ASNs (Autonomous System Numbers). eBGP functions as the protocol for interconnection of networks from different organizations.
Key Features:
- eBGP Neighborship: Both the routers forming eBGP neighborship should be in separate Autonomous Systems.
- eBGP Route Advertisement: A route learnt from an eBGP peer will be advertised back to another iBGP or eBGP neighbor by default.
- eBGP Scope: It is used between organization, or between organization and ISP(Internet Service Provider).
- eBGP Administrative Distance: eBGP routes have administrative distance of 20.
- eBGP Topology: It does not require full mesh neighborship.
- eBGP TTL: By default eBGP TTL value is 1 which means that neighbors(routers) should be directly connected. When the two neighbors/routers are not directly connected then we can still make it work but we’ll have to use multihop.
- eBGP Scope: It is used between organization, or between organization and ISP(Internet Service Provider).
- eBGP Administrative Distance: eBGP routes have administrative distance of 20.
- eBGP Topology: It does not require full mesh neighborship.
- eBGP TTL: By default eBGP TTL value is 1 which means that neighbors(routers) should be directly connected. When the two neighbors/routers are not directly connected then we can still make it work but we’ll have to use multihop.
Related – BGP Interview Questions
What is iBGP
It is abbreviation for Internal Border Gateway Protocol. iBGP protocol is used between the routers within the same autonomous system (AS). iBGP speaking Routers need to form full mesh to maintain full routing information. Full mesh (iBGP neighborship with all Routers in same AS) can be mitigated by using either Route reflectors or BGP confederation.
Key Features:
- iBGP Neighborship: Both the routers forming iBGP needs to be in the same Autonomous System.
- iBGP Advertisement: A route learnt from an iBGP peer will not be advertised back to another iBGP neighbor by default.
- iBGP Scope: iBGP is used within the same organisation.
- iBGP Administrative Distance: iBGP routes have administrative distance of 200.
- iBGP Toplogy: iBGP requires full mesh or else either of route reflectors or BGP confederation.
- iBGP TTL: iBGP TTL is set at 255 by default
Let’s differentiate them in detail now.
Comparison Table: eBGP vs iBGP
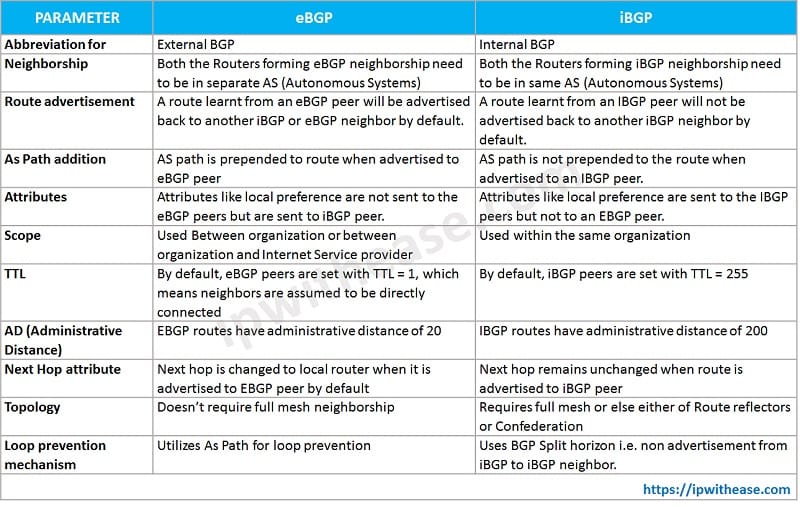
Comparison Table Source: https://ipwithease.com
Continue Reading:
BGP Interview Questions & Answers
BGP Local Preference Attribute
Tag:comparison



