Difference between Tree and Forest in Active Directory
Introduction to Tree and Forest
An Activity Directory is a product of Microsoft that runs on Server of Windows. It allows managing, accessing, and permissions for the network resources. The data is stored as an object in this directory and the object can be anyone such as user, files, shared folders, device, groups or an application. The categorization of these objects is done either by name or attribute.
An active directory can be found in most of the windows server operating system in the form of services and processes. The beginning of this directory was started with windows server 2001 and later on they became a part of various other directory-based identity-related services.
In the active directory, there is a domain which is the core unit in logical structure. All the objects that are named under common directory database, security policies and trust relationships with other domain are known as Domains. Each domain stores information only about the objects that belong to that domain.
All security polices and settings, such as administrative rights, security policies, and Access Control Lists (ACLs), do not cross from one domain to another. Thus, a domain administrator has full rights to set policies only within domain they belong to. Domains provide administrative boundaries for objects and manage security for shared resources and a replication unit for objects.
Thus, the active directory organizes all the information. Moreover, it allows the domain controller to perform authorization and authentication for users to access resources. An object is a physical entity of a network and there can be multiple objects in active directory. Tree and Forest are two such objects.
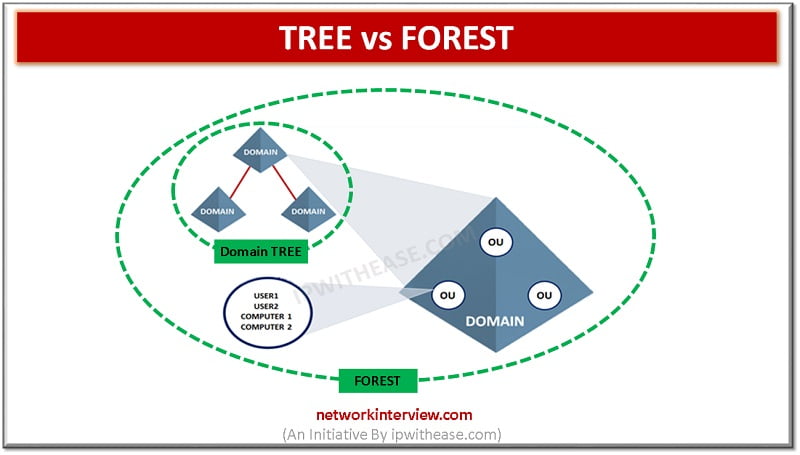
Tree
The tree can be defined as the collection of one or more domains that allow the sharing of resources globally. It comprises of single domain or multiple domain in the contiguous namespaces. Whenever we add the domain in the tree it becomes the offspring of the tree root domain and the domain it is attached with becomes the parent domain. Parent domain name is utilized by the child domain and further gets the unique Domain Name System (DNS).
As an example, if abc.com is the root domain, users can create one or more Child domains to abc.com such as south.abc.com and or north.abc.com. Further, these “child” domains may also have sub-child domains that can be created under them, such as profit.south.abc.com.
The domains created in a tree has two way of relationship named as Kerberos transitive trust relationships. A Kerberos transitive trust simply means that if Domain 1 trusts Domain 2 and Domain 2 trusts Domain 3, then Domain 1 trusts Domain 3. Therefore, it implies that a domain joining a tree immediately has trust relationships established with every domain in the tree.
Forest
A Forest can be explained as a collection of multiple trees which is shared by the common global catalogue, logical structure, directory schema, and directory configuration. It comprises of in built two ways transitive trust relationships. The very first domain created in the forest is called the forest root domain.
If there are different naming schemes than the forest allows each organisation to group their divisions and it may need to operate independently. But being as an organisation, they want to communicate with the entire organization via transitive trusts and share the same schema and configuration container.
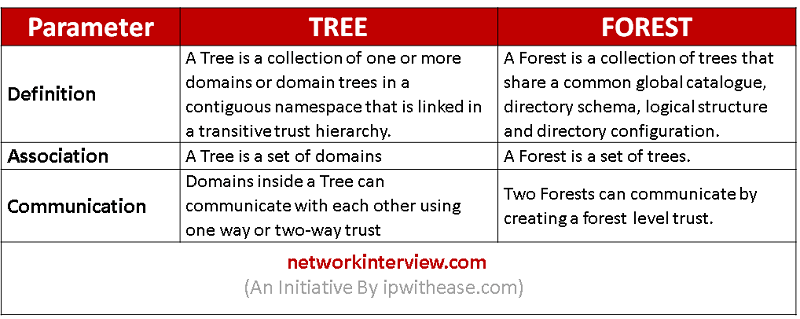
Difference between the Tree and Forest:
Conclusion
The main difference between Tree and Forest in Active Directory is that Tree is a collection of domains while forest is a set of trees in active directory. In brief, a tree is a collection of domains whereas a forest is a collection of trees.
Continue Reading:
Active Directory Interview Questions
Tag:comparison




1 Comment
Hello Rashmi,
The way you shared knowledge with us which is fabulous because the way of your explanation is to be totally understandable.
Thank you