Difference between File Level Storage and Block Level Storage
In this post, we will discuss the difference between File Level Storage and Block Level Storage.
File Level Storage:
The storage system of Network Attached Storage and hard drives is a file level storage. Here in this storage system, the NFS (Network file system) or Server Block Message (SBM) or Common Internet file system (CIFS) protocol is used for storage and the files are accessed from the bulk. The simplicity of file level storage is unbeatable in a situation where just some space is required to store the files. This system is centralized in control and can be accessed by any user who wants to use it. The maintenance of file storage system is much easier and inexpensive than the block level storage. The storage systems which are attached to any networks surely rely on this kind of storage system.
The costs of reserving the space in file level storage are much less compared to block level. Also, this level of storage also has to look into assigning permissions and access to other users and it can also be integrated into other security authentication systems. File sharing with other users is very easy using this level of storage.
There is Scale out NAS which is a kind of file level storage system which has the ability to scale up to a lot more petabytes. This solution enhances the capacity and also improves the performance.
Basically, the file level storage is used for mass storage of files.
Block Level Storage:
The storage system of Storage Area Networks is a block level storage. Here, in this kind, there are blocks created for storage which are just like a hard drive in the server. These hard drives or the blocks are used and managed by the operating systems based on the servers. Random files or virtual machine file system or databases can be stored in this level. Fibre channel or iSCSI (Internet Small Computer Systems Interface) mechanism of storage networking is used by this level of storage for the servers and data transfers. Block level storage can boot up the systems that are connected to it.
It has a reliable kind of transportation of the stored data which uses these blocks like a separate hard drive and is managed by the operating system based on an external server. Usually a larger enterprise or organization which is a part of such enormous storage area network, utilizes block storage for fulfilling their storage needs.
Block level storage is unbeatable for its versatility and flexibility as the server uses the raw storage blocks like hard drives. For this very reason, block level storage can be used for various applications like database storage, virtual machine file system volume, file storage, etc.
File sharing in this level of storage is a little longer process wherein an operating system is to be installed with which that block should be attached, only then sharing of files is possible with that host operating system.
For the backup of your storage load, third party tools for backup have to be used to keep your files safe. Also, talking in regard to the maintenance and management, the block level storage is more complex than the file level storage.
Comparison between File Level Storage and Block Level Storage
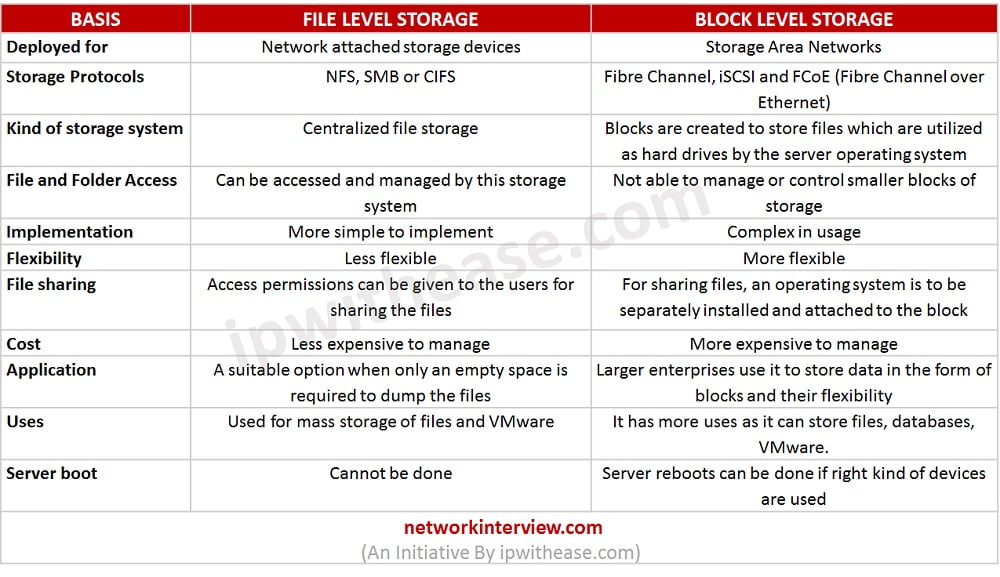
BASIS | FILE LEVEL STORAGE | BLOCK LEVEL STORAGE |
Deployed for | Network attached storage devices | Storage Area Networks |
Storage Protocols | NFS, SMB or CIFS | Fibre Channel, iSCSI and FCoE (Fibre Channel over Ethernet) |
Kind of storage system | Centralized file storage | Blocks are created to store files which are utilized as hard drives by the server operating system |
File and Folder Access | Can be accessed and managed by this storage system | Not able to manage or control smaller blocks of storage |
Implementation | More simple to implement | Complex in usage |
Flexibility | Less flexible | More flexible |
File sharing | Access permissions can be given to the users for sharing the files | For sharing files, an operating system is to be separately installed and attached to the block |
Cost | Less expensive to manage | More expensive to manage |
Application | A suitable option when only an empty space is required to dump the files | Larger enterprises use it to store data in the form of blocks and their flexibility |
Uses | Used for mass storage of files and VMware | It has more uses as it can store files, databases, VMware. |
Server boot | Cannot be done | Server reboots can be done if right kind of devices are used |
 | ||
Download the difference table here.
Tag:comparison



