AODV Routing Protocol
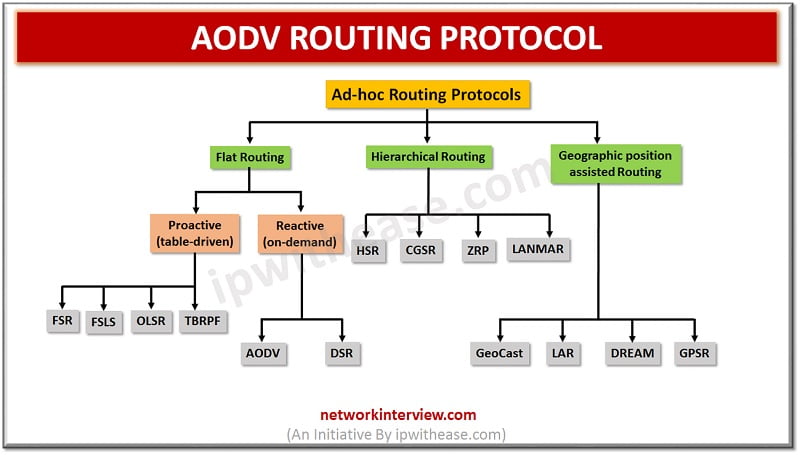
Hierarchy of Ad-hoc routing protocols
In this article, we will understand the concept of AODV Routing protocol, which is type of Reactive (On-Demand) protocol. So, before beginning let’s understand what is a reactive protocol.
Reactive Protocol
Reactive Routing Protocol is a bandwidth efficient on-demand routing protocol for Mobile Ad-Hoc Networks. Two key mechanism of reactive protocol are Route Discovery and Route Maintenance. Route Discovery mechanism is responsible for the discovery of new routes. Route Maintenance mechanism is for the detection of link breaks and repair of an existing route.
Ad-hoc On-Demand Distance Vector (AODV) is a reactive protocol where routes are created only when they are needed. Key application of AODV is in mobile network. It uses routing table with one entry for each destination. Sequence numbers are used to validate whether routing information is up-to-date and to prevent routing loops.
Ad-hoc Network Architecture
Operation of AODV Routing Protocol –
In scenario of AODV, when node initiates a packet toward destination, routing table lookup is performed and one of below action is performed –
- If route is found, packet is forwarded to next hop toward the destination.
- If no route is found, it initiate route discovery process.
Route discovery process starts with the creation of a Route Request (RREQ) packet. The packet contains
- Source node’s IP address
- Source node’s current sequence number
- Destination IP address and
- Destination sequence number.
Packet also contains broadcast ID number. Broadcast ID gets incremented by one each time a source node uses RREQ. Broadcast ID and source IP address form unique identifier for RREQ. Broadcasting is done via Flooding. Route discovery is supported on query and reply cycles, and route information is stored altogether with intermediate nodes along the route in the form of route table entries. Route maintenance is completed by means of route error (RERR) packets. When an intermediate node detects an outage or node unreachable, it generates a RERR packet. The RERR propagates towards all traffic sources which have a route via the failed link. It also erases all broken routes on the way.
The following Control Packets are used:
- Routing request message (RREQ) is broadcasted by a node requiring a route to different node.
- Routing reply message (RREP) is unicasted back to the sources of the RREQ.
- Route error message (RERR) is sent to notify other nodes of loss of the link.
- HELLO messages are used for the detecting and monitoring links to the neighbours status.
Key points about AODV Routing Protocol –
- Uses bi-directional links.
- Route discovery cycle like query and reply used for route finding.
- Route Maintenance of active routes.
- Sequence numbers are used for loop prevention and act as route freshness criteria.
- Provides unicast and multicast communication.
- Whenever routes are not used get expired and discarded.
- Reduces stale routes.
- Reduces need for route maintenance.
- Minimizes number of active routes from an active source and destination.
- AODV discovers and maintain routes as and when necessary.
- Does not maintain routes from every node to node.
- Sequence number gets incremented every time the node notices change in the neighbourhood topology.
- AODV uses routing tables to store routing information.
- A Routing table for unicast and multicast routes.
- Life-time timer updated every time the route is used. If route not used with in its life time it will declare expire.
- Reactive/On – demand protocol.
Merits of AODV Routing Protocol –
- Reactive protocols like AODV tend to minimise the control traffic messages overhead.
- AODV reacts relatively faster to the topological changes within the network and updates only the nodes suffering from these changes.
- The AODV routing protocol saves storage place also as energy. They respond to destination node reply only once to the first request and ignores the rest.
- The routing table maintains at the most one entry per destination.
- AODV is loop free and scale to large number of mobile nodes.
- AODV does not required any central administration to handle routing processing.
Demerits of AODV
- A Large number of control packets are generated when a link breakage occurs. These packets increase the congestion in the active route.
- AODV has a high processing demand.
- AODV consumes large share of the bandwidth.
- AODV takes long time to build routing table.
- As size of the network grows, various performance metrics begin decreasing.
Related – Proactive Routing Protocol in Ad-hoc Network



