Supercomputer vs Minicomputer: Detailed comparison
Different types of computers are in use today. There classification is based on their functionality, size, speed, and cost. Based on size, speed and functionality computers are classified into four categories.
In this article, we will take a look at the difference between Minicomputers and Supercomputers.
What is a Supercomputer?
History of Supercomputers
The first ‘Supercomputer’ was developed by Seymour Cray at Control Data Corporation (CDC) Cray research center. CDC 6600, it had a single processor with 10 peripheral processors, and it was released in 1964. It was about the size of four filling cabinets and operating speed of 40 MHZ.
It has cooling functionality built with Freon which circulated in pipes around four cabinets and generated heat was exchanged with a chilled external water supply unit.
In 1976, the Cray 1 was released and was used for Nuclear weapon modelling.
In 1982, the Cray X-MP supported four CPUs and in 1985 the Cray 2 was released, and it has 8 CPUs.
In 90s Japanese took over Supercomputer market and NEC SX-3, Fujitsu Numerical Wind Tunnel, and Hitachi SR2201 models of Supercomputers were launched.
The Supercomputer built in 1990 by Intel with name ‘Touchstone Delta’ had 512 microprocessors.
About Supercomputer
Extremely fast and very powerful and it can execute hundreds of millions of instructions per second. They are the fastest computers currently available in the market.
Supercomputers are very expensive and designed to perform very specialized operations involving processing of billion and trillion of calculations (in split seconds), that is why there computing power is not measured in terms of MIPS but in FLOPS (floating-point operations per second). The Supercomputer comprises of tens of thousands of microprocessors which can perform Their evolution happened from Grid to cluster computing and performs true parallel processing.
Characteristics of Supercomputer
- Supports hundreds of users at one point of time.
- Capable of handling massive data calculations which are beyond the capacity of humans.
- Very large in size can take up space sized up to two tennis courts.
- Very expensive and highly priced.
- Processing speed ranges from 100 to 900 MIPS.
- Designed to perform complex problems such as Modelling and Simulations of physical spectacles such as Climate changes, study molecular behaviour, data analytics related to astronomical observations, genetics sequencing ,virtual testing of nuclear weapons , high quality animations etc.
What is a Minicomputer?
Minicomputers are small digital computers which process data less than a Mainframe but more than Microcomputers. They have large storage capacity and more processing power than their nearest cousins ‘Microcomputers’.
Advent of Minicomputers changed the landscape of IT industry and brought systems in reach to general users. In 1960 Control Data Corporation (CDC), Packard Bell, and Digital Equipment Corporation introduced Minicomputers with PDP (Programmed Data Processor).
Minicomputers were used by small and medium industry segments for operating businesses. Minicomputer is also referred as ‘Mid-range’ system which could range from higher end SPARC, Power and Titanium based systems designed by Oracle Power Corporation and Hewlett-Packard.
The minicomputers are characterized by one or more processors, supported multiprocessing, and multi-tasking, and meant to be resilient for high workloads, they can be networked, they don’t require any specific power or cooling requirements.
Minicomputers are available in market today in the form of many electronic gadgets such as Smartphones, Tablet PC, iPAD, Drawing tablets, Desktop Mini PC and so on.
These small and powerful gadgets are packed with features and used for gaming, watching videos, net surfing, and a variety of computing tasks. Minicomputers were developed for tasks related to storage of records, calculations, controls etc.
Characteristics of Minicomputer
- Smaller size than a Supercomputer computer
- Low in cost than a super and mainframe computer
- Less powerful than a super and mainframe computer but more powerful than microcomputers
- Perform multitasking and multiprocessing
- Suitable for individual use and small businesses
- Ease of use and maintenance
- Small and lightweight easy to carry
- Fast and reliable
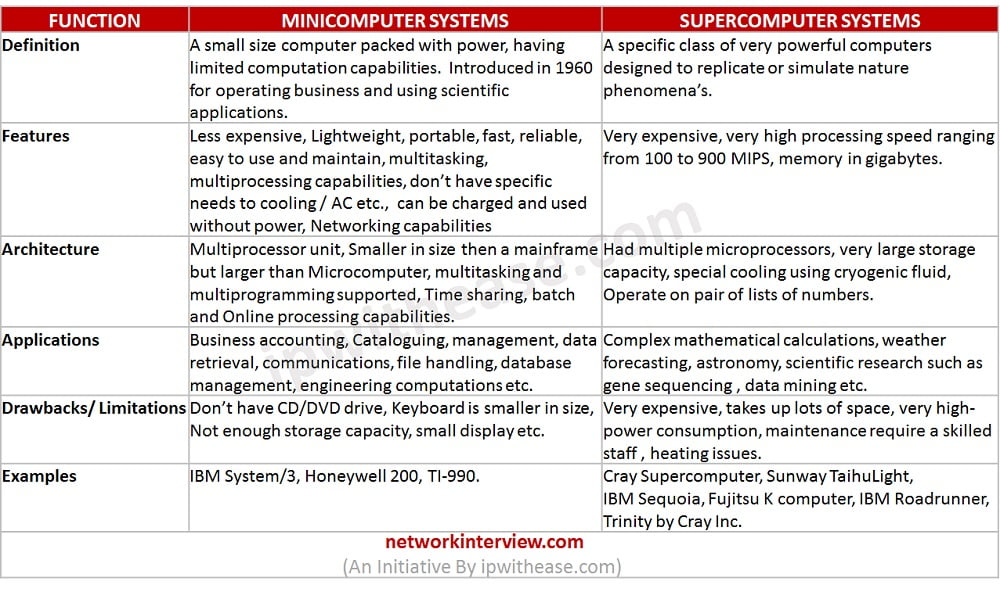
Comparison Table: Supercomputer vs Minicomputer
Below table summarizes the differences between supercomputers and minicomputers:
FUNCTION | MINICOMPUTER SYSTEMS | SUPERCOMPUTER SYSTEMS |
| Definition | A small size computer packed with power, having limited computation capabilities. Introduced in 1960 for operating business and using scientific applications. | A specific class of very powerful computers designed to replicate or simulate nature phenomena’s. |
| Features | Less expensive, Lightweight, portable, fast, reliable, easy to use and maintain, multitasking, multiprocessing capabilities, don’t have specific needs to cooling / AC etc., can be charged and used without power, Networking capabilities | Very expensive, very high processing speed ranging from 100 to 900 MIPS, memory in gigabytes. |
| Architecture | Multiprocessor unit, Smaller in size then a mainframe but larger than Microcomputer, multitasking and multiprogramming supported, Time sharing, batch and Online processing capabilities. | Had multiple microprocessors, very large storage capacity, special cooling using cryogenic fluid, Operate on pair of lists of numbers. |
| Applications | Business accounting, Cataloguing, management, data retrieval, communications, file handling, database management, engineering computations etc. | Complex mathematical calculations, weather forecasting, astronomy, scientific research such as gene sequencing , data mining etc. |
| Drawbacks/ Limitations | Don’t have CD/DVD drive, Keyboard is smaller in size, Not enough storage capacity, small display etc. | Very expensive, takes up lots of space, very high-power consumption, maintenance require a skilled staff , heating issues. |
| Examples | IBM System/3, Honeywell 200, TI-990. | Cray Supercomputer, Sunway TaihuLight, IBM Sequoia, Fujitsu K computer, IBM Roadrunner, Trinity by Cray Inc. |
Download the comparison table here.
Quick Facts:
Fastest supercomputer in world was Sunway TaihuLight China’s National Research center of Parallel Computer Engineering & Technology (NRCPC)
The Blue Gene/P Supercomputer setup at Argonne National Lab spanned across 72 racks/cabinets having more than 250,000 processors having normal data center air conditioning and runs on High speed fibre optical network.
Continue Reading:
Tag:comparison, New technology