Mainframes vs Cloud Computing
Introduction
Centralized architecture with high computing power and centralization of computing resources vs distributed computing architecture are two main directions in which IT technology has moved or progressed with the passing time.
Today, we look at two technologies that governed or decided the course and future of digitization – Mainframes and Cloud Computing.
History of Mainframes
The era of Mainframe dates to 1930s when the first mainframe came into existence named as ‘Harvard Mark’ it was bulk in size weighted five tons, taken up entire room space and costed about $200,000 to build. This mainframe was invented by Sir Howard Aiken teacher in Harvard to build a large-scale calculator to solve non liner equations.
ENIAC The next famous Mainframe build during World War II by government funds.
Initially data was stored on Vacuum tubes but later it is replaced by core memory which stored data magnetically using 5400-RPM disk and COBOL was the first language which was used for programming on mainframe systems. In 1998s Linux based operating systems have replaced Mainframes native OS.
Over period size of mainframes reduced in 1960s the mainframes are majorly used in US military and space programs and by large industries. IBM 700/7000 series of mainframes dominated the market these were based on vacuum tubes for data storage which was later replaced by IBM /360 which was compatible model across and used for commercial and scientific operations. The systems IBM/360 further developed into system/370, system/390 in addition to 64-bit series, z/z Enterprise machines.
About Mainframes
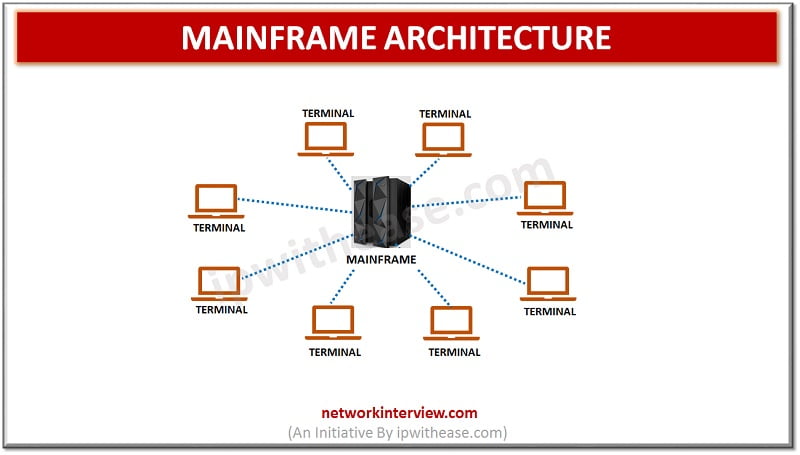
Mainframe computers are also referred as ‘Big iron’ is used by large organizations for critical applications , data processing in bulk , supported massive throughput, hot swapping of hardware such as hard disks and memory, backward compatibility to older hardware, extensive Input/Output facilities, operated in batch mode , Virtualization and so on.
Mainframe computers were characterised by – large size, high processing power and had multiple peripherals attached to them.
Mainframes have been used for applications such as Payroll management, accounting, business transactions, information access and retrieval, airline reservations, scientific and engineering computations.
History of Cloud Computing
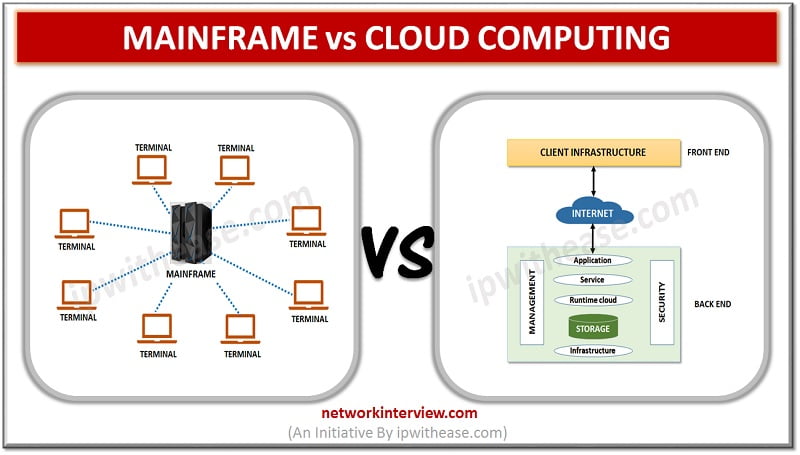
Mainframes was a client/server architecture-based system where all software applications, data , processing power, memory and controls were centralized or resided on server side.
With the advent of distributed computer architecture, the systems were networked and sharing of resources (CPU, Memory, disk etc.) started which gave emergence to Cloud computing.
John M MacCharty in 1961 during a speech in MIT that computing resources or power can be sold as a utility like electricity , water etc. but not much progress made on this thought which was again took a shape in 1991 when salesforce.com started delivery of applications to users over Internet / website. In 2002, Amazon.com started its Amazon web series and started providing services like storage, computation power and AI (Artificial Intelligence) and launched Elastic Compute Cloud in 2006
In 2009 Google APPS also started offering Enterprise applications based on cloud infrastructure.
In 2009 Microsoft launched Windows Azure
About Cloud Computing
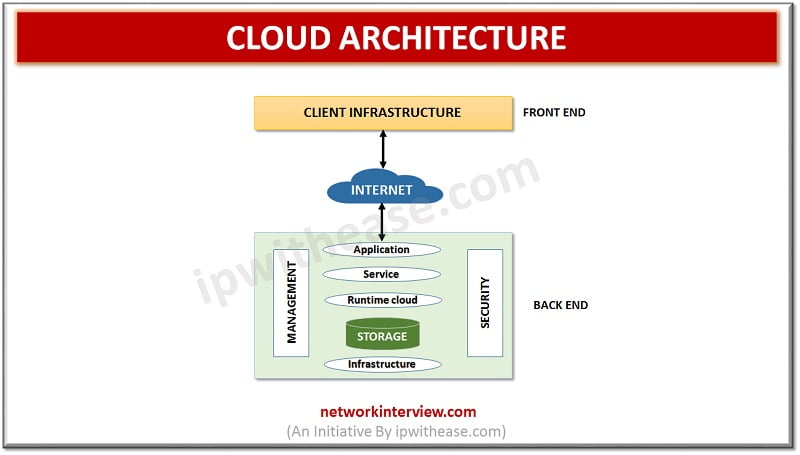
Cloud refers to Internet or a Network. Cloud computing allows remote servers hosted on Internet to manage, store , process, and access data online instead of stored locally on disks. The data can be in any form – files, images, videos, Audio and so on.
The cloud works in distributed model and allows sharing of computing resources across users. It helped to build agile infrastructure , ensured high availability and reliability, scalability by on demand provisioning of resources as per business need, allowed multi-sharing , devices are location independent and users can connect from anywhere, low cost of ownership and services availability like a utility with pay per use made it an attractive preposition for organizations.
Cloud Service Models
There are 3 types of representations w.r.t. Cloud service Models: –
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) – this is also known as HaaS (Hardware as a service) . In this model infrastructure is managed on Internet and provides hardware / computing resources on demand / pay per use. Some illustrations of IaaS are AWS (Amazon Web Services) AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Compute Engine (GCE), Rackspace, and even Cisco Metacloud.
Platform as a Service (PaaS) – provided a computing platform to developers to develop, test , run and manage applications on Internet. It supports multiple languages and frameworks and provides ability to ‘Auto scale’. PaaS examples include AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Windows Azure, Force.com, Heroku, Google App Engine, Apache Stratos as well as OpenShift.
Software as a Service (SaaS) – In this cloud provider hosts application on a software. And users can access the applications using Internet and web connectivity. Users are not to be bothered about hardware/software updates and services are obtained on Pay per use basis. Some examples of SaaS are Google Apps, Salesforce, Dropbox, ZenDesk, Cisco WebEx, Slack, and GoToMeeting.
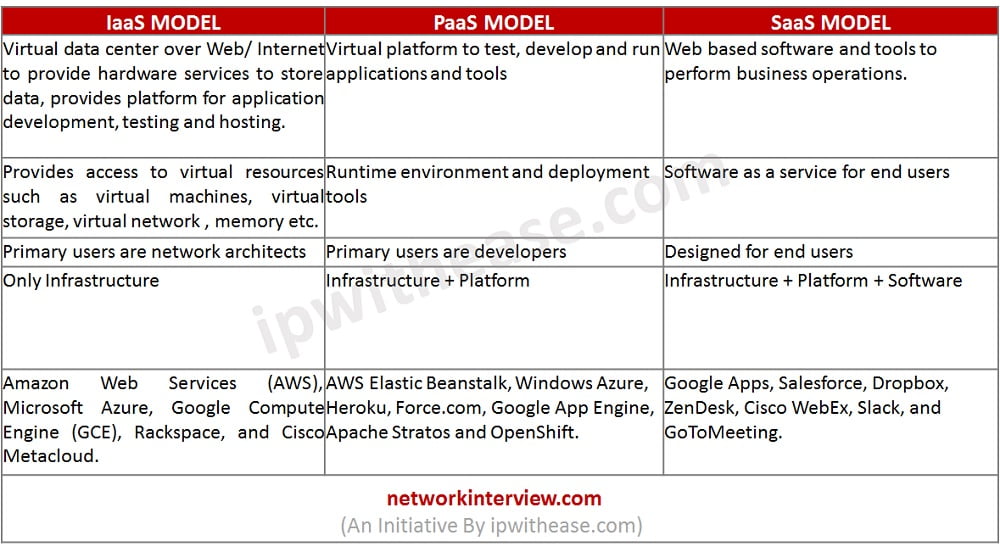
Difference between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS:
Iaas Model | PaaS Model | SaaS Model |
| Virtual data center over Web / Internet to provide hardware services to store data , provides platform for application development, testing and hosting. | Virtual platform to test , develop and run applications and tools | Web based software and tools to perform business operations |
| Provides access to virtual resources such as virtual machines, virtual storage, virtual network , memory etc. | Runtime environment and deployment tools | Software as a service for end users |
| Primary users are network architects | Primary users are developers | Designed for end users |
| Only Infrastructure | Infrastructure + Platform | Infrastructure + Platform + Software |
| Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Compute Engine (GCE), Rackspace, and Cisco Metacloud. | AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Windows Azure, Heroku, Force.com, Google App Engine, Apache Stratos and OpenShift. | Google Apps, Salesforce, Dropbox, ZenDesk, Cisco WebEx, Slack, and GoToMeeting. |
![]()
Download the difference table here.
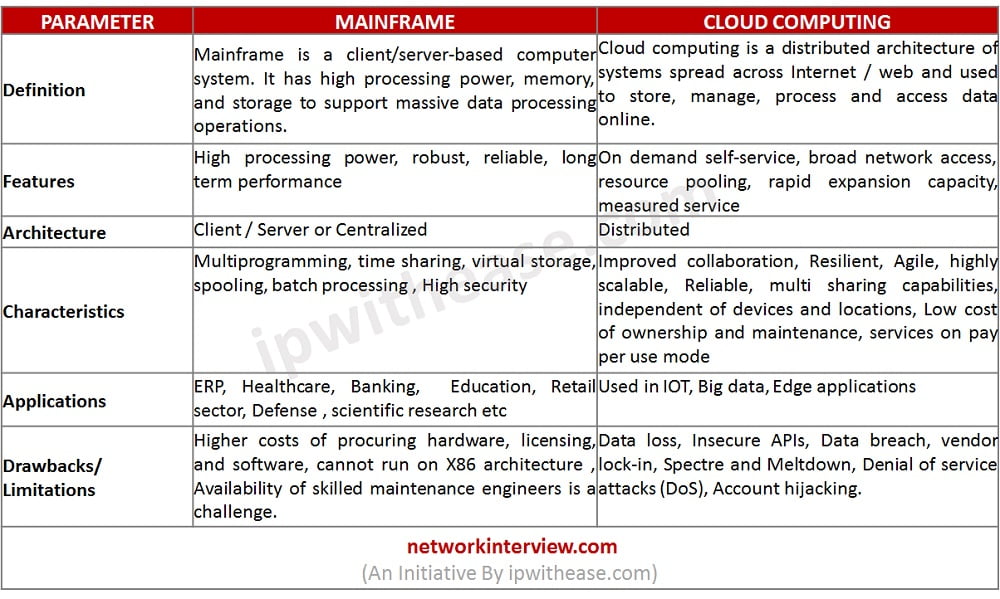
Comparison Table: Mainframes vs Cloud Computing
Below table summarizes the differences between Mainframes and Cloud Computing:
Parameter | Mainframe | Cloud computing |
| Definition | Mainframe is a client/server-based computer system. It has high processing power, memory, and storage to support massive data processing operations. | Cloud computing is a distributed architecture of systems spread across Internet / web and used to store , manage, process and access data online. |
| Features | High processing power, robust , reliable, long term performance | On demand self-service, broad network access, resource pooling, rapid expansion capacity, measured service |
| Architecture | Client / Server or Centralized | Distributed |
| Characteristics | Multiprogramming, time sharing, virtual storage, spooling, batch processing , High security | Improved collaboration, Resilient, Agile, highly scalable, Reliable, multi sharing capabilities, independent of devices and locations, Low cost of ownership and maintenance , services on pay per use mode |
| Applications | ERP, Healthcare, Banking, Education, Retail sector, Defense , scientific research etc | Used in IOT , Big data, Edge applications |
| Drawbacks/ Limitations | Higher costs of procuring hardware, licensing, and software, cannot run on X86 architecture , Availability of skilled maintenance engineers is a challenge | Data loss, Insecure APIs, Data breach, vendor lock-in, Spectre and Meltdown, Denial of service attacks (DoS), Account hijacking. |
![]()
Download the difference table here.
Quick Facts !
Source : Cloud computing Energy efficiency report
Cloud computing lead in reduction of 38% worldwide energy consumption in Year’2020.
Cost of data center power consumption come down to $16.0 billion from $23.3 billion in 2010.
Continue Reading:
Tag:cloud, comparison