What is Packet Capture?
Introduction to Packet Capture
“Packet Capture” is defined as network interception of a data packet that is traversing a specific point through a data network. These kind of packets are captured using appropriate tools in real time which are stored for a short stint in order to be analyzed, downloaded, archived or discarded. The reason for capturing and examining network packets, is chiefly for identification of security threats, undesirable network behaviors, network congestions, packet loss and network analysis.
Packet capture is generally performed via two methods. The first one is by capturing the whole packet and the second is by capturing specific portions of a packet. A full packet is made up of two things: a payload and a header. The payload is defined as the main content of the packet, while the header contains metadata, the packet’s source and the destination’s address.
Packet Capture Tools
Some of the most frequently used tools across IT ecosystem for packet capturing are enlisted below:
- SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor: It is one of the best network monitoring platform in the industry. It contains a network packet analyzer that can capture data from upto 1200 applications at the same time. The most interesting part is the ability to measure packet transfer in real time using the embedded dashboard called Quality of Experience (QoE).
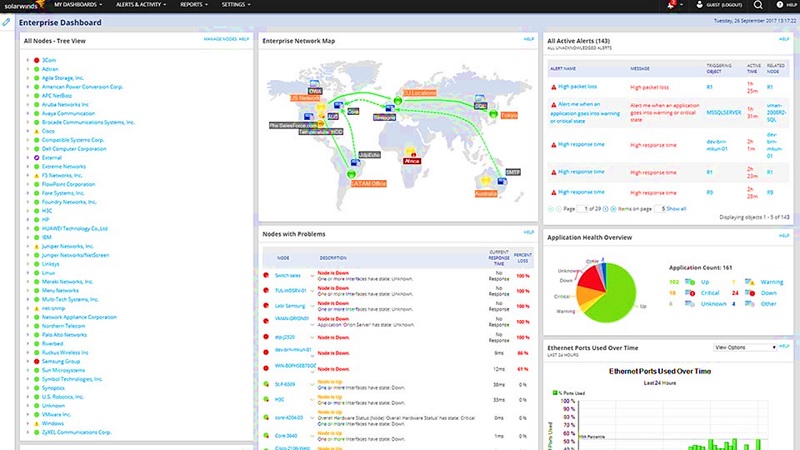
- Paessler PRTG Network Monitor: This platform is preferred for the internal packet sniffer-bandwidth monitoring service, which uses sensors in order to analyses IRC AIM, Citrix, FTP, Mail, HTTP, RDP, SSH, Telnet, and VNC The sensors also include a library of the Top Talkers, Top Connections, and Top Protocols. Each of these libraries can be visualized as percentage charts, making accurate estimations on how network resources are consumed across the devices.
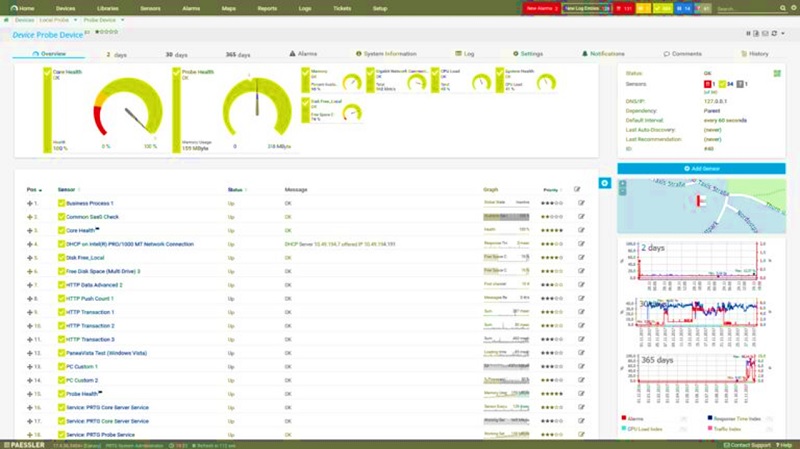
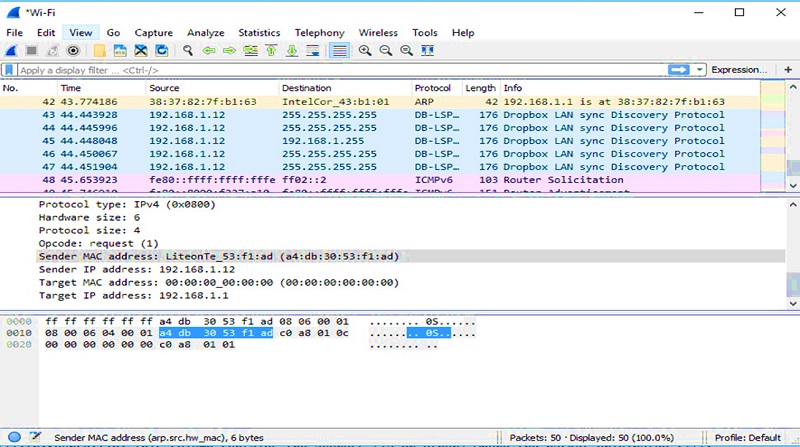
- Wireshark: Wireshark is one of the best choices, when cost savings is one of key and functional requirements. It is a free open source packet analyzer which inspects network traffic in real time. The main advanced service that it offers, is the execution of a “Scan” in order to view the captured packets on screen. The amount of traffic captured can be modified/abstracted by applying display filters and can be exported in different file formats such as Text, CSV, XML or Postscript. Another key advantage of Wireshark is the distinction of different type of traffics by using different colors. For example, the user can set blue for TCP and red for UDP traffic. All the color options are available in the user’s interface.
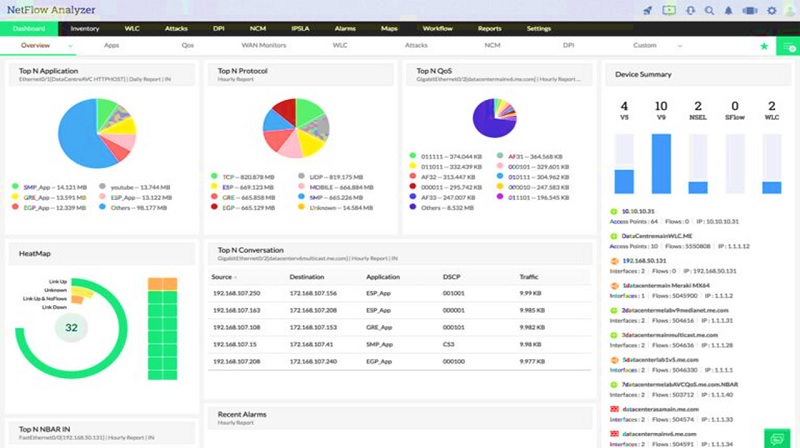
- ManageEngine Netflow Analyzer: This particular tool can analyze real time network traffic with graphs, using NetFlow, sFlow, IPFIX, Netstream, J-Flow, and This software tool also provides metrics of the network bandwidth for different users, devices or applications and helps to allocate resources. Additionally, performance issues can be represented in Pie Charts and exported to various reports according to Data Points, Time Period, Device and Type.
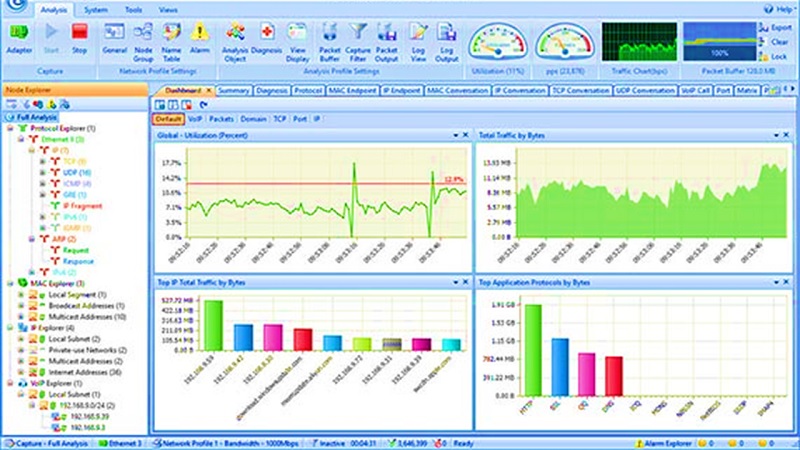
- Collasoft Capsa: This platform is a network analyzer for Windows that monitors packets in real-time. It supports over 1800 different protocols that the user can monitor through the embedded dashboard technology. Furthermore, dashboard offers network usage visualization with different graphs and charts such as Top Application Protocols or Top IP Total Traffic. Colasoft Capsa is suitable for organizations that need a competitively priced network analyzer for Windows.
Conclusion on Packet Capture
This brings us the fag end of the article. Briefly, we discussed about packet capture techniques and how it can be implemented for understanding traffic flow, network troubleshooting, and investigating security incidents.
Previous sections shared some of the best tools in the industry and how they can be used for packet capture and analysis.
It is almost certain that in future need of packet capturing will continue to grow and more research and tools will be created. Every scientist and engineer will hunt for funding opportunities to improve portability, user interface and introduce new techniques for different network traffic loads.
Finally, from a security aspect it must be taken into account that such a technique is helpful in identifying and avoiding network attacks and vulnerabilities. Especially for system and infra administrators, this can be a crucial advantage considering that confidential & business critical information is stored with company’s domain (Company systems only) and not accessible to outside parties or attackers



