3 Different Types of Artificial Intelligence – ANI, AGI and ASI
Rapid adoption of cloud technology across the globe has accelerated and drastically brought changes in the way enterprises are operating now. The introduction of Artificial intelligence or ‘cognitive technologies’ across enterprises to increase productivity, efficiency and accuracy of business operations and customer or end user experience has completely changed the outlook for the future. AI emerged as a business accelerator and brought into focus process automation, cognitive insight, and cognitive engagement.
Today we look more in detail about Artificial intelligence or cognitive technologies and its types, and usage.
What is Artificial Intelligence?
The term Artificial intelligence term was coined in the year 1956 by John McCarthy. The definition of Artificial intelligence (AI) is ‘Science of engineering of making intelligent machines’. Artificial intelligence (AI) is also defined as development of systems which are capable of performing tasks which require human intelligence such as decision making, rational thinking, object detection, solving complex problems and so on.
Related: Artificial Intelligence vs Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence Types
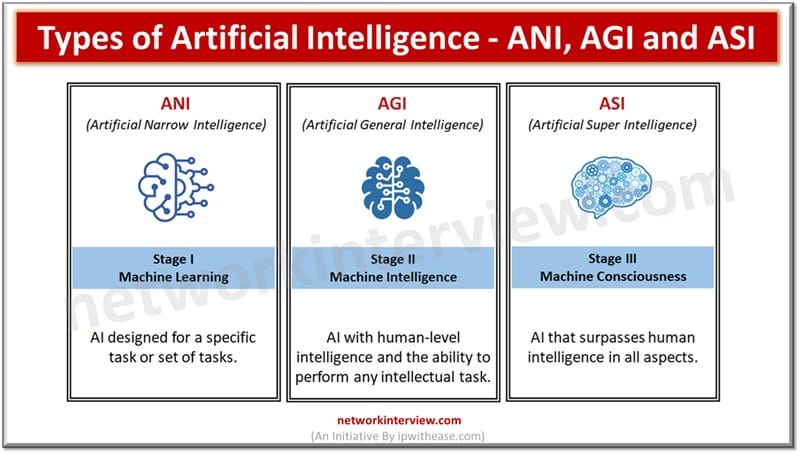
Artificial intelligence can be categorized into 3 main types based on its capabilities.
Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI) – Stage I Machine Learning
It is also called weak AI/Narrow AI. It is able to perform dedicated tasks intelligently. The most commonly available AI is narrow AI. It cannot perform beyond its field as it is trained only to perform a specific task. One commonly used example of this AI is Apple Siri, Alexa and Google Assistant.
Common use cases of narrow AI are playing chess, purchase decisions on e-commerce websites, self-driving cars, speech, and image recognition. Narrow AI is also used in the medical field, for analyzing MRI or computed tomography images and in the manufacturing industry for car production or management of warehouses.
Narrow AI is not able to reason independently or learn from new situations unlike humans or perform tasks which require creativity and intuition.
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) – Stage II Machine Intelligence
It can perform any intellectual task with human-like efficiency. There is no such system that could think and act like humans and perform tasks with perfection just like humans. It is a theoretical concept having human level cognitive function, across a wide variety of domains such as processing of languages, images, computational functioning, and reasoning.
To have a system like this would require Artificial narrow systems working together, communicating with each other like human beings. Even the most advanced computing systems in the world such as IBM Watson takes approximately 40 minutes to simulate a single second of neuronal activity.
Artificial Super Intelligence (ASI) – Stage I Machine Consciousness
It is one level ahead of human intelligence which means machines could perform tasks with more accuracy than humans with cognitive properties. It includes capabilities such as ability to think, reason, solve, make judgements. plan, learn and communicate on its own.
Super AI is a hypothetical concept and development of such systems in the real world is yet a dream come true.
Comparison Table: ANI vs AGI vs ASI
Feature | ANI (Artificial Narrow Intelligence) | AGI (Artificial General Intelligence) | ASI (Artificial Super Intelligence) |
| Definition | AI designed for a specific task or set of tasks. | AI with human-level intelligence and the ability to perform any intellectual task. | AI that surpasses human intelligence in all aspects. |
| Scope | Limited to predefined tasks. | Broad and capable of learning multiple tasks. | Far beyond human capabilities, with self-improving intelligence. |
| Examples | Chatbots, recommendation systems, self-driving cars. | Hypothetical but would include AI that can reason, plan, and adapt like a human. | AI that could surpass human experts in all fields and innovate independently. |
| Learning Ability | Learns within its specific domain but lacks generalization. | Learns across domains, similar to human cognition. | Self-improving and exponentially growing intelligence. |
| Creativity | No real creativity, follows predefined rules. | Can create, innovate, and think critically. | Potentially capable of groundbreaking scientific discoveries. |
| Autonomy | Fully dependent on human programming. | Can function independently and adapt to new situations. | Completely autonomous, with decision-making abilities surpassing humans. |
| Existence Today? | Yes, widely used in various industries. | No, still theoretical and in research phases. | No, purely hypothetical and speculative. |
| Potential Risks | Minimal, unless misused (e.g., biased algorithms). | Ethical concerns regarding decision-making and autonomy. | Existential risk if it surpasses and outperforms human control. |
| Impact on Society | Enhances efficiency in specific industries. | Could revolutionize work, creativity, and problem-solving. | Could change civilization, possibly making human decisions obsolete. |
Download the comparison table: ANI vs AGI vs ASI
Artificial Intelligence – Based on Functionality
In addition, based on functionality, the AI can be further divided as:
- Reactive Machines – basic types of artificial intelligence which do not store memories or past experiences for any future actions. They focus only on the current scenario and react as per possible best action. IBM Deep Blue and Google AlphaGo are examples of reactive machines.
- Limited Memory – Limited data and past experiences can be stored for a short period. These systems use stored data for a limited time only. Self-driving cars are one of the ideal examples of this type of systems which store recent speed of nearby cars, distance to other cars, speed limit etc.
- Theory of Mind – understanding of human emotions, people, beliefs and being able to interact socially with human beings. These machines are still in theory and not developed yet.
- Self-Awareness – is the future of artificial intelligence. These machines will be super intelligent and will have their own consciousness, sentiments, and self-awareness and smarter than human beings.



