2FA vs MFA: What is the Difference?
Data security is a major concern for enterprises especially dealing with sensitive data. Creating a safe and secure environment becomes top most priority for them. In 2023 cyber attacks worldwide increased by 7%. Each company experiencing on an average 1200+ cyberattacks per week a 7% increase from previous year. Considering this organizations wont rely alone on a single strong password mechanism to protect business and customer information.
Today we look more in detail about comparison 2FA vs MFA, key differences between the two, which is more secure and why?
What is 2FA or Two-factor Authentication
2FA provides an additional layer of security for online accounts. Users need a username, a password, and additional information to establish their identity. Some examples of 2FA are fingerprint scans, OTP, security questions etc. users can access their account or private information only after the verification process is complete.

3 Aspects of 2FA
2FA works on three aspects – knowledge, possession, and biology.
- Knowledge – users will provide information such as security questions, a PIN or a pattern, specific keystroke, apart from login credentials to gain access to their account.
- Possession – to prove identity, the user must have access to physical devices used in authentication such as USB, card, mobile phone.
- Biology – users add biological features such as fingerprint or voice in authentication factor. Post approval users can access their account.
2FA could be based on hardware tokens, SMS and voice, software tokens, push notifications, biometrics, location etc.
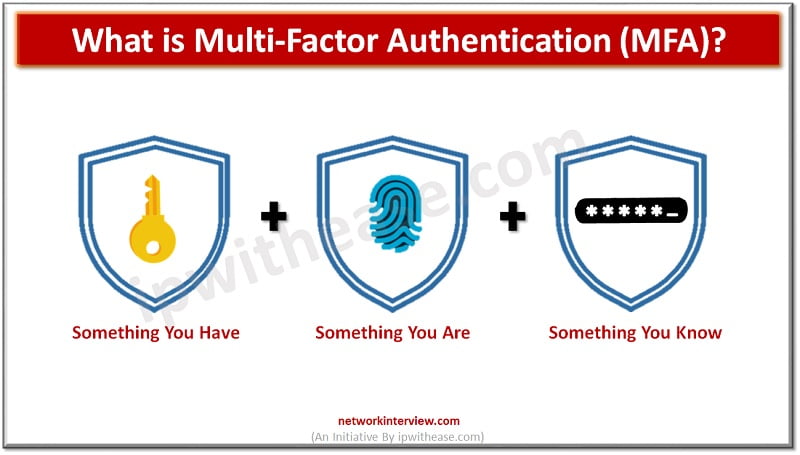
What is MFA or Multi-factor Authentication
MFA has a number of authentication layers. In MFA users need to go through several authentication steps to access their account. Only after passing all layers of authentication can a user access a web service or account such as Netflix, bank accounts, social media accounts etc. Integration of account login with security devices such as emails or mobile to ramp up security.
How MFA works
MFA works in four steps as under:
- Registration – in MFA user link items such as mobile phone or any other device connected to the system to gain account access.
- Login – user enter credentials such as username and password to gain access to secure system
- Verification – The system verifies the registered item (in this case mobile phone)
- Reaction – User will complete registration process with the help of key registration
How the system is integrated with MFA authentication might differ. Some systems are integrated with login while some maintain the history of devices used to access the account. Any deviation from pre-set parameters will trigger an alert and hold the process until the user validates the login attempt.
MFA could be based on SMS tokens, mail tokens, hardware tokens, software tokens, time-based OTP, social logins, biometric tokens.
Related: How to Prevent Against MFA Fatigue Attacks?
Comparison: 2FA vs MFA
PARAMETER | 2FA | MFA |
| Purpose | Subset of multi-factor authentication having fewer authentication layers compared to MFA | Having multiple layers of authentication being the primary authentication mechanism |
| Every 2FA is a MFA | Every MFA may need not necessary be 2FA | |
| Layers of protection | 2FA as the name suggest has two step authentication | MFA requires a user to complete more than one authentication steps to login to their account |
| Security | 2FA is secure compared to single step authentication but less compared to MFA | MFA is highly secure as there is an additional layer of security involved |
| Ease of implementation | 2FA is easy to deploy as it involves only two authentication methods | MFA is complex to deploy and may require additional hardware or software to be implemented as additional authentication layer such as fingerprint, facial recognition etc. |
| Flexibility | 2FA is less flexible compared to MFA | MFA is fairly flexible as enables a wider range of security options an organization can use or customize for its specific authentication needs |
| Scalability | 2FA may not be able to handle large number of users or large number of applications | MFA is scalable and can handle larger number of users or large number of applications |
Download the comparison table: 2FA vs MFA
Why MFA is Generally More Secure
- Increased Complexity for Attackers: With MFA, attackers need to compromise multiple factors from different categories (knowledge, possession, inherence), making it substantially more challenging.
Flexibility: MFA allows for a combination of multiple factors, enhancing security. For instance, an attacker who has stolen a password and a phone might still be thwarted by a fingerprint requirement.
Customization: MFA systems can be tailored to include more rigorous or diverse authentication methods, depending on the security requirements.
In summary, MFA is generally more secure than 2FA due to the added layers of security and complexity it offers, making it more difficult for unauthorized users to gain access.
Tag:Security



