20 Types of Malware
Malware software is a constant concern in the digital age. Cyber criminals continuously come up with innovative ways to break into computer systems and steal personal data, cause disruption to businesses, ask for ransomware, cause data destruction. Malware software is designed to infiltrate systems and other devices without the consent of the user. Often masquerading as legitimate applications such as antivirus programs, malware tricks users into its installation, once it is placed it can perform a wide range of malicious activities.
In today’s topic we will learn about different types of malware software, their key characteristics, how to protect systems from malware etc.
What is Malware
Malware comes in diverse forms, and each is meant for a specific purpose. Broadly all malware can be divided into two categories namely – functional malware which executes specific actions on infected devices and other one is installable malware which focuses on installing itself on the target system.
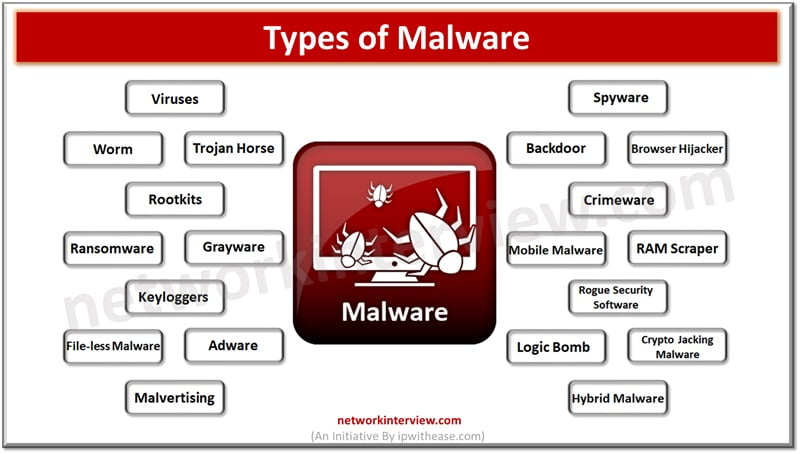
Types of Malware
Let’s look at each type of malware and understand its working.
- Viruses (network infiltrators) – are a form of malware, which infiltrate systems and force them to perform unwanted actions. Usually viruses are transmitted via Emails, social media, file sharing platforms. They enter the device while visiting a compromised website or download virus infected files. They require human intervention or application infiltration to get into the system.
- Worm (Network propagator) – is a type of computer worm which can self-replicate and transmit from one system to another exploiting vulnerabilities of the operating system on the target machine. This is designed to exploit specific weaknesses, they spread rapidly and are usually deployed for stealing personal data or for service disruption. It does not require human intervention to initiate.
- Trojan horse (Disguised data stealer) – is disguised as a legitimate program and installed without user knowledge, trojans pilfer sensitive personal information such as credit card details, credentials. They corrupt or destroy system data.
- Rootkits (Stealthy malware threats) – is a sneaky category malware which conceal presence of other malware in the system. This is employed to access systems and install malware programs. These can infiltrate systems using emails, harmful websites or contaminated USB drives.
- Ransomware (Holding data hostage) is a type of malicious software which encrypts user data and demands payment for data decryption. Cybercriminals request cryptocurrency payments like Bitcoin to have an anonymous identity.
- Grayware (Annoying malware) is less harmful but causes user inconvenience and nuisance. This malware steals user information, monitors its activities, and causes damage to systems.
- Keyloggers (Stealthy monitoring tools) is a type of malware which captures user keystrokes. Frequently used by cyber criminals to swipe passwords and sensitive data.
- File-less Malware (Elusive threats) is a malware which operates without leaving its trace, utilizes computer memory and executes code from there. Cyber criminals use this malware to bypass antivirus software.
- Adware (Intrusive and unwanted advertising) – malware bombard users with unwarranted ads on their devices. This is usually installed without user consent or downloads from compromised websites. Adware disrupt users’ browsing experience with product promotion ads and redirect them to harmful websites.
- Malvertising (Unleash Malware Through Online Ads) – is a form of malware wherein online advertising is used to infiltrate systems by distribution of malware through ads on creditable or hacked websites.
- Spyware (Stealthy Surveillance Software) is a type of malware which infiltrates a system without the consent of the user and enables remote monitoring and control.
- Backdoor (Another Way In) – this malware enables hackers to bypass system security features. Installed on systems or mobile devices by exploitation of existing vulnerabilities.
- Browser Hijacker (Your Details are at Risk) – this is a specific type of malware that alters browser web settings without taking user consent. It modifies homepage, search engine, and new tab preferences.
- Crimeware (Used for Crimes) – malware is meant for criminal activities. Used to pilfer information, fraud, physical damage. Usually used to steal credit card information, impersonate victims to access personal data, identity theft or computer-based scams.
- Mobile Malware (Unknown Applications) – malicious mobile apps downloaded from third-party app stores or downloaded through infected ads on official app stores are harmful and spread via phishing mails and SMS messages.
- RAM Scraper (RAM Data Stealers) – infiltrate systems and steal data from their RAM. Installed via phishing mail or by exploiting system vulnerabilities
- Rogue Security Software (Fake Antivirus) – masquerade as legit security program, rough s/w lure users into purchase of fake protection against malware.
- Logic Bomb (Triggers on a Logic) is hidden within a system code and executes harmful actions after a specific event or time frame.
- Crypto Jacking Malware (Unveiling the Hidden Threat) – harnesses the processing power of a device for mining cryptocurrency.
- Hybrid Malware (The Evolving Cyber Threat) is a latest category of sophisticated malware which can infect a user system and steal sensitive data simultaneously.
Tag:Security



