What is TPRM (Third Party Risk Management)
As business environments are changing rapidly third-party relationships are on boom creating a pivotal role in the business success. But it has a flip side too as a third-party introduction in your ecosystem brings a host of risks, cyber security risks as we understand. As per Gartner risk outlook third party or supply chain is at the third position in terms of contribution to cyber threats. It is crucial to understand these third-party risks. The vulnerabilities of third-party connections present a tough challenge for organizations navigating into the cyber security landscape.
In today’s topic we will learn about implementing proactive and strategic methodology of third-party risk management (TPRM), its importance in today’s scenario, examples of third-party risks and how to manage them using third party risk management strategies.
About Third Party Risk Management
It is a strategic process to identify, assess, monitor and mitigate risks arising due to collaboration with third party service providers such as external vendors, supplier, service providers or contactors. This involves evaluation of potential risks to security, compliance and privacy along with operational challenges.
Third party risk management (TPRM) enables organizations to understand the third parties they work with, how their services are used, what safeguards are in place by third party providers. An effective third-party risk management program ensures businesses can safeguard their data, maintain regulatory compliances and protect their brand and reputation along with operational efficiencies.
Why is Third-Party Risk Management important?
As per Deloitte last year 62% of global leaders identified cyber information and security risk in top third-party risk. This brings in focus and highlights challenges faced in third party risk management across businesses. The factors contributing to bring focus and mitigate risks associated with third-parties due to:
- Increased regulatory requirements – The focus is more on data protection and privacy regulations such as GDPR, MAS TRM, CCPA, AI EU act etc. Regulatory acts such as AI EU act, DORA, NYDFS and NIS 2 are mandating mapping of third-party assets, evaluating their criticality and proactive risk management strategies.
- Evolved threat landscape – As more and more businesses are adopting cloud services the attack surface has grown exponentially. It is crucial to identify and mitigate emerging risks including the ones introduced with third party partnerships. Due to shared responsibility of assets and data on cloud with major cloud providers such as Microsoft, AWS, Google, etc. risks are getting shifted to SaaS providers.
Third Party Risks
Organizations face various third-party risks. Let’s look more in detail about them.
- Cybersecurity Risk – Routine vendor evaluations and tracking help in addressing this risk where a third party becomes the cause of data breach or loss.
- Operational Risk – Third party initiatives or disruptions prevent business operations to function in normalcy. To eliminate this risk, usually SLAs are implemented.
- Compliance Risk – Industries operating in regulatory space such as banking, telecom etc. are at high risk due to non-compliances to established standards and contracts.
- Reputational Risk – Any businesses working with third parties face reputational risks due to adverse incidents such as security failures, data breaches etc.
- Financial Risk – Inadequate management of third-party relationships poses financial risks. Inadequate security measures could lead to fines, penalties etc.
- Strategic Risk – Due to lapses on the third party side there could be potential risks to business operations, customer data loss, brand reputation etc.
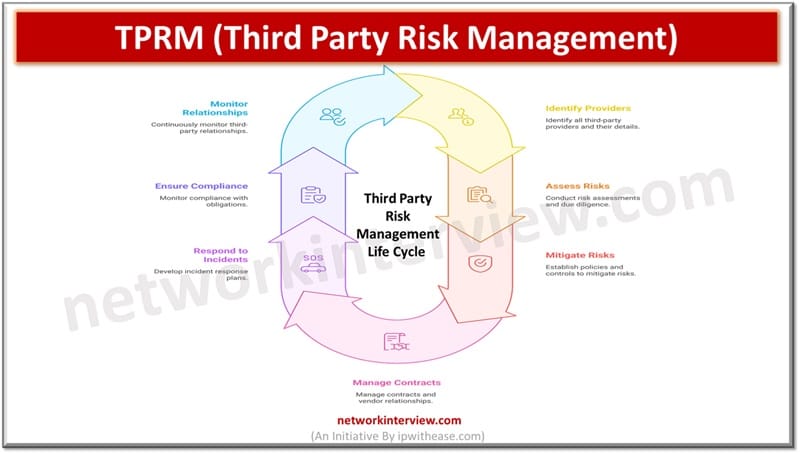
Third Party Risk Management Life Cycle
- Recognize and categorize third party relationships – Effective third-party risk management starts with identification of all third-party providers engaged with the business , their access levels , industry or sector, relationship type, requirements of regulatory compliance and financial stability.
- Risk assessment and due diligence – Conduct a comprehensive risk assessment to determine risks associated with solution or service in use, probability and potential impact of risks. Due diligence involves assessing reliability and capabilities of service providers, creating policies and procedures aligned with organization security policy to which providers are required to be aligned.
- Risk mitigation and management – Policies, controls and processes establishment to reduce third party risks such as contractual clauses, continuous monitoring etc.
- Contracting management – This involves establishing SLAs, managing relationships, ongoing monitoring of vendor performance and regular reviews.
- Incident response and remediation – Establish incident response and management plans involving third parties , post event evaluations.
- Ensuring compliance – Monitor and validate third party compliance with contractual obligations, regulatory requirements.
- Monitoring third party relationships – Establishing clear SLAs, defining response times, availability and problem resolution timeframe. Ongoing audits to ensure continuous compliances.



