What is Secure Real-Time Transport Protocol? (SRTP or Secure RTP)
There are a set of protocols which define how real time traffic handling will be taken care of such as audio and video over the Internet. These protocols are known as Real Time Transport protocol (RTP). RTP protocol is used with UDP or user datagram protocol. In itself UDP is considered an unsecured protocol so how to ensure encryption, authentication, integrity and shielding against cyber attacks while doing real time traffic handling here Secure RTP comes into the picture.
Today we look more in detail about the secured extension of Real time Transport protocol (RTP) known as Secure Real-Time Transport Protocol, its packet structure, how it works, its advantages and use cases.
SRT or Secure Real-Time Transport Protocol
Voice over IP (VoIP) has taken over traditional PSTN networks over years and more and more voice calls are shifting from PSTN to VoIP where most people are not aware that security vulnerabilities introduced by VoIP are susceptible to denial of service (DDoS) attacks and VoIP traffic can be mislead or corrupted using DNS hijacking.
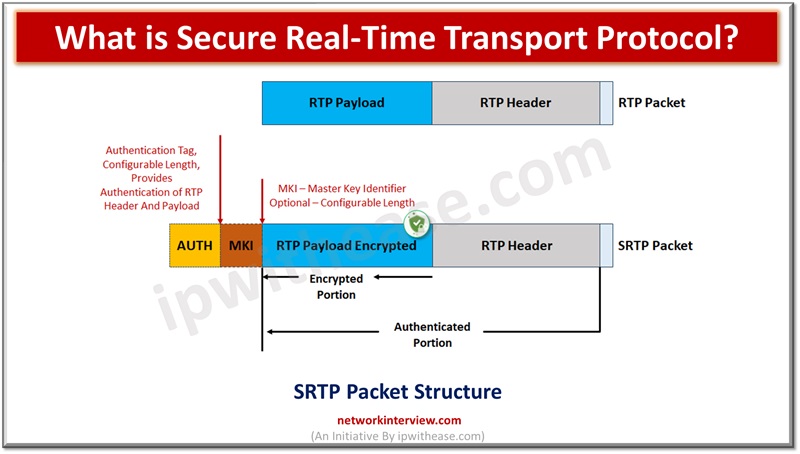
It was published in 2004 by IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force) under RFC 3711. SRTP or Secure RTP is a security profile for RTP which adds confidentiality, integrity, message authentication, and replay protection to RTP protocol. SRTP provides protection for voice over IP traffic as it has minimal impact during usage on voice quality and payload overhead. Its secure variants provide support for authentication algorithms such as HMAC-SHA1 and MD5 and key definition schemes such as PSK, MKI and FT.
Secure RTP is the profile of RTP and not a different protocol but when security is used and packet payload is encrypted it is Secure RTP. RTP is designed to handle play out requirements of real time media streams using time stamps and jitter buffering. Due to the real time nature of data streams, transmissions requests could be a costly affair, it is used in conjunction with UDP to provide lower overhead communication between two systems or endpoints.
Pros and Cons of Secure RTP
PROS
- Wider acceptance to new encryption algorithms
- Secure for unicast and multicast RTP applications
- High throughput and low packet expansions
- Lower bandwidth and computational costs
- Higher tolerance for packet loss and packet recording
- Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) used as default cipher for encryption / decryption by Secure RTP
- Works independently of transport, network and physical layers used by RTP
CONS
- Only encrypts the payload of RTP packets and not for RTP extension headers
- Only available for business applications not meant for individual consumers
- Usage of selective forwarding mixer to optimize RTP parameters results in disruption of end-to-end security between peer-peer systems
How does SRTP (Secure Real-Time Transport Protocol or Secure RTP) work?
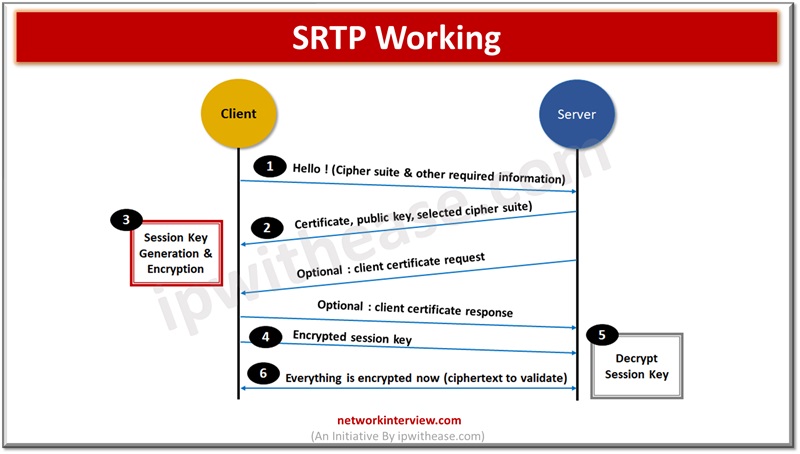
Secure RTP uses TLS for encryption, using a handshake (which is depicted in figure below).
The client and server exchange the keys which are unique for each session, and used to encrypt and decrypt data for data getting transferred between them. SRTP uses AES-CTM – VoIP standard and AES-f8 – used in 3g data networks.
Continue Reading:
12 Most Important Network Protocols Explained
GLBP: Gateway Load Balancing Protocol
Tag:Protocols



