How to Identify the MAC Address of a Port?
In the world of computer networks, communication between devices or systems happens using a unique identifier which facilitates data exchange and communication between interconnected systems.
Unique identification of network interface controller (NIC) for network communication happens at the data link layer of OSI model through MAC address assignment to the device. The MAC address is used in local area networks to send data to the correct receiver or device. MAC address or hardware address combines device manufacturer identification and manufacturer assigned device identification number for unique identification.
In this article we will learn more in detail about how to identify the MAC address of a port and types of MAC addresses.
What is a MAC Address
MAC or media access control is a 48-bit hexadecimal unique identifier represented as six pairs of hexadecimal digits separated with (:) or (-) which represents a unique hardware address for network interfaces.
MAC address structure is represented in figure below:
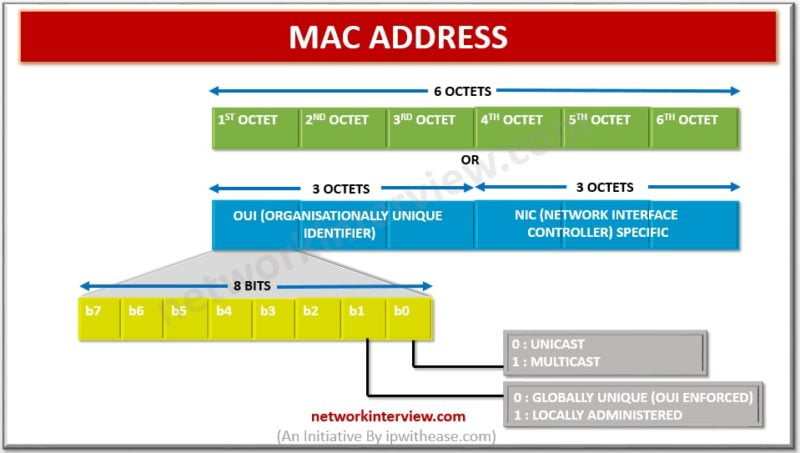
The first 3 octets (24 Bits) are initial three hexadecimal pairs are OUI (organizationally unique identifier) which is network card manufacturer unique identification code to identify device and aid in troubleshooting.
The last 3 octets (24 bits) is a unique identifier assigned by the manufacturer of the device to specific NIC or network interface. This is unique globally and referred to as Universally Administered Address (UAA) so as to prevent network conflicts due to duplicity.
MAC addresses are used for device identification uniquely within the local area networks and also used by network security protocols. Access control lists (ACLs) are configured on switches and routers with traffic allow/deny on the basis of MAC address. Media access control layer (a sublayer in data link layer) encapsulates MAC address of source and destination in data frame header to ensure network communication.
Steps to find the MAC Address of a Port
MAC addresses are of two types – unicast and multicast.
Unicast is most commonly used MAC address to uniquely identify a network interface and used for point-to-point communication and used to while sending data from one device to another device. The MAC table contains the Unicast address and detail of the specific port it is mapped to.
To identify MAC address of a specific port, follow the below steps:
Step 1
Login to the switch by using SSH or console connection
Step 2
Enter privilege EXEC mode
Switch> enable Provide the password if prompted
Step 3
To view MAC address table of for specific MAC address
Switch# show mac address-table address [mac-address] Replace [mac-address] with actual MAC address For example, Switch# show mac address-table address a1c2.a4t4.f9g7 This command displays the MAC table
Vlan MAC address Type Ports
11 a1c2.a4t4.f9g7 DYNAMIC Gi2/0/2
In above example a1c2.a4t4.f9g7 MAC address is connected to Gi2/0/2 port
Related FAQs
Q.1 Can I find a MAC address from an IP address on a specific port? Yes, it is possible by using the following steps:
- Use ping to ensure connectivity.
- Run arp -a (Windows) or arp -n (Linux) to map the IP to a MAC.
- Check the switch’s MAC address table to see which port that MAC address is associated with.
Q.2 Why the port is showing multiple MAC addresses? This usually happens when:
- The port is connected to another switch, hub, or access point.
- The port is configured as a trunk or uplink.
- Multiple devices are behind that single physical connection.
Q.3 What if the MAC address does not appear on the port? This can be due to any of the following reasons:
- The device is turned off or idle (not sending traffic).
- Port security is restricting learned MACs.
- The MAC address has aged out from the switch’s table (inactive for some time).
- Wrong VLAN lookup (MACs are stored per VLAN).



