Data Mining vs Data Analytics
The mammoth increase in data volumes had led to an information knowledge revolution triggered. Key aspect of research and strategy formulation to gather meaningful information and insights into the data already available is primary focus. All this information is gathered and stored in a data warehouse which is later used for business intelligence purposes. Data mining and Data analytics are two subsets of business intelligence.
Today we look more in detail about two most popular and widely used terminologies data mining and data analytics and how they differ from each other , purpose for which they are collected and their use cases.
About Data Mining
Since the 1990s data mining has been a buzz word which is a systematic and sequential process for identification and discovery of hidden patterns and information in large data sets. Data mining helps to transform raw data into useful information which could help businesses to achieve their goals. Data mining tasks require various techniques and tools such as data cleaning , Artificial intelligence, association rule, clustering, classification etc. Let’s look at each one of them more in detail.
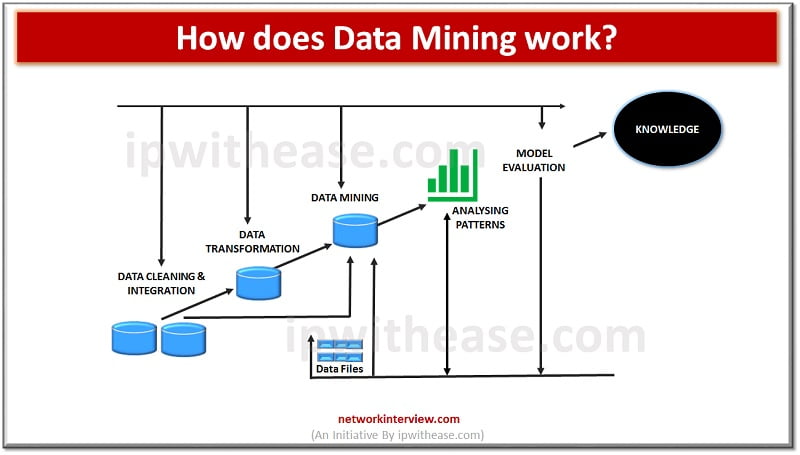
- Data cleaning – all raw data is taken from various sources and converted into a specific standard format which can be processed and analysed.
- Artificial intelligence – system performs analytical activities such as planning, learning and problem solving
- Association rule – is also called market basket analysis. And it is used to determine the relationship between different data set variables.
- Clustering – refers to the process of splitting huge data sets into smaller and manageable subsets called clusters.
- Classification – is used to assign categories to data collection to obtain more in-depth analysis and prediction
About Data Analytics
Data analytics is a superset of data mining which involves extraction, cleaning, transformation, modelling and visualization of data in a meaningful and useful way. It helps in deriving a conclusion and making informed decisions. Data analytics has been a process since the 1960s.
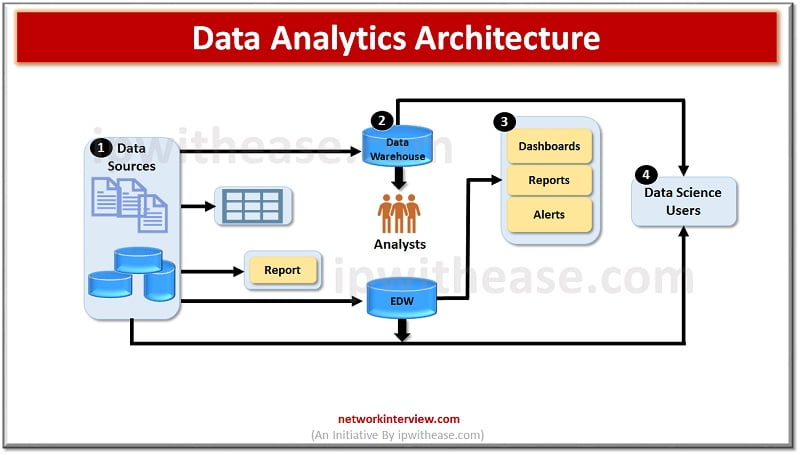
Data analytics goes through various phases as under :
- Discovery – Analyse the data and investigate the problem related to data to develop a context and understanding.
- Data preparation – An analytics sandbox is made to accomplish the analysis’s process for project duration. Various tasks are carried out such as extraction, transformation and data update in the sandbox.
- Model planning – process and techniques are determined for a specific model building phase. Data sets are analysed to learn about relationships between various variables and choose most suited model
- Model building – data sets are created for different purposes such as test, production, training etc
- Communicate results – interaction with stakeholders and find if output of project is failure or success
- Operationalize – outcome is delivered
Comparison Table: Data Mining vs Data Analytics
Below table summarizes the differences between the two:
FUNCTION | DATA MINING | DATA ANALYTICS |
| Definition | Process of extraction of specific pattern from larger data sets | Process of ordering and organization of raw data in such a manner that it provides useful insights and help in making informed decisions |
| Expertise area | Involves intersection of machine learning , statistics and databases | It requires knowledge of computer science, statistics, mathematics, subject knowledge and AI/Machine learning capabilities |
| Synonyms | Also known as knowledge discovery in databases (KDD) | Data analysis could be explanatory, descriptive, text analytics, predictive analysis, data mining etc. |
| Work Profile | Data mining professionals build algorithms to gather meaningful structure in data. | A data analyst may not be a single individual. The profile of data analyst involves multiple tasks such as raw data preparation, cleansing, transformation and modelling , presentation in pictorial format or non-chart-based visualizations |
| Responsibilities | Responsible for extraction and discovery of meaningful patterns and structure in data | Responsible for development of models, explanations, tests and analytical measures to propose hypothesis |
| Output | Data pattern is output from mining, trends | Verified hypothesis |
| Actionable insights into data | ||
| Datasets | Large (Big data) | Small, medium, large |
| Structured | Structured, unstructured, semi-structured | |
| Goal | Make data usable | Aid in data driven decisions |
| Identification of pattern | Conclusions | |
| Examples | e-commerce sector | Time series study of unemployment during last 15 years |
Download the Comparison Table: Data Mining vs Data Analytics
Continue Reading:
Difference between Data Warehousing and Data Mining
Tag:comparison, services



