Common SSL Certificate Errors and How to Fix Them
Secure Socket layer (SSL) certificates are used widely by organizations to secure websites and every business needs to have a valid SSL certificate to safeguard client’s security and credibility of brand. Secure Socket layer (SSL) is an encryption protocol and provides security for all online transactions and sensitive information. Sometimes SSL errors do occur if there is a certificate or configuration issue.
Today we look more in detail about common SSL certificate errors, why they occur and possible causes and how to fix them?
What is an SSL Certificate?
Secure Socket Layer (SSL) is encryption protocol to provide security to online transactions and sensitive data protection. It is a digitally signed certificate to authenticate website identity and allows connection which is secured by encryption. A website enabled with SSL will have a padlock symbol icon and HTTPS preceding domain name.
Related: SSL Certificate types
SSL Certificate Errors
SSL certificate errors could result from issues on website certificates or due to configuration issues on the server. If the web browser is not able to establish a secure connection with the website due to a variety of reasons (as mentioned below) then errors will be flashed.
Installation Error
Lets encrypt installation error – during installation you might encounter error such as
“429 Too Many Requests”
“No Domains Authorized,”
“Certificate is not for the chosen domain.”
These errors are received because the domain name is not pointed properly or registration is recent. After a DNS change, the domain goes into DNS propagation period which might take 72 hours. Domain should point to the right server and not propagate before installation of Let’s encrypt SSL.
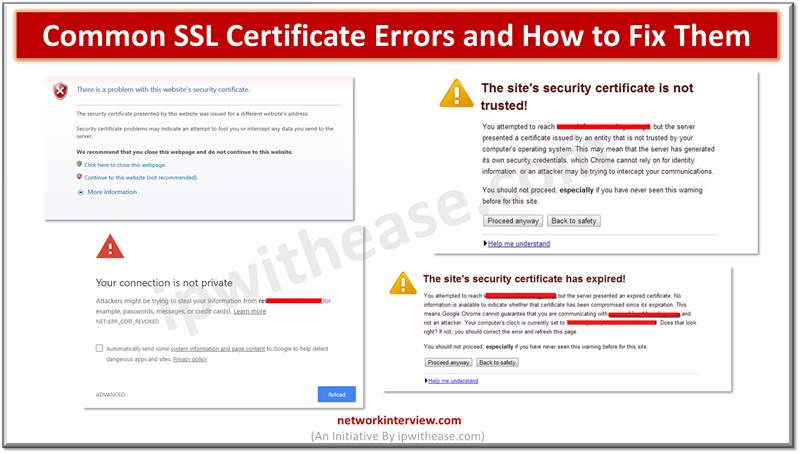
SSL Certificate is Expired
This means the SSL certificate has expired and you have not renewed it in a timely manner. Usually, SSL certificates have validity of one year and free ones like lets encrypt have validity of three months.
SSL Certificate not Trusted
This means the SSL certificate issued by an organization is not recognized as a trusted one by your web browser. You will get the error:
‘Connection not private.’
The certificate of authority (CA) which issued the certificate is not available in local trust root certificate stores. Usually this happens when SSL certificates are self-signed and browsers do not trust them.
Name Mismatch
Name Mismatch occurs when the domain name listed in the SSL certificate does not match the URL we are trying to reach. This error indicates its security certificate is issued by another domain name or subdomain name.
Mixed Content
Web browsers usually display this error when a site we are trying to access has content which is not secure. Mixed content can be caused by non-secure external resources or files requested via HTTP.
Generic SSL Protocol
This error could happen due to
- browser extensions or settings which are blocking encrypted connection,
- chain certificates between yours and root are not properly installed,
- SSL signature is not verified,
- encryption algorithm using obsolete cryptographic standards,
- firewall or local system settings sometimes disrupt SSL corruption etc.
SSL Certificate Revoked
SSL occurs also when certificate authority revoked or cancelled domain SSL certificates. CA will revoke certificate if there is a sign of compromise in private keys. Revoked certificates stored in certificate revocation list (CRL) and if browser locates them error will be displayed.
Fixing SSL Certificate Errors
SSL errors prevent website access and need to be addressed and troubleshooted in a timely manner. Let’s look at some of the ways we can use to fix SSL errors.
- SSL certificate is installed – Make sure that SSL certificate is installed on a website and on a web hosting account.
- Reinstallation of SSL certificate – If an SSL certificate is installed already accessing it with HTTPS might fail. This is usually resolved by a reinstallation certificate.
- Diagnose issue with SSL checker- Use SSL checker to diagnose SSL errors. Online tool will check the certificate chain of trust and verify to ensure it validates back to certificate authority. They provide information about expiry date of SSL certificate, host name, serial number of certificates, signature algorithm etc.
- Renewing SSL certificate – If SSL certificate is expired then the site will not be accessible. So, it needs to be tracked proactively and needs to be renewed before expiry.
- Change URLs to HTTPS – Post installation of SSL certificate on your website, reconfigure to open it via HTTPS. Some items opening with HTTP are referred to as mixed content.
- Update browser and OS version – If SSL is installed and renewed still if error is coming then verity OS and browser version.
- Installation of intermediate certificate – If browser cannot trace back SSL certificate back to root, then SSL error will be displayed. You may need to install an intermediary certificate.
- Generate new certificate sign request – SSL might be incorrectly installed sometimes so generate a new certificate sign request
- Upgrade to dedicated IP address – ‘Name mismatch error’ indicates the web browser is not able to define to which domain the SSL is signed. If you are on a shared hosting account your site might be sharing the same IP address and not able to confirm SSL matches domain name. preferable for such scenario upgrade to a dedicated IP address.
Continue Reading:
What is Digital Certificate and it’s Types?
How to configure SSL Forward Proxy on SRX?
Tag:Security



