Checkpoint Packet Flow Troubleshooting: Common Issues
Troubleshooting Checkpoint Packet Flow issues can be complex. Here are common Checkpoint Packet Flow troubleshooting issues and steps to address them.
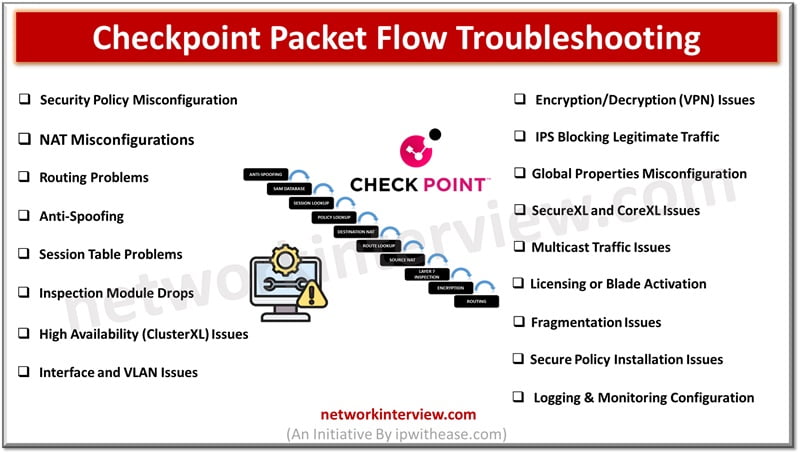
Checkpoint Packet Flow Troubleshooting Issues
1. Security Policy Misconfiguration
- Issue: Traffic is dropped due to incorrect or missing security policies.
- Troubleshooting:
- Review security policies in the SmartDashboard.
- Use the command fw monitor to see how packets traverse through policy layers.
- Ensure that source, destination, services, and actions in policies are configured correctly.
2. NAT Misconfiguration
- Issue: Traffic fails due to incorrect or missing NAT rules.
- Troubleshooting:
- Check NAT rules in the SmartDashboard.
- Use fw monitor or tcpdump to verify that the NAT translation is happening as expected.
- Ensure proper ordering of manual NAT rules and automatic NAT rules.
3. Routing Problems
- Issue: Packets do not reach the destination due to routing issues.
- Troubleshooting:
- Check the routing table using netstat -rn or ip route show.
- Verify that static or dynamic routing protocols (e.g., OSPF, BGP) are correctly configured.
- Perform a traceroute from the firewall to the destination to check path availability.
4. Anti-Spoofing
- Issue: Traffic is dropped due to Check Point’s anti-spoofing protection.
- Troubleshooting:
- Review anti-spoofing settings in the network interface settings.
- Ensure that the interfaces’ networks and the anti-spoofing configuration match.
- Use fw ctl zdebug + drop to identify if traffic is being dropped due to anti-spoofing.
5. Session Table Problems
- Issue: Packets dropped due to session state issues or session table being full.
- Troubleshooting:
- Use fw tab -t connections -s to check the session table size and utilization.
- Clear specific sessions using fw tab -x if necessary.
- Review session timeouts and adjust if needed.
6. Inspection Module Drops
- Issue: The firewall’s inspection engine drops traffic for security reasons.
- Troubleshooting:
- Review SmartLog and the fw ctl zdebug output to see inspection engine logs.
- Ensure the inspection profiles are correctly configured (IPS, Application Control, etc.).
- Disable or modify specific inspection rules if they are triggering false positives.
7. High Availability (ClusterXL) Issues
- Issue: Traffic disruption due to HA failover or ClusterXL synchronization problems.
- Troubleshooting:
- Check ClusterXL status using cphaprob stat.
- Ensure that synchronization between cluster members is healthy (cphaprob syncstat).
- Use tcpdump to capture traffic during failover events.
8. Interface and VLAN Issues
- Issue: Traffic may be dropped due to incorrect interface or VLAN configuration.
- Troubleshooting:
- Check interface and VLAN configurations in the SmartConsole and the Gaia portal.
- Use tcpdump to verify that traffic is reaching the correct interface.
- Ensure that VLAN tagging is properly configured on both firewall and connected devices.
9. Encryption/Decryption (VPN) Issues
- Issue: VPN tunnels fail to establish or traffic is dropped inside the VPN.
- Troubleshooting:
- Verify VPN configuration for phase 1/2 settings (IKE and IPSec).
- Use vpn tu to reset tunnels and verify their state.
- Review logs for encryption and decryption errors.
10. IPS Blocking Legitimate Traffic
- Issue: Legitimate traffic blocked due to IPS false positives.
- Troubleshooting:
- Review the IPS logs and check if legitimate traffic is flagged.
- Add exceptions or tune IPS profiles to reduce false positives.
- Use SmartEvent or SmartLog to analyze the specific attack signatures triggered.
11. Global Properties Misconfiguration
- Issue: Traffic may be affected by incorrect global properties settings.
- Troubleshooting:
- Review global properties, such as NAT settings, logging, and session timeouts.
- Ensure that the security settings are aligned with your network requirements.
- Use fw ctl debug to see if global property settings are affecting traffic.
12. SecureXL and CoreXL Issues
- Issue: Performance degradation due to incorrect configuration of SecureXL/CoreXL.
- Troubleshooting:
- Check SecureXL status using fwaccel stat to ensure acceleration is enabled.
- Review CoreXL CPU distribution using fw ctl affinity -l -a.
- Disable SecureXL temporarily (fwaccel off) to see if acceleration is causing the issue.
13. Multicast Traffic Issues
- Issue: Multicast traffic not reaching its destination due to improper configuration.
- Troubleshooting:
- Ensure multicast routing is configured correctly using cphaprob -a if and IGMP settings.
- Use tcpdump to monitor multicast traffic on relevant interfaces.
- Verify that routing protocols like PIM are correctly set up if needed.
14. Licensing or Blade Activation
- Issue: Features not functioning or traffic being blocked due to licensing issues.
- Troubleshooting:
- Verify licenses using cplic print or the SmartUpdate tool.
- Ensure that all required security blades (e.g., IPS, Application Control) are activated.
- Check SmartLog for traffic that might be blocked due to license limitations.
15. Fragmentation Issues
- Issue: Large packets may be dropped due to improper handling of fragmented packets.
- Troubleshooting:
- Use fw ctl debug to monitor for packet fragmentation issues.
- Check the Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) settings on interfaces.
- Enable fragmented packet handling in the global properties if necessary.
16. Secure Policy Installation Issues
- Issue: New policies are not being installed or causing traffic issues after installation.
- Troubleshooting:
- Use the fw stat command to verify if the policy has been installed.
- Review policy installation logs in SmartConsole.
- Reinstall or recompile policies if needed using the “Install Policy” button in the SmartDashboard.
17. Logging and Monitoring Configuration
- Issue: Insufficient logging or monitoring settings may prevent proper troubleshooting.
- Troubleshooting:
- Ensure logging is enabled on relevant rules and features (e.g., IPS, VPN, etc.).
- Use SmartView Tracker or SmartLog for real-time log monitoring.
- Increase log verbosity for deeper analysis of traffic issues.
Each of these common issues can be diagnosed with Check Point’s packet capture tools (tcpdump, fw monitor), session monitoring, and log analysis, allowing administrators to quickly pinpoint and resolve packet flow problems.
Tag:Checkpoint, troubleshoot



