ISL vs Dot1Q
The differences between ISL and Dot1Q are as follows –
PARAMETER | ISL | DOT1Q |
| Abbreviation for | ISL (Inter Switch Link) | – |
| Standard | Cisco proprietary protocol | IEEE Standard |
| Vlans Supported | Supports up to 1000 Vlans | Supports 4096 Vlans |
| Encapsulation | Original frame is encapsulated and a new header is inserted during encapsulation process. A 26 byte header and a 4 byte FCS (frame check sequence) are inserted which makes it total of 30 Bytes of overhead. | 802.1q encapsulation inserts a 4 byte tag into original frame and FCS (Frame Check Sequence) is re-calculated. |
| PVST | Supported | Not Supported |
| Supported on Cisco NX-OS | Not Supported | Supported |
| Frame Format | 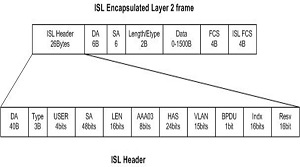 | 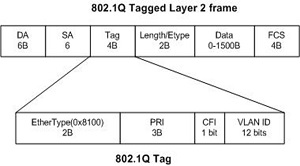 |
| CPU Intensive | ISL uses more processor cycles than 802.1q because of the modification of the header and recalculation of FCS. | Les intensive than ISL |
| Native frame | ISL does not tag frames from native Vlans | 802.1q does not tag frames from native Vlans |
| Configuration | Switch(config)#interface Fa1/1 Switch(config-if)#switchport trunk encapsulation isl Switch(config-if)#switchport mode trunk | Switch(config)#interface Fa 1/1 Switch(config-if)#switchport trunk encapsulation 802.1q Switch(config-if)#switchport mode trunk |
| Fields used | ·DA (Destination Address) ·Type ·User ·SA (Source Address) ·Len ·SNAP ·HSA (High Bits of Source Address) ·VLAN (Destination VLAN ID) ·BPDU ·Index ·Res ·ISL CRC: | ·TPID ·User Priority ·CFI ·VLAN ID |
| Supported models | ISL is supported in Cisco 1900 series switches only | All cisco and non-cisco models |
SOURCE:https://ipwithease.com
Tag:comparison