Difference between VDOM and VLAN
The majority of enterprises large, medium and small are moving to the cloud ecosystem to run their IT operations. Cloud service providers require a multi-tenancy strategy and products to support multi-tenant scenarios. Networking is one of the most crucial elements of cloud computing which enables networking capabilities for multi-tenancy customer environments. Since most of the services in the cloud ecosystem are virtualized and hosted on the same physical hardware, network level isolation becomes critical to ensure data security and protection.
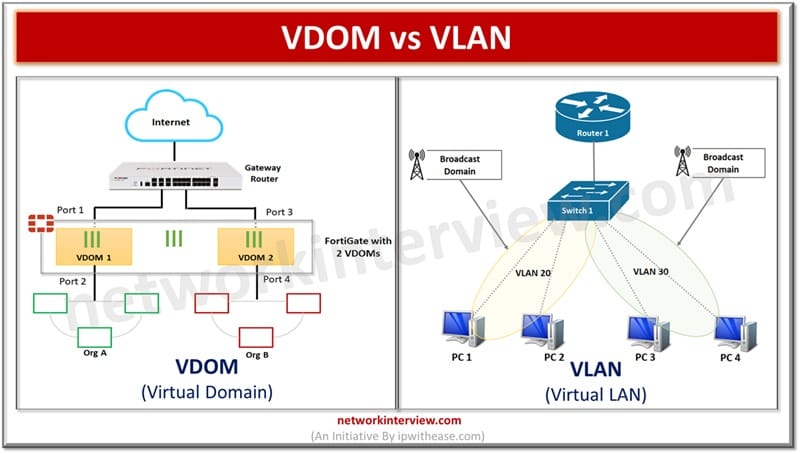
In today’s topic we will learn and compare Virtual domains i.e. VDOM and virtual LANs or VLANs. Their purpose and usage, how they work, their key differences and use cases.
What is VDOM
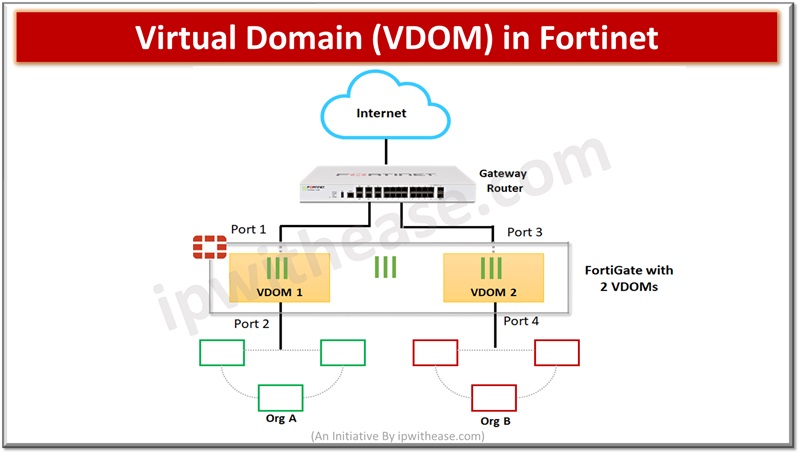
Virtual domains (VDOM) are a very common component in the cloud ecosystem and are used to divide a single physical unit into multiple virtual devices and operate as an independent firewall with its own interface, policies and configurations. This capability is useful in multi-tenancy environments to provide logical segregation in network infrastructure.
Each virtual domain (VDOM) operates as a separate firewall which allows network administrators to create separate security policies and configurations as per network segment requirements, physical resources which are shared. Segmentation of networks helps in improving security. VDOM is also used in segregation of network traffic.
 What is VLAN
What is VLAN
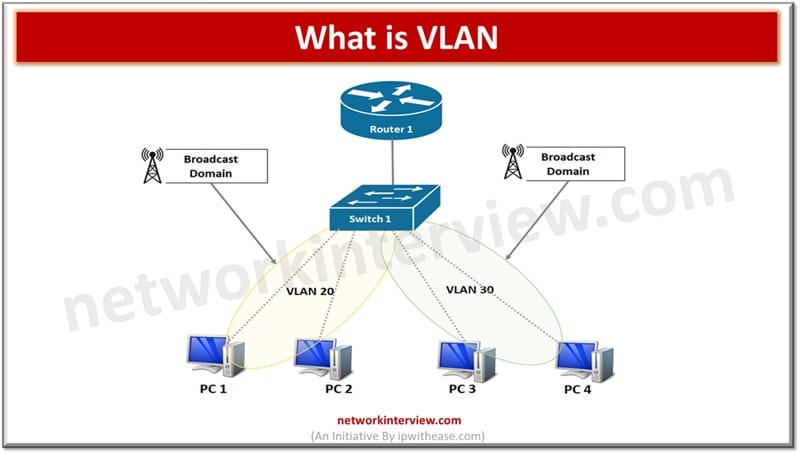
Virtual LANs (VLANs) divide networks at layer 2 (data link layer) and are also used to divide broadcast domains. It allows hosts to group together under a single broadcast domain even if they are connected to a different switch (physical) layer. VLANs can be static and dynamic:
- Static VLANs or port based VLAN is assigned to respective port switches. The association of the port with VLAN does not change until port assignment is modified by the network administrator.
- Dynamic VLAN port is configured as dynamic, and it receives VLAN information based on the VMPS server as per the MAC address. This reduces overhead of management. When an end user system connects to a switch port the switch queries a database to establish its membership with VLAN. The VLAN database is updated by network administrator.
Comparison: VDOM vs VLAN
| FEATURES | VDOM | VLAN |
| Definition | Used in logical segmentation of physical FortiGate device into independent virtual firewalls having their own policies and configurations | Used to divide network at layer 2 and 3. VLANs logically separate a local area network (LAN) into individual small broadcast domains |
| Boundary | Implemented on a single FortiGate hardware device | VLANs can be implemented across multiple physical interfaces |
| Purpose | Used in multi-tenancy environments for logical segregation at layer 3 having separate security policies, VPN and routing services configurations for connected networks | VLANs are used to create different networks in a VDOM |
| VLANs reduce traffic and increase network security | ||
| Used for | Isolation of virtual networks over a single physical hardware | VLANs are used to limit access to specified group of users into isolated LAN segments |
| Function | VDOMs are managed via administrative domains (ADOMs) | VLANs are managed via routers and layer 3 switches |
| Support | FortiGate supports up to 10 VDOMs and some models support extension of VDOMs beyond default limit with licenses | Maximum number of VLANs a switch can support is 4096 |
| Use cases | Ideal for cloud service providers who hosts several customers IT services | Used for limiting broadcasts as per security requirements of different departments and groups |
| Scalability | Limited by capacity and resources of underlying physical hardware device | VLANs provide scalability up to a limit of 4096 VLANs on a physical switch |
| Resource usage | VDOMs use CPU and memory of underlying physical hardware device hence it has performance impact | Usage of VLAN increases CPU demand a bit |
| Deployment | It can be deployed without requiring FortiManager instance as a standalone component | VLANs are deployed on a switch it has no specific software or interface requirement |
Download the comparison table: vdom vs vlan