Zero Trust Architecture: Why It’s Becoming a Security Standard
Since organizations are moving away from the traditional IT landscape to cloud computing, cloud-based assets, remote working models, the perimeter based old and traditional model of security is not sufficient enough for protection of data and sensitive systems. The modern security model is based on the principle of ‘trust no one’ the way organizations assets are being secured and used.
In today’s topic we will learn about the zero trust architecture approach, its need, how zero trust security is achieved and its benefits.
What is Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA)
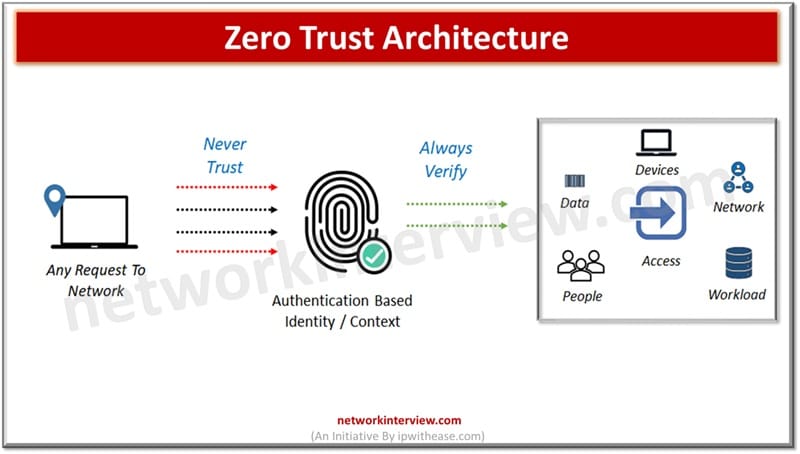
Zero trust architecture’s basic principle is ‘Never trust, always verify’ which focuses on stringent access controls and user authentication. It helps organizations to improve their cyber defenses and reduce network complexity. Pre-authorized user access concept no longer exists in zero trust architecture.
Due to cloud computing penetration and diminishing physical boundaries and network complexity of enterprises is increased. Implementing several layers of security is tough to manage and maintain. Traditional perimeter-based security is no longer adequate. Zero trust architecture helps organizations build policy-based access which are meant to prevent lateral movement across networks with more stringent access controls. User policies can be defined based on location, device and role requirement.
How Zero Trust works
Zero trust works by combination of encryption, access control, next generation endpoints security, identity protection and cloud workloads advantages. Below set principles are the basis for NIST zero trust architecture as under:
- Access to resources is managed at organization policies level considering several factors such as user, IP address of user, operating system and location.
- Corporate network or resource access is based on with secure authentication for every individual request
- User or device authentication do not automatically provide resources access
- All communication is encrypted and authenticated
- Servers, endpoints and mobile devices are secured with zero trust principals which together are considered corporate resources
How to implement Zero Trust Architecture?
The very first step is to define the attack surface which means identify what you need to protect which areas? Based on this you need to deploy policies and tools across the network. The focus should be protection of your digital assets.
Define Attack Surface
- Sensitive data – the organization collects and stores what kind of sensitive data such as employees and customers personal information
- Critical applications – used by business to tun its operations or meant for customers
- Physical assets – IoT devices, POS devices any other equipment
- Corporate services – all internal infrastructure meant to provide day to day operations
Implement controls around network traffic
The routing of requests within the network for example access to a corporate database which could be critical to business so as to ensure access is secure. Network architecture understanding will help to implement network controls relevant to its placement.
Create a Zero-Trust Policy
Use the Kipling method here to define the zero-trust policy : who, what , when , where , why and how need to be well thought out for every device, user.
- Architect a zero-trust network
- Use a firewall to implement segmentation within the network.
- Use multi-factor authentication to secure users
- Eliminate implicit trust
- Consider all components of organization infrastructure in zero-trust implementation scope such as workstations, servers, mobile devices, IoT devices, supply chain , cloud etc.
Monitor the Network
Once a network is secured using zero trust architecture it is important to monitor it.
Reports, analytics and logs are three major components of monitoring. Reports are used to analyze data related to system and users and could be an indication of anomalous behaviour. Data collected by systems can be used to gain insight into behaviour and performance of users. Logs produced by different devices in your network provide a record of all kinds of activities. These can be analyzed using the SIEM tool to detect anomalies and patterns.
Tag:Security



