What is a Virtual Firewall? 3 Virtual Firewall Use Cases
Firewalls have evolved a lot since their inception. The gatekeeper or epitome of perimeter security used to enhance network security. Initial days firewalls were simple packet filters which examined packets of information passing through them and blocked which did not meet the predetermined criteria. Over a period of time as cyber attacks become more sophisticated, firewall technology also becomes more advanced from stateful inspection firewalls to Next generation firewalls.
In today’s topic we will learn about virtual firewalls and three use cases of virtual firewalls in detail.
About Virtual Firewall
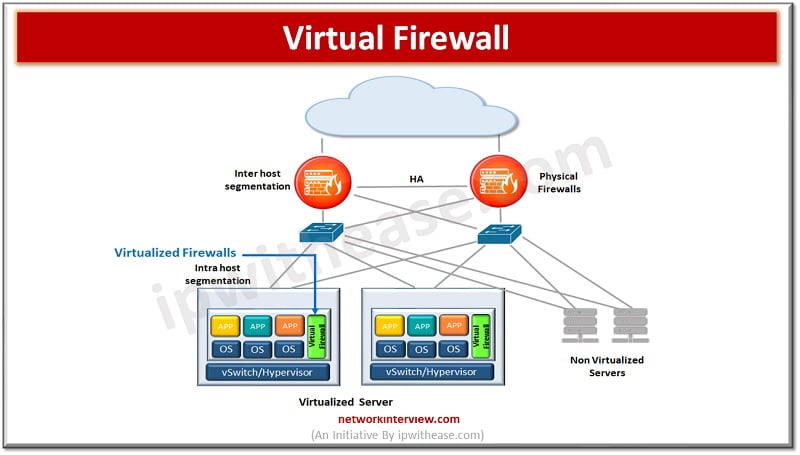
A virtual firewall provides network security for virtualized environments such as cloud. Virtualization process allows creation of multiple virtual instances of a physical device or a server and allows more efficient utilization of underlying physical resources and more flexibility for network management. Virtualization technologies brought some new set of security risks as well such as unauthorised access to virtual resources and increased data breaches.
The virtual firewalls become the gatekeeper or keeper of perimeter security again like their physical avatars. Virtual firewalls operate at the virtualization layer and protect virtual machines (VMs) or any other virtualized resources in cloud networks. Virtual firewalls provide additional functions such as VPN connections, intrusion detection and prevention and malware protection.
Virtual firewalls secure cloud deployments and so they are also called cloud firewalls. They can scale with virtual environments and protect against north-south traffic and allow fine grained network segmentation within virtual networks.
Benefits of using a Virtual / Cloud Firewall
- Cloud native virtual firewalls centralize security and apply policies consistently to all virtual machines and applications
- Virtual firewall upgrades are easier compared to management and upgrades of physical firewalls
- Virtual firewalls are safest way to quickly rollout cloud applications
- More cost effective as compared to their physical counterparts
- Provide cloud native threat detection and prevention capabilities to secure data and applications.
Virtual Firewall Use Cases
Use Case 1: Securing Public Clouds
Public clouds such as Google cloud platform (GCP), Amazon web services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure host virtual machines to support different types of workloads, virtual firewalls secure these workloads.
Virtual firewalls are deployed to implement advanced security capabilities such as threat detection and segmentation to isolate critical workloads to meet regulatory requirements such as GDPR, HIPAA, PCI-DSS etc.
To secure flow of traffic moving laterally within cloud networks Virtual firewalls implement inline threat prevention mechanism.
Use Case 2: Security Extension to branches and SDNs
Virtual firewalls help in securing systems at branch offices and for software defined networks. In SDN environments data routing and networking is controlled with software virtualization. Deployment of virtual firewalls in SDN environments allow organizations to secure their perimeter, segmentation of network and extend protection to remote branches.
Advanced firewalls in SDN networks provide consistent network security and help to manage branch network security from a centralized console, segmentation of networks to support isolation, secures the live network flow and sets the stage for secure migration of applications to cloud.
Use Case 3: Protection of Cloud Assets
Virtual firewalls enhance security of private cloud assets. They come with policy based, auto provisioning of security capabilities for networks and help in securing private cloud assets quickly and support in workload isolation from one another.
Tag:firewall, virtualization



